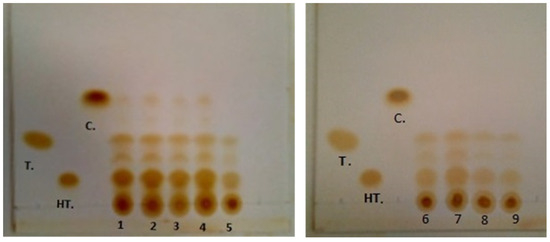
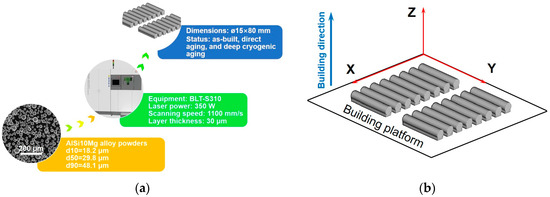
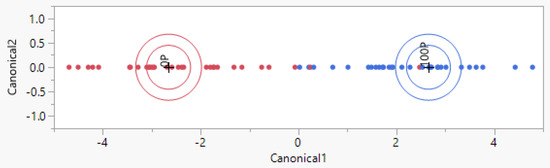
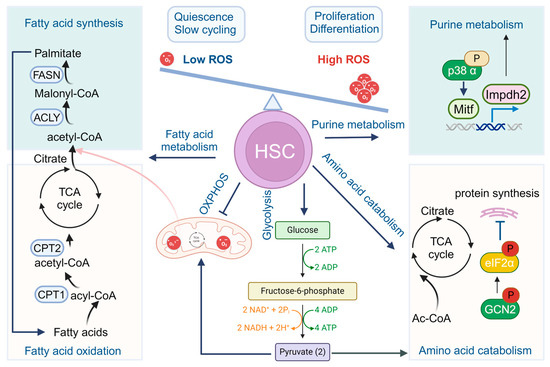
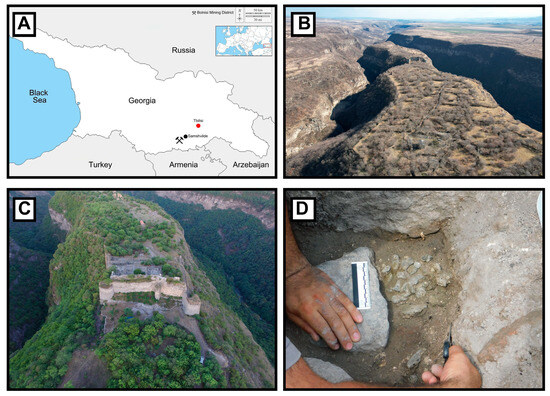
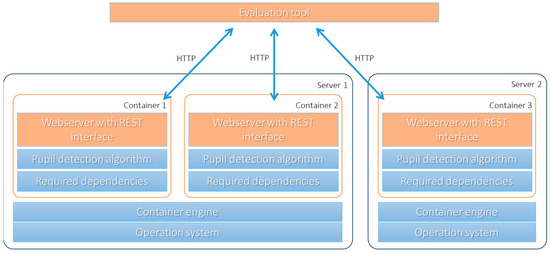
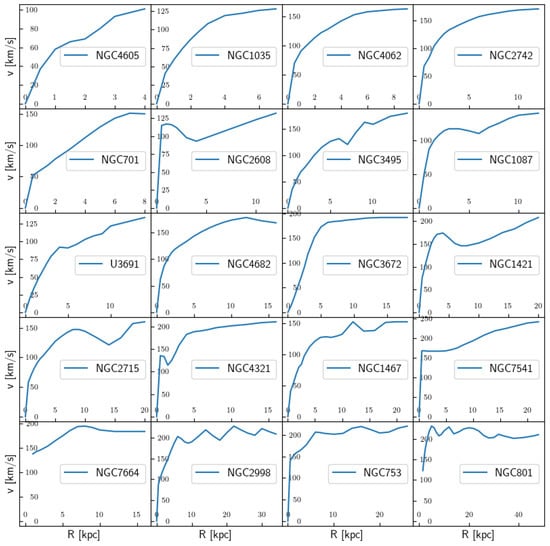
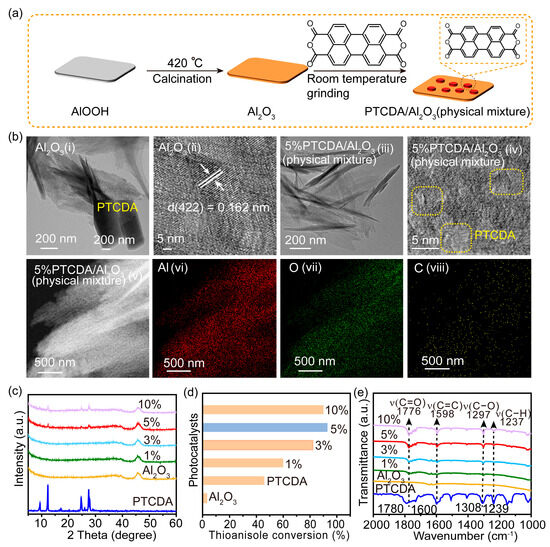
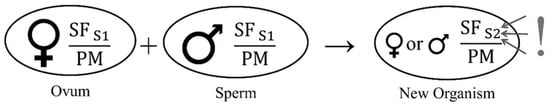
As constituents of one of the vital agricultural ecosystems, paddy fields exert significant influence on the global carbon cycle. Therefore, conducting observations and simulations of CO
2 flux in rice paddy is of significant importance for gaining deeper insights into the functionality of agricultural ecosystems. This study utilized an eddy covariance system to observe and analyze the CO
2 flux in a rice paddy field in Eastern China and also introduced and parameterized the Jarvis multiplicative model to predict the CO
2 flux. Results indicate that throughout the observation period, the range of CO
2 flux in the paddy field was −0.1 to −38.4 μmol/(m
2·s), with a mean of −12.9 μmol/(m
2·s). The highest CO
2 flux occurred during the rice flowering period with peak photosynthetic activity and maximum CO
2 absorption. Diurnal variation in CO
2 flux exhibited a “U”-shaped curve, with flux reaching its peak absorption at 11:30. The CO
2 flux was notably higher in the morning than in the afternoon. The nocturnal CO
2 flux remained relatively stable, primarily originating from respiratory CO
2 emissions. The rice canopy CO
2 flux model was revised using boundary line analysis, elucidating that photosynthetically active radiation, temperature, vapor pressure deficit, phenological stage, time, and concentration are pivotal factors influencing CO
2 flux. The simulation of CO
2 flux using the parameterized model, compared with measured values, reveals the efficacy of the established parameter model in simulating rice CO
2 flux. This study holds significant importance in comprehending the carbon cycling process within paddy ecosystems, furnishing scientific grounds for future climate change and environmental management endeavors.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT