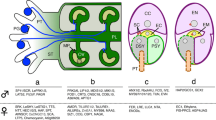
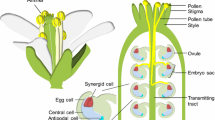
Summary
Since its discovery at the end of the last century, double fertilization remains of central interest in plant reproductive biology research. Although the sequence of events leading to fertilization is well known from cytological studies, the underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated. This now seems feasible by the diversification and refinement of recently developed technologies presented in this review. The progress made during the last five years in understanding pollen tube guidance, discharge into the embryo sac, and gametic fusion are described. Future directions are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida EAC, Huovila A-PJ, Sutherland AE, Stephens LE, Calarco PG, Shaw LM, Mercurio AM, Sonnenberg A, Primakoff P, Myles D, White JM (1995) Mouse egg integrin α6β1 functions as a sperm receptor. Cell 81: 1095–1104
Blobel CP, Wolfsberg TG, Turk CW, Myles DG, Primakoff P, White JM (1992) A potential fusion peptide and integrin ligand domain in a protein active in sperm-egg fusion. Nature 356: 248–252
Brawley SH (1990) The fast block against polyspermy in fucoid algae is an electrical block. Dev Biol 144: 94–106
Breton C, Faure J-E, Dumas C (1995) From in vitro fertilization to early embryogenesis in maize. Protoplasma 187: 3–12
Brewbaker JL, Kwack PK (1963) The essential role of calcium ion in pollen germination and pollen tube growth. Am J Bot 50: 859–865
Campenot MK, Zhang G, Cutler AJ, Cass DD (1992)Zea mays embryo sacs in culture. I. Plant regeneration from 1 day after pollination embryos. Am J Bot 79: 1368–1373
Capus MG (1878) Anatomie du tissu conducteur. Ann Sci Nat 7: 207–291
Chaboud A, Perez R (1992) Generative cells and male gametes: isolation, physiology, and biochemistry. Int Rev Cytol 140: 205–232
Chasan R (1992) Frontiers in fertilization. Plant Cell 4: 369–371
Chaubal R, Reger BJ (1990) Relatively high calcium is localized in synergid cells of wheat ovaries. Sex Plant Reprod 3: 98–102
— — (1992a) Calcium in the synergid cells and other regions of pearl millet ovaries. Sex Plant Reprod 5: 34–46
— — (1992b) The dynamics of calcium distribution in the synergid cells of wheat after pollination. Sex Plant Reprod 5: 206–213
— — (1993) Prepollination degeneration in mature synergids of pearl millet: an examination using antimonate fixation to localize calcium. Sex Plant Reprod 6: 225–238
Cheung AY (1995) Pollen-pistil interactions in compatible pollination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 3077–3080
—, Wang H, Wu H-M (1995) A floral transmitting tissue-specific glycoprotein attracts pollen tubes and stimulates their growth. Cell 82: 381–393
Dresselhaus T, Lörz H, Kranz E (1994) Representative cDNA libraries from few plant cells. Plant J 5: 605–610
Dumas C, Faure J-E (1995) Use of in vitro fertilization and zygote culture in crop improvement. Curr Opin Biotech 6: 183–188
—, Mogensen HL (1993) Gametes and fertilization: maize as a model system for experimental embryogenesis in flowering plants. Plant Cell 5: 1337–1348
Dupuis I (1992) In vitro pollination: a new tool for analysing environmental stress. Int Rev Cytol 140: 391–405
—, Dumas C (1990) Biochemical markers of female receptivity in maize (Zea mays L.) assessed using in vitro fertilization. Plant Sci 70: 11–19
Faure J-E, Mogensen HL, Kranz E, Digonnet C, Dumas C (1992) Ultrastructural characterization and three-dimensional reconstruction of isolated maize (Zea mays L.) egg cell protoplasts. Protoplasma 171: 97–103
— —, Dumas C, Kranz E, Lörz H (1993) Karyogamy after electrofusion of single egg and sperm cell protoplast from maize (Zea mays L.): cytological evidences and time course. Plant Cell 5: 747–755
—, Digonnet C, Mól R, Matthys-Rochon E, Dumas C (1994a) In vitro pollination and fertilisation in maize (Zea mays L.): technical procedures and prospects for the dissection of the double fertilisation process. Plant Sci 104: 1–10
— —, Dumas C (1994b) An in vitro system for adhesion and fusion of maize gametes. Science 263: 1598–1600
Foltz KR, Partin JS, Lennarz WJ (1993) Molecular characterization of the sea urchin egg receptor for sperm. Science 259: 1421–1425
Friedman WE (1994) The evolution of embryogeny in seed plants and the developmental origin and early history of endosperm. Am J Bot 81: 1468–1486
Guǵuen MF (1901) Anatomie comparée du tissu conducteur de style et du stigmate des phanérogames. J Bot Paris 14: 140–300
Guignard L (1899) Sur les anthérozoïdes et la double copulation sexuelle chez les végétaux angiospermes. Rev Gén Bot 11: 129–135
Heslop-Harrison J, Heslop-Harrison Y (1986) Pollen-tube chemotropism: fact or delusion? In: Cresti M, Romano D (eds) Biology of reproduction and cell motility in plants and animals. University of Siena Press, Siena, pp 169–174
Holm PB, Knudsen S, Mouritzen P, Negri D, Olsen FL, Roué C (1994) Regeneration of fertile barley plants from mechanically isolated protoplasts of the fertilized egg cell. Plant Cell 6: 531–543
— — — — — — (1995) Regeneration of the barley zygote in ovule culture. Sex Plant Reprod 8: 49–59
Huang B-Q, Russel SD (1992a) Female germ unit: organization, isolation, and function. Int Rev Cytol 140: 233–293
— — (1992b) Synergid degeneration inNicotiana: a quantitative, fluorochromatic and chlorotetracycline study. Sex Plant Reprod 5: 151–155
— — (1994) Fertilization inNicotiana tabacum: cytoskeletal modifications in the embryo sac during synergid degeneration. Planta 194: 200–214
—, Sheridan WF (1994) Female gametophyte development in maize: microtubular organization and embryo sac polarity. Plant Cell 6: 845–861
— —, Strout GW, Mao L-J (1990) Organization of isolated embryo sacs and eggs ofPlumbago zeylanica (Plumbaginaceae) before and after fertilization. Am J Bot 77: 1401–1410
— —, Russell SD (1993a) Fertilization inNicotiana tabacum — ultrastructural organization of propane-jet-frozen embryo sacs in vivo. Planta 191: 256–264
—, Pierson ES, Russell SD, Tiezzi A, Cresti M (1993b) Cytoskeletal organization and modification during pollen tube arrival, gamete delivery and fertilization inPlumbago zeylanica. Zygote 1: 143–154
Hülskamp M, Kopczak S, Horejsi TF, Kihl BK, Pruitt RE (1995a) Identification of genes required for pollen-stigma recognition inArabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 8: 703–714
—, Schneitz K, Pruitt RE (1995b) Genetic evidence for a long-range activity that directs pollen tube guidance inArabidopsis. Plant Cell 7: 57–64
Iwanami Y (1953) Physiological researches of pollen. 5. On the conductive tissue and the growth of the pollen tube in the style. Bot Mag Tokyo 66: 189–196
Jaffe LA (1976) Fast block to polyspermy in sea urchin is electrically mediated. Nature 261: 68–71
Janson J, Willemse MTM (1995) Pollen tube penetration and fertilization inLilium longiflorum (Liliaceae). Am J Bot 82: 186–196
Jauh GY, Lord EM (1995) Movement of the tube cell in the lily style in the absence of the pollen grain and the spent pollen tube. Sex Plant Reprod 8: 168–172
Jensen WA (1964) Observations on the fusion of nuclei in plants. J Cell Biol 23: 669–672
—, Fisher DB (1968) Cotton embryogenesis: the entrance and discharge of the pollen tube in the embryo sac. Planta 78: 158–183
Keijzer CJ, Reinders MC, Leferinkten Klooster HB (1988) A micromanipulation method for artificial fertilization inTorenia. In: Cresti M, Gori P, Pacini E (eds) Sexual reproduction in higher plants. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 119–124
