Abstract
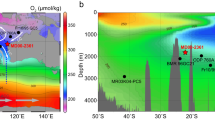
The global circulation of the oceans and the atmosphere transports heat around the Earth. Broecker and Denton1 suggested that changes in the global ocean circulation might have triggered or enhanced the glacial–interglacial cycles. But proxy data for past circulation taken from sediment cores in the South Atlantic Ocean have yielded conflicting interpretations of ocean circulation in glacial times—δ13C variations in benthic foraminifera2,3,4,5,6 support the idea of a glacial weakening or shutdown of North Atlantic Deep Water production, whereas other proxies, such as Cd/Ca, Ba/Ca and 231Pa/230Th ratios, show little change from the Last Glacial Maximum to the Holocene epoch7,8,9. Here we report neodymium isotope ratios from the dispersed Fe–Mn oxide component of two southeast Atlantic sediment cores. Both cores show variations that tend towards North Atlantic signatures during the warm marine isotope stages 1 and 3, whereas for the full glacial stages 2 and 4 they are closer to Pacific Ocean signatures. We conclude that the export of North Atlantic Deep Water to the Southern Ocean has resembled present-day conditions during the warm climate intervals, but was reduced during the cold stages. An increase in biological productivity may explain the various proxy data during the times of reduced North Atlantic Deep Water export.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broecker, W. S. & Denton, G. H. The role of ocean-atmosphere reorganizations in glacial cycles. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 53, 2465–2501 ( 1989).
Curry, W. B. & Lohmann, G. P. Reduced advection into Atlantic Ocean deep eastern basins during last glaciation maximum. Nature 308, 317–342 ( 1983).
Oppo, D. W. & Fairbanks, R. G. Variability in the deep and intermediate water circulation of the Atlantic Ocean during the past 25,000 years: Northern Hemisphere modulation of the Southern Ocean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 86, 1–15 (1987).
Charles, C. D. & Fairbanks, R. G. Evidence from Southern Ocean sediments for the effect of North Atlantic deep-water flux on climate. Nature 355, 416–419 ( 1992).
Labeyrie, L. et al. Hydrographic changes of the Southern Ocean (southeast Indian sector) over the last 230 kyr. Paleoceanography 11, 57–76 (1996).
Charles, C. D., Lynch-Stieglitz, J., Ninnemann, U. S. & Fairbanks, R. G. Climate connections between the hemisphere revealed by deep sea sediment core/ice core correlations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 142, 19–27 (1996).
Lea, D. W. & Boyle, E. A. Foraminiferal reconstruction of barium distributions in water masses of the glacial ocean. Paleoceanography 5, 719–742 ( 1990).
Boyle, E. A. Cadmium and δ13C paleochemical ocean distributions during the Stage 2 glacial maximum. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 20, 245–87 (1992).
Yu, E. -F., Francois, R. & Bacon, M. P. Similar rates of modern and last glacial ocean thermohaline circulation inferred from radiochemical data. Nature 379, 689–694 (1996).
Albarède, F. & Goldstein, S. L. World map of Nd isotopes in sea-floor ferromanganese deposits. Geology 20, 761–761 (1992).
Albarède, F., Goldstein, S. L. & Dautel, D. The neodymium isotopic composition of manganese nodules from the Southern and Indian oceans, the global oceanic neodymium budget, and their bearing on deep ocean circulation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61, 1277–1291 ( 1997).
Piepgras, D. J. & Wasserburg, G. J. Isotopic composition of neodymium in waters from the Drake Passage. Science 217, 207–214 ( 1982).
Jeandel, C. Concentration and isotopic composition of Nd in the South Atlantic Ocean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 117, 581– 591 (1993).
Stordal, M. C. & Wasserburg, G. J. Neodymium isotopic study of Baffin Bay water: sources of REE from very old terranes. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 77, 259– 272 (1986).
Piepgras, D. J. & Wasserburg, G. J. Rare earth element transport in the western North Atlantic inferred from Nd isotopic observations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 51, 1257–1271 (1987).
Piepgras, D. J. & Jacobsen, S. B. The isotopic composition of neodymium in the North Pacific. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 52, 1373–1381 ( 1988).
Levitus, S., Burgett, R. & Boyer, T. World Ocean Atlas 1994: Nutrients (US Department of Commerce, Washington DC, 1994).
Tucholke, B. E. & Embley, R. W. in Interregional Unconformities and Hydrocarbon Acumulation (ed. Schlee, J. S.) 145–164 (American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Tulsa, 1984).
