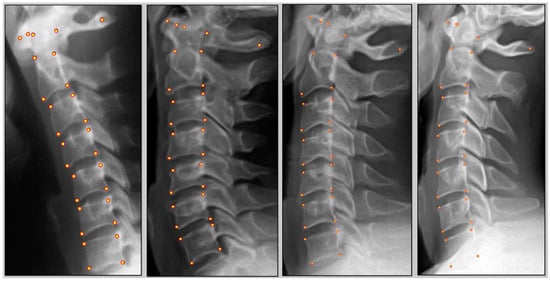
Background: The biomechanical analysis of spine and postural misalignments is important for surgical and non-surgical treatment of spinal pain. We investigated the examiner reliability of sagittal cervical alignment variables compared to the reliability and concurrent validity of computer vision algorithms used in the PostureRay
® software 2024.
Methods: A retrospective database of 254 lateral cervical radiographs of patients between the ages of 11 and 86 is studied. The radiographs include clearly visualized C1–C7 vertebrae that were evaluated by a human using the software. To evaluate examiner reliability and the concurrent validity of the trained CNN performance, two blinded trials of radiographic digitization were performed by an extensively trained expert user (US) clinician with a two-week interval between trials. Then, the same clinician used the trained CNN twice to reproduce the same measures within a 2-week interval on the same 254 radiographs. Measured variables included segmental angles as relative rotation angles (RRA) C1–C7, Cobb angles C2–C7, relative segmental translations (RT) C1–C7, anterior translation C2–C7, and absolute rotation angle (ARA) C2–C7. Data were remotely extracted from the examiner’s PostureRay
® system for data collection and sorted based on gender and stratification of degenerative changes. Reliability was assessed via intra-class correlations (ICC), root mean squared error (RMSE), and R
2 values.
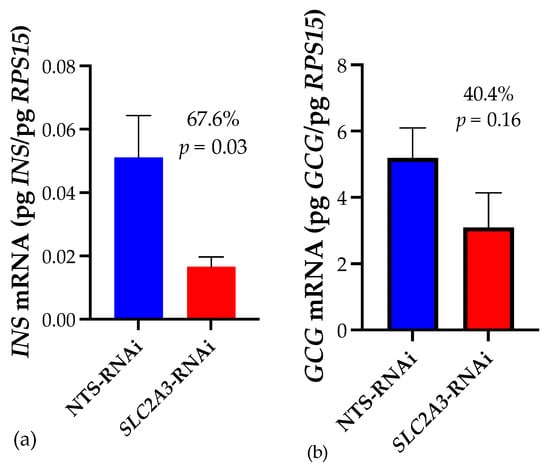
Results: In comparing repeated measures of the CNN network to itself, perfect reliability was found for the ICC (1.0), RMSE (0), and R
2 (1). The reliability of the trained expert US was in the excellent range for all variables, where 12/18 variables had ICCs ≥ 0.9 and 6/18 variables were 0.84 ≤ ICCs ≤ 0.89. Similarly, for the expert US, all R
2 values were in the excellent range (R
2 ≥ 0.7), and all RMSEs were small, being 0.42 ≤ RMSEs ≤ 3.27. Construct validity between the expert US and the CNN network was found to be in the excellent range with 18/18 ICCs in the excellent range (ICCs ≥ 0.8), 16/18 R
2 values in the strong to excellent range (R
2 ≥ 0.7), and 2/18 in the good to moderate range (R
2 RT C6/C7 = 0.57 and R
2 Cobb C6/C7 = 0.64. The RMSEs for expert US vs. the CNN network were small, being 0.37 ≤ RMSEs ≤ 2.89.
Conclusions: A comparison of repeated measures within the computer vision CNN network and expert human found exceptional reliability and excellent construct validity when comparing the computer vision to the human observer.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT