Abstract
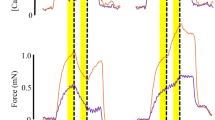
Contraction of cardiac muscle depends on a transient rise of intracellular calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) which is initiated by the action potential1. It has, however, also been suggested that [Ca2+]i can fluctuate in the absence of changes in membrane potential. The evidence for this is indirect and comes from observations of (1) fluctuations of contractile force in intact cells2–5, (2) spontaneous cellular movements6, and (3) spontaneous contractions in cells which have been skinned to remove the surface membrane7. The fluctuations in force are particularly prominent when the cell is Ca2+-loaded, and have been attributed to a Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum7. In these conditions of Ca2+-loading the normal cardiac contraction is followed by an aftercontraction8 which has been attributed to the synchronization of the fluctuations5. The rise of [Ca2+]i which is thought to underlie the aftercontraction also produces a transient inward current3. This current, which probably results from a Ca2+-activated nonspecific cation conductance9, has been implicated in the genesis of various cardiac arrhythmias. However, despite the potential importance of such fluctuations of [Ca2+]i their existence has, so far, only been inferred from tension measurement. Here we present direct measurements of such oscillations of [Ca2+]i.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, D. G. & Blinks, J. R. Nature 273, 509–513 (1978).
Glitsch, H. G. & Pott, L. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 358, 11–25 (1975).
Kass, R. S., Lederer, W. J., Tsien, R. W. & Weingart, R. J. Physiol., Lond. 281, 187–208 (1975).
Eisner, D. A. & Lederer, W. J. J. Physiol., Lond. 294, 255–277 (1979).
Kass, R. S. & Tsien, R. W. Biophys. J. 38, 259–269 (1982).
Lakatta, E. G. & Lappe, D. L. J. Physiol., Lond. 315, 369–394 (1981).
Fabiato, A. & Fabiato, F. J. Physiol., Lond. 249, 469–495 (1975).
Reiter, M. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archs Pharmak. 242, 497–507 (1962).
Colquhoun, D., Neher, E., Reuter, H. & Stevens, C. F. Nature 294, 752–754 (1981).
Allen, D. G. & Orchard, C. H. J. Physiol., Lond. 335, 555–567 (1983).
Reuter, H. & Seitz, N. J. Physiol., Lond. 195, 451–470 (1968).
Blinks, J. R., Wier, W. G., Morgan, J. P. & Hess, P. in Advances in Pharmacology and Therapeutics II Vol. 3 (eds Yoshida, H., Hagihara, Y. & Ebashi, S.) (Pergamon, Oxford, 1982).
Bers, D. M. & Ellis, D. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol. 393, 171–178 (1982).
Sheu, S-S. & Fozzard, H. A. J. gen. Physiol. 80, 325–351 (1982).
Lee, C. O., Uhm, D. Y. & Dresdner, K. Science 209, 699–701 (1980).
Allen, D. G. & Blinks, J. R. in Detection and Measurement of Free Ca2+ in Cells (eds Ashley, C. C. & Campbell, A. K.) 159–174 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1979).
Allen, D. G., Eisner, D. A., Lab, M. J. & Orchard, C. H. J. Physiol., Lond. (in the press).
Stern, M. D., Kort, A. A., Bhatnagar, G. M. & Lakatta, E. G. Biophys. J. 33, 284a (1981).
Eisner, D. A. & Lederer, W. J. J. Physiol., Lond. 322, 48P–49P (1982).
Karagueuzian, H. S. & Katzung, B. G. J. Physiol., Lond. 327, 255–271 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orchard, C., Eisner, D. & Allen, D. Oscillations of intracellular Ca2+ in mammalian cardiac muscle. Nature 304, 735–738 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1038/304735a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/304735a0
This article is cited by
-
Generation of myocyte agonal Ca2+ waves and contraction bands in perfused rat hearts following irreversible membrane permeabilisation
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Transmural and rate-dependent profiling of drug-induced arrhythmogenic risks through in silico simulations of multichannel pharmacology
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Carvedilol analog modulates both basal and stimulated sinoatrial node automaticity
Heart and Vessels (2014)
-
The ryanodine receptor store-sensing gate controls Ca2+ waves and Ca2+-triggered arrhythmias
Nature Medicine (2014)
-
Carvedilol and its new analogs suppress arrhythmogenic store overload–induced Ca2+ release
Nature Medicine (2011)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.