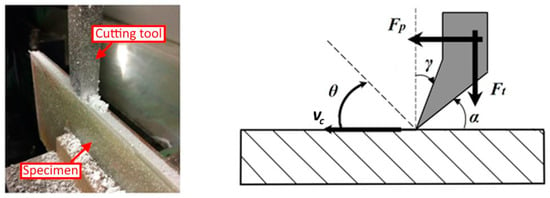
Honey is a natural sweetener made by bees that exhibits antimicrobial activity, mainly related to its H
2O
2 content. The aim of this work was to research the H
2O
2 concentration of 24 Spanish honeys from different botanical origins,
[...] Read more.
Honey is a natural sweetener made by bees that exhibits antimicrobial activity, mainly related to its H
2O
2 content. The aim of this work was to research the H
2O
2 concentration of 24 Spanish honeys from different botanical origins, studying their possible correlation with glucose oxidase (GOx), catalase (CAT), and anti-
Staphylococcus aureus activities (minimal inhibition concentration (MIC), minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC), and percentage of inhibition at 5% (
w/
v) honey against
Staphylococcus aureus), as well as possible correlations among all the analyzed parameters. The results showed that the H
2O
2 concentration did not depend on the botanical origin of the honeys. There were neither correlations between the H
2O
2 concentration and the activities of GOx and CAT, nor between GOx and antimicrobial activity. However, CAT and antimicrobial activities were positively correlated. Therefore, CAT could be successfully used as a possible marker of the antimicrobial activity of honeys against
Staphylococcus aureus. Furthermore, a linear regression model has been fitted to explain the antimicrobial activity from CAT and GOx activity and H
2O
2 concentration. Although H
2O
2 is one of the compounds involved in honey’s antibacterial activity, this capacity also strongly depends on other honey components (such as low water activity, acidity, osmolarity, and phenolic compounds). The very high anti-
Staphylococcus aureus activity exhibited by all samples could be interesting for commercial honey-based formulations also helping to promote local beekeeping.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT