Abstract
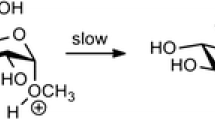
Cotton cellulose was swollen in a sodium hydroxide solution and carboxymethylated by a two-bath method for different periods of time for each process. The kinetics of acid hydrolysis and the crystallinity of the swollen and carboxymethylated samples were measured. The proportion of broken bonds, rate constants for hydrolysis, and permeability of cellulose to hydrolyzing agents were calculated. The susceptibility of glycosidic linkages to acid hydrolysis was improved by carboxymethylation more than by swelling in alkali. The increased accessibility of carboxymethylcellulose to acid was regarded as a consequence of increased intra-and intercrystalline swelling and of the glycosidic bonds' weakness caused by the electron-attracting carboxymethyl group on the C-6 position.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowland SP, Bertoniere NR (1985) Chemical methods of studying supramolecular structure. In: Nevell TP, Zeronian SH (eds) Cellulose Chemistry and Its Applications, Wiley, New York p 112
Tripp WV, Orr RS, Ziifle HM, Conrad CM (1958) Text Res J 28:404
Trividi SS, Chitale J (1959) J Text Inst 50:T390
Handu JL, Mythili K, Gupta RC (1974) 44:476
Hebeish A, Waly A, Tawfik M, Abou-Zeid NY, Shalaby S, El-Rafie MH (1979) Cellul Chem Technol 13:543
Schleicher H, Philipp B, Kunze J, Fink HP (1985) Lenzinger Berichte 59:45
Warwicker JO, Jeffries R, Colbran RL, Robinson RN (1966) A Review of the Literature on the Effect of Caustic Soda and Other Swelling Agents on the Fine Structure of Cotton, Shirley Institute Pamphlet No 93, Shirley Institute, Manchester, England
Kálmán F, Borsa J, Rusznák I (1988) Colloid Polym Sci 266:716
Kálmán F, Borsa J, Madarász R, Rusznák I (1989) Colloid Polym Sci 267:349
Borsa J, Kálmán F, Rusznák I Colloid Polym Sci in print
Daul GC, Reinhardt RM, Reid JD (1952) Text Res J 22:787
Neale SM, Stringfellow WA (1937) Trans Faraday Soc 33:881
Shishko AM, Volkovich SM, Skrigan AI (1977) Khimiia Dreves 3:69
Yerofeiev BV, Shishko AM, Pesniakevich LG (1979) Dokl Akad Nauk BSSR 23:39
Szentpály T, Leitner R (1963) Chemical Investigations of Textiles (in Hungarian) Műszaki Könyvkiadó Budapest
Roy L, Whistler RL, Wolfram ML (1962) Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry, Academic Press, v 1:388
Albrecht J (1964) Textilrundschau 5:257
Rusznák I, Lepenye Gy (1968) Kolorisztikai Értesitő 10:226
Atalla RH (1979) Conformational Effects in the Hydrolysis of Cellulose. In: Brown RS Jr and Jurasek L (eds) Hydrolysis of Cellulose: Mechanisms of Enzymatic and Acid Catalysis American Chemical Society Advances in Chemistry Series 181:55
Nevell TP (1985) Degradation of Cellulose by Acids, Alkalis and Mechanical Means. In: Nevell TP and Zeronian SH (eds) Cellulose Chemistry and its Applications, Wiley, New York 223
Croon I, Purves CB (1959) Svensk Paperstidn 62:876
Krässig H (1984) Das Papier 38:571
Rogovin ZA (1972) Khimiia tsellulosi, Moscow, Khimiia, 403
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borsa, J., Tánczos, I. & Rusznák, I. Acid hydrolysis of carboxymethylcellulose of low degree of substitution. Colloid & Polymer Sci 268, 649–657 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01410407
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01410407