Knox RB (1994) 13th International Congress on Sexual Plant Reproduction 1994 — frontiers in sexual plant reproduction research. Sex Plant Reprod 7: 363–365
Koornneef M, Hanhart CJ, Thiel F (1989) A genetic and phenotypic description ofEceriferum (cer) mutants inArabidopsis thaliana. J Hered 80: 118–122
Kovacs M, Barnabas B, Kranz E (1994) The isolation of viable egg cells of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sex Plant Reprod 7: 311–312
Kranz E, Lörz H (1993) In vitro fertilization with isolated, single gametes results in zygotic embryogenesis and fertile maize plants. Plant Cell 5: 739–746
— — (1994) In vitro fertilization of maize by single egg and sperm cell protoplast fusion mediated by high calcium and high pH. Zygote 2: 125–128
—, Bautor J, Lörz H (1991a) In vitro fertilization of single isolated gametes by electrofusion. Sex Plant Reprod 4: 12–16
— — — (1991b) Electrofusion-mediated transmission of cytoplasmic organelles through the in vitro fertilization process, fusion of sperm cells with synergids and central cells, and cell reconstruction in maize. Sex Plant Reprod 4: 17–21
—, Lörz H, Digonnet C, Faure J-E (1992) In vitro fusion of gametes and production of zygotes. Int Rev Cytol 140: 407–423
—, Von Wiegen P, Lörz H (1995) Early cytological events after induction of cell division in egg cells and zygote development following in vitro fertilization with angiosperm gametes. Plant J 8: 9–23
Leduc N, Matthys-Rochon E, Dumas C (1995) Deleterious effect of minimal enzymatic treatments on the development of isolated maize embryo sacs in culture. Sex Plant Reprod 8: 313–317
Lord EM, Sanders LC (1992) Roles for the extracellular matrix in plant development and pollination: a special case of cell movement in plants. Dev Biol 153: 16–28
Malhó R, Read ND, Pais MS, Trewavas AJ (1994) Role of cytosolic free calcium in the reorientation of pollen tube growth. Plant J 5: 331–341
— —, Trewavas AJ, Pais MS (1995) Calcium channel activity during pollen tube growth and reorientation. Plant Cell 7: 1173–1184
Mascarenhas JP (1993) Molecular mechanisms of pollen tube growth and differentiation. Plant Cell 5: 1303–1314
—, Machlis L (1964) Chemotropic response of the pollen tube ofAntirrhinum to calcium. Plant Physiol 39: 70–77
Matthys-Rochon E, Mòl R, Heizmann P, Dumas C (1994) Isolation and microinjection of active sperm nuclei into egg cells and central cells of isolated maize embryo sac. Zygote 2: 29–35
Miller DD, Callaham DA, Gross DJ, Hepler PK (1992) Free Ca2+ gradient in growing pollen tubes ofLilium. J Cell Sci 101: 7–12
Mo Y, Nagel C, Taylor LP (1992) Biochemical complementation of chalcone synthase mutants defines a role for flavonols in functional pollen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 7213–7217
Modrusan Z, Reiser L, Feldman KA, Fisher RL, Haughn GW (1994) Homeotic transformation of ovules into carpelle-like structures inArabidopsis. Plant Cell 6: 333–349
Mogensen HL (1988) Exclusion of male mitochondria and plastids during syngamy in barley as a basis for maternal inheritance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 2594–2597
— (1990) Fertilization and early embryogenesis. In: Chapman CP (ed) Reproductive versatility in the grasses. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 76–99
— (1992) The male germ unit: concept, composition, and significance. Int Rev Cytol 140: 129–147
— (1996) The hows and whys of cytoplasmic inheritance in seed plants. Am J Bot 83: 383–404
—, Holm PB (1995) Dynamics of nuclear DNA quantities during zygote development in barley. Plant Cell 7: 487–494
—, Leduc N, Matthys-Rochon E, Dumas C (1995) Nuclear DNA amounts in the egg and zygote of maize (Zea mays L.). Planta 197: 641–645