Boyle, E. A. & Keigwin, L. North Atlantic thermohaline circulation during the past 20,000 years linked to high-latutude surface temperature. Nature 350, 35–40 (1987).
Matsumoto, K. & Lynch-Stieglitz, J. Similar glacial and Holocene deep water circulation inferred from southeast Pacific benthic foraminiferal carbon isotope composition. Paleoceanography 14, 149–163 (1999).
Pudsey, C. J. & Howe, J. A. Quaternary history of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current: evidence from the Scotia Sea. Mar.Geol. 148, 83–112 (1998).
Petit, J. R. et al. Palaeoclimatological and chronological implications of the Vostok core dust record. Nature 343, 56– 58 (1990).
Basile, I. et al. Patagonian origin of glacial dust deposited in East Antarctica (Vostok and Dome C) during glacial stages 2, 4 and 6. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 146, 573–589 (1997).
Jones, C. E., Halliday, A. N., Rea, D. K. & Owen, R. M. Neodymium isotopic variations in North Pacific modern silicate sediment and the insignificance of detrital REE contributions to seawater. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 127, 55–66 (1994).
Jeandel, C., Bishop, J. K. & Zindler, A. Exchange of neodymium and its isotopes between seawater and small and large particles in the Sargasso Sea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 59, 535–547 ( 1995).
Fowler, S. W. et al. Rapid removal of Chernobyl fallout from Mediterranean surface waters by biological activity. Nature 329, 56–58 (1987).
Abouchami, W., Goldstein, S. L., Galer, S. J. G., Eisenhauer, A. & Mangini, A. Secular changes of Pb and Nd isotopes in central Pacific seawater as recorded by a Mn crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61, 3957– 3974 (1997).
Broecker, W. S. & Peng, T.-H. Tracers in the Sea (Eldigio, Palisades, New York, 1982).
Schmitz, W. On the World Ocean Circulation: the Pacific and Indian Oceans (Technical Report WHOI 96–08, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, 1996).
Lea, D. W. A trace metal perspective on the evolution of Antarctic Circumpolar Deep Water Chemistry. Paleoceanography 4, 733– 747 (1995).
Mackensen, A., Hubberten, H. -W., Bickert, T., Fischer, G. & Futterer, D. K. The δ13C in benthic foraminiferal tests of Fontbiotia Wuellerstorfi (Schwager) relative to the δ13C of dissolved inorganic carbon in Southern Ocean deep water: implications for glacial ocean circulation models. Paleoceanography 8, 587–610 (1993).
McCorckle, D. C. Evidence of a dissolution effect on benthic foraminiferal shell chemistry: δ13C, Cd/Ca, Ba/Ca, and Sr/Ca results from the Ontong Java Plateau. Paleoceanography 10, 699– 714 (1995).
Kumar, N. et al. Increased biological productivity and export production in the glacial Southern Ocean. Nature 378, 675– 679 (1995).
Asmus, T. et al. Variations of biogenic particle flux in the southern Atlantic section of the Subantarctic Zone during the late Quaternary: evidence from 231Paex and 230Thex. Mar. Geol. 159, 63–78 ( 1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank R. Anderson, W. Broecker, L. Burckle and N. Frank for discussions; J. Lynch-Stieglitz for providing the benthic δ13C stratigraphy of RC11-83; and D. Hodell for sharing the stratigraphy of TNO57-6PC. R.R. thanks M. Fleisher, G. Hemming, M. Klas-Mendelson, and G. Mandal for help in the laboratory. We also thank A.N. Halliday for comments on the manuscript. This work was partly supported by the NSF and NOAA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rutberg, R., Hemming, S. & Goldstein, S. Reduced North Atlantic Deep Water flux to the glacial Southern Ocean inferred from neodymium isotope ratios. Nature 405, 935–938 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35016049
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35016049
This article is cited by
-
Southern Ocean glacial conditions and their influence on deglacial events
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment (2023)
-
Last 10000 years Variation in the Intensity of OMZ-Core Reconstructed from Sediment of the Eastern Arabian Sea
Journal of the Geological Society of India (2021)
-
Calcareous nannofossils identify the age and precipitation rates of manganese deposits of the Mozambique Ridge and Mozambique Basin, SW Indian Ocean
Geo-Marine Letters (2021)
-
Increased chemical weathering during the deglacial to mid-Holocene summer monsoon intensification
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
North Atlantic Deep Water Production during the Last Glacial Maximum
Nature Communications (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.