Abstract
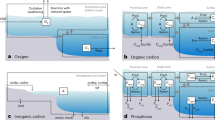
THE net exchange of carbon dioxide between the atmosphere and the ocean, and thus the nature of the oceanic carbon sink, is dominated by the seasonal dynamics of carbon cycling in the upper ocean. This cycle represents a balance between abiotic and biotic carbon transport into, and export out of, the ocean's upper layer. Here we report measurements of these processes made over five years in the Sargasso Sea off Bermuda, as part of the US Joint Global Ocean Flux Study (JGOFS). We find that the decrease in carbon stocks from the spring to the autumn in the upper 150 m of the ocean is three times larger than the measured sum of biotic and abiotic fluxes out of this layer. This discrepancy can be explained either by failure to account for horizontal advection of carbon or by inaccuracies in the fluxes of sinking particles as measured using sediment traps. Either the traps miss 80% of the sinking particles, or 70% of the carbon cycling is due to advection (or a combination of both processes is responsible). Sediment-trap measurements of the 234Th flux during this period suggest that most of the discrepancy may be due to inaccuracies in the trap methods, which would require a very general reassessment of existing ideas about particle export and remineralization of carbon in the oceans. If, on the other hand, advection is the main source of the discrepancy, the traditional one-dimensional (vertical) modelling of the oceanic carbon cycle cannot give a full account of carbon dynamics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michaels, A. F. et al. Deep-Sea Res. 41, 1013–1038 (1994).
Lohrenz, S. E. et al. Deep-Sea Res. 39, 1373–1391 (1992).
Knap, A. H. et al. BATS Methods Manual Version 3 1–108 (US JGOFS Planning Office, Woods Hole, MA 1993).
Menzel, D. W. & Ryther, J. H. Deep-Sea Res. 6, 351–367 (1960).
Asper, V. L., Deuser, W. G., Knauer, G. A. & Lohrenz, S. E. Nature 357, 670–672 (1992).
Sambrotto, R. N. et al. Nature 363, 248–250 (1993).
Michaels, A. F., Siegel, D. A., Johnson, R. J., Knap, A. H. & Galloway, J. N. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 7, 339–351 (1993).
Sarmiento, J. L., Theile, G., Key, R. M. & Moore, W. S. J. geophys. Res. 95, 18303–18315 (1990).
Spitzer, W. S. & Jenkins, W. J. J. mar. Res. 47, 169–196 (1989).
Jenkins, W. J. Nature 300, 246–248 (1982).
Jenkins, W. J. & Goldman, J. C. J. mar. Res. 43, 465–491 (1985).
Jenkins, W. J. Nature 331, 521–523 (1988).
Carlson, C. A., Ducklow, H. W. & Michaels, A. F. Nature 371, 405–408 (1994).
McCave, I. N. Deep-Sea Res. 22, 491–502 (1984).
Bates, N. R., Michaels, A. F. & Knap, A. H. Mar. Chem. (submitted).
Longhurst, A. R. & Harrison, W. G. Deep-Sea Res. 35, 881–889 (1988).
Longhurst, A. R., Bedo, A. W., Harrison, W. G., Head, E. J. H. & Sameoto, D. D. Deep-Sea Res. 37, 685–694 (1990).
McClain, C. R. & Firestone, J. J. geophys. Res. 98, 12327–12339 (1993).
Keeling, C. D. in The Global Carbon Cycle NATO ASI Series I (ed. Heimann, M.) 413–429 (Springer, Berlin, 1993).
US JGOFS Sediment Trap Technology and Sampling Planning Report 10 1–94 (US JGOFS, Woods Hole, MA, 1989).
Eppley, R. W. & Peterson, B. J. Nature 282, 677–680 (1979).
Coale, K. H. & Bruland, K. W. Limnol. Oceanogr. 32, 189–200 (1987).
Coale, K. H. & Bruland, K. W. Limnol. Oceanogr. 30, 22–33 (1985).
Laws, E. A., Ditullio, G. R., Betzer, P. R., Karl, D. M. & Carder, K. L. Deep-Sea Res. 36, 103–120 (1989).
Buesseler, K. O. Nature 353, 420–423 (1992).
Buesseler, K. O., Michaels, A. F., Siegel, D. A. & Knap, A. H. Globl Biogeochem. Cycles 8, 179–193 (1994).
Knauer, G. A., Redalje, D. G., Harrison, W. G. & Karl, D. M. Deep-Sea Res. 37, 1121–1134 (1990).
Knauer, G. A. in Interactions of C, N, P and S Biogeochemical Cycles and Global Change (eds Wollast, R., MacKenzie, F. T. & Chou, I.) 211–231 (Springer, Berlin, 1993).
Karl, D. M. & Knauer, G. A. Oceanography 2, 32–35 (1989).
Michaels, A. F., Silver, M. W., Gowing, M. M. & Knauer, G. A. Deep-Sea Res. 37, 1285–1296 (1990).
Hansell, D. A. & Newton, J. A. Limnol. Oceanogr. 39, 1487–1495 (1994).
Gust, G., Bowles, W., Giordano, S. & Huettel, M. Aquatic Sciences (in the press).
Martin, J. H., Fitzwater, S. E., Gordon, R. M., Hunter, C. N. & Tanner, S.J. Deep-Sea Res. II 40, 115–134 (1993).
Knauer, G. A., Martin, J. H. & Bruland, K. W. Deep-Sea Res. 26, 97–108 (1979).
Martin, J. H., Knauer, G. A., Karl, D. M. & Broenkow, W. W. Deep-Sea Res. 34, 267–285 (1987).
Worthington, L. V. The Johns Hopkins Oceanographic Studies 6, 1–110 (1976).
Platt, T. & Harrison, W. G. Nature 318, 55–58 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michaels, A., Bates, N., Buesseler, K. et al. Carbon-cycle imbalances in the Sargasso Sea. Nature 372, 537–540 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/372537a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/372537a0
This article is cited by
-
Nanomolar phosphate supply and its recycling drive net community production in the subtropical North Pacific
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Revisiting the distribution of oceanic N2 fixation and estimating diazotrophic contribution to marine production
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Nitrate supply from deep to near-surface waters of the North Pacific subtropical gyre
Nature (2010)
-
Marine microorganisms and global nutrient cycles
Nature (2005)
-
Zooplankton biomass and indices of grazing and metabolism during a late winter bloom in subtropical waters
Marine Biology (2004)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.