Abstract
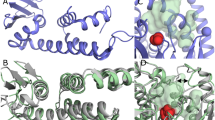
THERE are several methods for the prediction of secondary structural features of protein molecules from the amino acid sequence1–5. Application of these methods to proteins of unknown tertiary structure has met with mixed results6,7, and it has been suggested that it is the protein structural type which will determine which predictive method will succeed8. There is also great interest in the ab initio prediction of tertiary structures of proteins9–11, but this has not yet been achieved. One possible method for predicting the tertiary structure of an enzyme is by the use of a known amino acid sequence and a previously determined tertiary structure of another related homologous isofunctional enzyme. This method was used by McLachlan and Shotton12 in an attempt to fit the α-lytic protease sequence into the polypeptide chain folding of elastase13 and chymotrypsin14. It has also been used to predict the tertiary structure of troponin C (ref. 15). Now that the structure of α-lytic protease is known16 to a resolution of 2.8 Å, we can assess the accuracy of such predictions. The tertiary structures of two related bacterial serine proteases, SGPA and SGPB and their structural relationship to the pancreatic enzymes have been published previously17–19. Many of the conclusions drawn from those studies are also applicable to the present discussion on α-lytic protease and need not be repeated. Rather, we shall consider the basic premise of sequence homology in phylogenetically distant proteins being used to deduce tertiary structures. A recent realignment20 of the amino acid sequences of Gly-Asp-Ser-Gly-Gly proteases, which was based on the known topological equivalences of α-carbon atoms, indicates an overall sequence identity of only 18% between α-lytic protease and elastase. We show here that this low value is independent of the environment of the topologically equivalent polypeptide chains (whether the residues are internal or external) and that the sequence identity is associated with only those residues which are in the immediate vicinity of the active site quartet, Asp 102, His 57, Ser 195 and Ser 214.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chou, P. Y. & Fasman, G. D. Biochemistry 13, 222–245 (1974).
Lewis, P. N., Momany, F. A. & Sheraga, H. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 68, 2293–2298 (1971).
Lim, V. I. J. molec. Biol. 88, 873–878 (1974).
Finkelstein, A. V. & Ptisyn, O. B. J. molec. Biol. 62, 613–616 (1971).
Kabat, E. A. & Wu, T. T. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 1473–1478 (1973).
Schulz, G. E. et al. Nature 250, 140–142 (1974).
Matthews, B. W. Biochim. biophys. Acta 405, 442–451 (1975).
Schulz, G. E. Angew. Chemie (Intl Edn) 16, 23–32 (1977).
Levitt, M. & Warshel, A. Nature 253, 694–698 (1975).
Kuntz, I. D. et al. J. molec. Biol. 106, 983–994 (1976).
Ptitsyn, O. B. & Rashin, A. A. Biophys. Chem. 3, 1–20 (1975).
McLachlan, A. D. & Shotton, D. M. Nature 229, 202–205 (1971).
Shotton, D. M. & Watson, H. C. Nature 225, 811–816 (1970).
Birktoft, J. J., Blow, D. M., Henderson, R. & Steitz, T. A. Phil Trans. R. Soc. B 257, 67–76 (1970).
Kretsinger, R. H. & Barry, C. D. Biochim. biophys. Acta 405, 40–52 (1975).
Brayer, G. D., Delbaere, L. T. J. & James, M. N. G. J. molec. Biol. (in the press).
Delbaere, L. T. J., Hutcheon, W. L. B., James, M. N. G. & Thiessen, W. E. Nature 257, 758–763 (1975).
Brayer, G. D., Delabere, L. T. J. & James, M. N. G. J. molec. Biol. 124, 261–283 (1978).
Delbaere, L. T. J., Brayer, G. D. & James, M. N. G. Can. J. Biochem. 57, 135–144 (1979).
James, M. N. G., Delbaere, L. T. J. & Brayer, G. D. Can. J. Biochem. 56, 396–402 (1978).
Olson, M. O. J., Nagabhushan, N., Dzwiniel, M., Smillie, L. B. & Whitaker, D. R. Nature 228, 438–442 (1970).
Kaplan, H. & Whitaker, D. R. Can. J. Biochem. 47, 305–316 (1969).
Sawyer, L. et al. J. molec. Biol. 118, 137–208 (1978).
Rossmann, M. G. & Argos, P. J. biol. Chem. 250, 7525–7532 (1975).
Freer, S. T., Kraut, J., Robertus, J. D., Wright, H. T. & Xuong, N. H. Biochemistry 9, 1997–2009 (1970).
Bode, W., Schwager, P. & Huber, R. J. molec. Biol. 118, 99–112 (1978).
Narayanan, A. S. & Anwar, R. A. Biochem. J. 114, 11–17 (1969).
Birktoft, J. J. & Blow, D. M. J. molec. Biol. 68, 187–240 (1972).
Matthews, D. A., Alden, R. A., Birktoft, J. J., Freer, S. T. & Kraut, J. J. biol. Chem. 252, 8875–8883 (1977).
Biochem J. 113, 1–4 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DELBAERE, L., BRAYER, G. & JAMES, M. Comparison of the predicted model of α-lytic protease with the X-ray structure. Nature 279, 165–168 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/279165a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/279165a0
This article is cited by
-
Molecular structure of a new family of ribonucleases
Nature (1982)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.