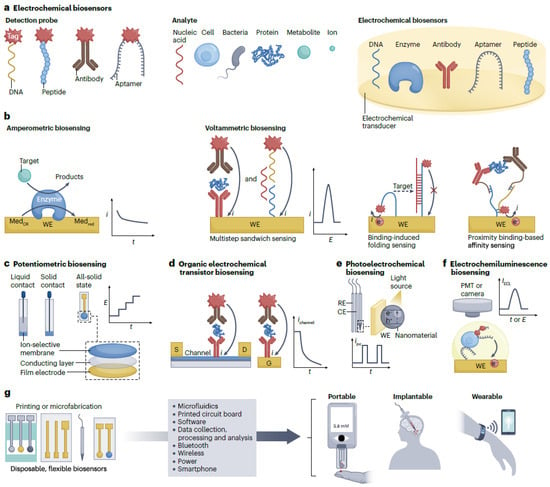
Background: Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms can be applied in breast cancer risk prediction and prevention by using patient history, scans, imaging information, and analysis of specific genes for cancer classification to reduce overdiagnosis and overtreatment. This scoping review aimed to identify the barriers encountered in applying innovative AI techniques and models in developing breast cancer risk prediction scores and promoting screening behaviors among adult females. Findings may inform and guide future global recommendations for AI application in breast cancer prevention and care for female populations.
Methods: The PRISMA-SCR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews) was used as a reference checklist throughout this study. The Arksey and O’Malley methodology was used as a framework to guide this review. The framework methodology consisted of five steps: (1) Identify research questions; (2) Search for relevant studies; (3) Selection of studies relevant to the research questions; (4) Chart the data; (5) Collate, summarize, and report the results.
Results: In the field of breast cancer risk detection and prevention, the following AI techniques and models have been applied: Machine and Deep Learning Model (ML-DL model) (
n = 1), Academic Algorithms (
n = 2), Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium (BCSC), Clinical 5-Year Risk Prediction Model (
n = 2), deep-learning computer vision AI algorithms (
n = 2), AI-based thermal imaging solution (Thermalytix) (
n = 1), RealRisks (
n = 2), Breast Cancer Risk NAVIgation (
n = 1), MammoRisk (ML-Based Tool) (
n = 1), Various MLModels (
n = 1), and various machine/deep learning, decision aids, and commercial algorithms (
n = 7). In the 11 included studies, a total of 39 barriers to AI applications in breast cancer risk prediction and screening efforts were identified. The most common barriers in the application of innovative AI tools for breast cancer prediction and improved screening rates included lack of external validity and limited generalizability (
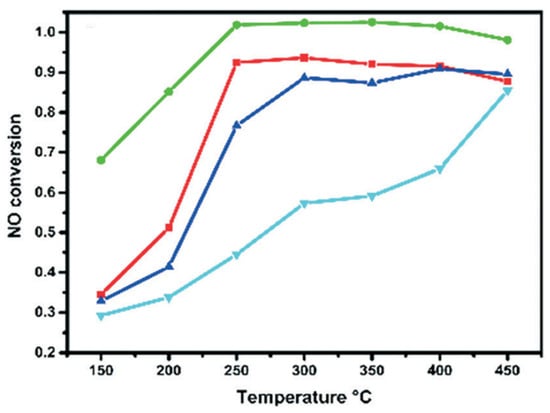
n = 6), as AI was used in studies with either a small sample size or datasets with missing data. Many studies (
n = 5) also encountered selection bias due to exclusion of certain populations based on characteristics such as race/ethnicity, family history, or past medical history. Several recommendations for future research should be considered. AI models need to include a broader spectrum and more complete predictive variables for risk assessment. Investigating long-term outcomes with improved follow-up periods is critical to assess the impacts of AI on clinical decisions beyond just the immediate outcomes. Utilizing AI to improve communication strategies at both a local and organizational level can assist in informed decision-making and compliance, especially in populations with limited literacy levels.
Conclusions: The use of AI in patient education and as an adjunctive tool for providers is still early in its incorporation, and future research should explore the implementation of AI-driven resources to enhance understanding and decision-making regarding breast cancer screening, especially in vulnerable populations with limited literacy.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT