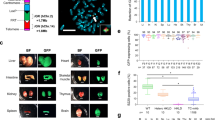
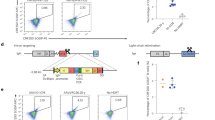
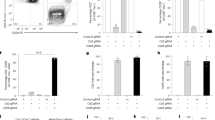
Abstract
We constructed two megabase-sized YACs containing large contiguous fragments of the human heavy and kappa (κ) light chain immunoglobulin (Ig) loci in nearly germline configuration, including approximately 66 VH and 32 Vκ genes. We introduced these YACs into Ig-inactivated mice and observed human antibody production which closely resembled that seen in humans in all respects, including gene rearrangement, assembly, and repertoire. Diverse Ig gene usage together with somatic hypermutation enables the mice to generate high affinity fully human antibodies to multiple antigens, including human proteins. Our results underscore the importance of the large Ig fragments with multiple V genes for restoration of a normal humoral immune response. These mice are likely to be a valuable tool for the generation of therapeutic antibodies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cook, G.P. & Tomlinson, I.M. The human immunoglobulin VH repertoire. Immunol. Today 16, 237–242 (1995).
Matsuda, F. & Honjo, T. Organization of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in Advances in Immunology 62, 1–29 (1993).
Cox, J.P.L., Tomlinson, I.M & Winter, G. A directory of human germ-line Vx segments reveals a strong bias in their usage. Eur. J. Immunol. 24, 827–836 (1994).
Weichhold, G.M., Ohnheiser, R. & Zachau, H.G. The human immunoglobulin κ locus consists of two copies that are organized in opposite polarity. Genomics 16, 503–511 (1993).
Max, E. Molecular genetics of immunoglobulins in Fundamental Immunology (ed. Paul, WE.) 315–382 (Raven Press, New York, 1993).
Bruggemann, M. et al. Human antibody production in transgenic mice: expression from 100 kb of the human IgH locus. Eur. J. Immunol. 21, 1323–1326 (1991).
Taylor, L.D. et al. A transgenic mouse that expresses a diversity of human sequence heavy and light chain immunoglobulins. Nucl. Acids Res. 20, 6287–6295 (1992).
Green, L.L. et al. .Antigen-specific human monoclonal antibodies from mice engineered with human Ig heavy and light chain YACs. Nature Genet. 7, 13–21 (1994).
Wagner, S.D. et al. The diversity of antigen-specific monoclonal antibodies from transgenic mice bearing human immunoglobulin gene miniloci. Eur. J. Immunol. 24, 2672–2681 (1994).
Jakobovits, A. Humanizing the mouse genome. Curr. Biol. 4, 761–763 (1994).
Bruggemann, M. & Neuberger, M.S. Strategies for expressing human antibody repertoires in transgenic mice. Immunol. Today 17, 391–397 (1996).
Lonberg, N. et al. Antigen-specific human antibodies from mice comprising four distinct genetic modifications. Nature 368, 856–859 (1994).
Fishwild, D.M. et al. High-avidity human IgG? monoclonal antibodies from a novel strain of minilocus transgenic mice. Nature Biotech. 14, 845–851 (1996).
Tuaillon, N., Taylor, L.D., Lonberg, N., Tucker, P.W. & Capra, J.D. Human immunoglobulin heavy-chain minilocus recombination in transgenic mice: gene-segment use in m and g transcripts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 3720–3724 (1993).
Taylor, L.D. et al. Human immunoglobulin transgenes undergo rearrangement, somatic mutation and class switching in mice that lack endogenous IgM. Int. Immun. 6, 579–591 (1994).
Silverman, G.A. et al. Meiotic recombination between yeast artificial chromosomes yields a single clone containing the entire BCL2 protooncogene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 9913–9917 (1990).
den Dunnen, J.T. et al. Reconstruction of the 2.4 Mb human DMD-gene by homologous YAC recombination. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1, 19–28 (1992).
Mendez, M.J. et al. Analysis of the structural integrity of YACs comprising human immunoglobulin genes in yeast and in embryonic stem cells. Genomics 26, 294–307 (1995).
Huber, C., Huber, E., Lautner-Rieske, A., Schable, K. F. & Zachau, H.G. The human immunoglobulin κ locus. Characterization of the partially duplicated L regions. Eur. J. Immun. 23, 2860–2967 (1993).
Jakobovits, A. et al. Germ-line transmission and expression of a human-derived yeast artificial-chromosome. Nature 362, 255–258 (1993).
Jakobovits, A. et al. Analysis of homozygous mutant chimaeric mice: Deletion of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain joining region blocks B-cell development and antibody production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 90, 2551–2555 (1993).
Yamada, M. et al. Preferential utilization of specific immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity and joining segments in adult human peripheral blood B lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 173, 395–407 (1991).
Brezinschek, H.P., Brezinschek, R.I. & Lipsky, P.E. Analysis of the heavy chain repertoire of human peripheral B cells using single-cell polymerase chain reaction. J. Immun. 155, 190–202 (1995).
Feeney, A.J. Lack of N regions in fetal and neonatal mouse immunoglobulin V-D-J junctional sequences. J. Exp. Med. 172, 137–1390 (1990).
Marks, J.D., Tristem, J., Karpas, A. & Winter, G. Oligonucleotide primers for polymerase chain reaction amplification of human immunoglobulin variable genes and design of family-specific oligonucleotide probes. Eur. J. Immun. 21, 985–991 (1991).
Sato, J.D. et al. Biological effects in vitro of monoclonal antibodies to human epidermal growth factor receptors. Mol. Biol. Med. 1, 511–529 (1983).
Kawamoto, T. et al. Growth stimulation of A431 cells by epidermal growth factor: Identification of high affinity receptors for EGF by an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 1337–1341 (1983).
Gill, G.N. et al. Monoclonal anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibodies which are inhibitors of epidermal growth factor binding and antagonists of epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 7755 (1984).
Vaughan, T.J. et al. Human antibodies with sub-nanomolar affinities isolated from a large non-immunized phage display library. Nature Biotech. 14, 309–314 (1996).
Brownstein, B.H. et al. Isolation of single-copy human genes from a library of yeast artificial chromosome clones. Science 244, 1348–1351 (1989).
Abertsen, H.M. et al. Construction and characterization of a yeast artificial chromosome library containing seven haploid human genome equivalents. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA. 87, 4256 (1990).
Berman, J.E. et al. Content and organization of the human Ig VH locus: definition of three new VH families and linkage to the Ig CH locus. EMBO J. 7, 727–738 (1988).
Anand, R., Villasante, A. & Tyler-Smith, C. Construction of yeast artificial chromosome libraries with large inserts using fractionation by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nucl. Acids Res. 17, 3425–3433 (1989).
Sherman, F., Fink, G.R. & Hicks, J.B. Laboratory course manual for methods in yeast genetics. (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, 1986).
Schiestl, R.H. & Gietz, R.D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr. Genet. 16, 339–346 (1989).
Mendez, M., David, N., Abderrahim, H. & Klapholz, S. A set of YAC targeting vectors for the interconversion of centric and acentric arms Genome Mapping and Sequencing meeting, 163 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, 1993).
Hermanson, G.G., Hoekstra, M.F., McElligott, D.L. & Evans, G.A. Rescue of end fragments of yeast artificial chromosomes by homologous recombination in yeast. Nucl. Acids Res. 19, 4943–4948 (1991).
Flanagan, J.G. & Rabbitts, T.H. Arrangement of human immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes implies evolutionary duplication of a segment containing γ, ε and α genes. Nature 300, 709–713 (1982).
Dariavach, P., Williams, G.T., Campbell, K., Pettersson, S. & Neuberger, M.S. The mouse IgH 3′-enhancer. Eur. J. Immun. 21, 1499–1504 (1991).
Gemmill, R.M. et al. Protocols for pulsed field gel electrophoresis: Separation and detection of large DNA molecules. Adv. Genome Biol. 1, 217–251 (1991).
Ray, S. & Diamond, B. Generation of a fusion partner to sample the repertoire of Splenic B cells destined for apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 5548–5551 (1994).
Galfre, G. & Milstein, C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Meth. Enzym. 73, 3–46 (1981).
Coligan, J.E., Kruisbeek, A.M., Margulies, D.H., Shevach, E.M. & Strober, W. Unit 2. 1, Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays in Current Protocols in Immunology (John Wiley and Sons, Inc. New York, 1994 ).
Lusti-Marasimhan, M. et al. Mutation of Leu 25 and Val 27 introduces CC chemokine activity into interleukin-8. J Biol. Chem. 270, 2716–2721 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendez, M., Green, L., Corvalan, J. et al. Functional transplant of megabase human immunoglobulin loci recapitulates human antibody response in mice. Nat Genet 15, 146–156 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0297-146
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0297-146
This article is cited by
-
Biparatopic antibody BA7208/7125 effectively neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants including Omicron BA.1-BA.5
Cell Discovery (2023)
-
Development of therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of diseases
Journal of Biomedical Science (2020)
-
CD146, from a melanoma cell adhesion molecule to a signaling receptor
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2020)