Mól R, Matthys-Rochon E, Dumas C (1993) In vitro culture of fertilized embryo sacs of maize: zygotes and two-celled proembryos can develop into plants. Planta 189: 213–217
— — — (1994) The kinetics of cytological events during double fertilization inZea mays L. Plant J 5: 197–206
Murgia M, Huang B-Q, Tucker SC, Musgrave ME (1993) Embryo sac lacking antipodal cells inArabidopsis thaliana (Brassicaceae). Am J Bot 80: 824–838
Nawaschin SG (1898) Resultate einer Revision der Befruchtungs-vorgänge beiLilium martagon undFritillaria tenella. Bull Acad Imp Sci St Petersburg 33: 39–47
O'Driscoll D, Kann C, Read SM, Steer MW (1993) Endocytotic uptake of fluorescent dextrans by pollen tubes grown in vitro. Protoplasma 175: 126–130
Obermeyer G, Weisenseel MH (1991) Calcium channel blocker and calmodulin antagonists affect the gradient of free calcium ions in lily pollen tubes. Eur J Cell Biol 56: 319–327
Pierson ES, Miller DD, Callaham DA, Shipley AM, Rivers BA, Cresti M, Hepler PK (1994) Pollen tube growth is coupled to the extracellular calcium ion flux and the intracellular calcium gradient: effect of BAPTA-type buffers and hypertonic media. Plant Cell 6: 1815–1828
Pollak PE, Hansen K, Astwood JD, Taylor LP (1995) Conditional male fertility in maize. Sex Plant Reprod 8: 231–241
Preuss D, Lemieux B, Yen G, Davis RW (1993) A conditional sterile mutation eliminates surface components fromArabidopsis pollen and disrupts cell signaling during fertilization. Genes Dev 7: 974–985
Rathore KS, Cork RJ, Robinson KR (1991) A cytoplasmic gradient of Ca2+ is correlated with the growth of lily pollen tubes. Dev Biol 148: 612–619
Reger BJ. Chaubal R, Pressey R (1992a) Chemotropic responses by pearl millet pollen tubes. Sex Plant Reprod 5: 47–56
—, Pressey R, Chaubal R (1992b) In vitro chemotropism of pearl millet pollen tubes to stigma tissue: a response to glucose produced in the medium by tissue-bound invertase. Sex Plant Reprod 5: 201–205
Reiser L, Fisher RL (1993) The ovule and the embryo sac. Plant Cell 5: 1291–1301
Robinson-Beers K, Pruitt RE, Gasser CS (1992) Ovule development in wild-typeArabidopsis and two female-sterile mutants. Plant Cell 4: 1237–1249
Roeckel P, Dumas C (1993) Survival at 20 °C and cryopreservation of isolated sperm cells fromZea mays pollen grains. Sex Plant Reprod 6: 212–216
Russell SD (1991) Isolation and characterization of sperm cells in flowering plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 42: 189–204
— (1992) Double fertilization. Int Rev Cytol 140: 357–388
— (1993) The egg cell: development and role in fertilization and early embryogenesis. Plant Cell 5: 1349–1359
—, Rougier M, Dumas C (1990) Organization of the early post-fertilization megagametophyte ofPopulus deltoides: ultrastructure and implications for male cytoplasmic transmission. Protoplasma 155: 153–165
Sanders LC, Lord EM (1989) Directed movement of latex particles in the gynoecia of three species of flowering plants. Science 243: 1606–1608
— — (1992) A dynamic role for the stylar matrix in pollen tube extension. Int Rev Cytol 140: 297–318
—, Wang C-S, Walling LL, Lord EM (1991) A homolog of the substrate adhesion molecule, vitronectin, occurs in four species of flowering plants. Plant Cell 3: 629–635
Schatten G (1994) The centrosome and its mode of inheritance: the reduction of the centrosome during gametogenesis and its restoration during fertilization. Dev Biol 165: 299–335
Strasburger E (1884) Neue Untersuchungen über den Befruchtungsvorgang bei den Phanerogamen. G Fischer, Jena
Swope RE, Kropf DL (1993) Pronuclear positioning and migration during fertilization inPelvetia. Dev Biol 157: 269–276
Tirlapur UK, Van Went JL, Cresti M (1993) Visualization of membrane calcium and calmodulin in embryo sacs in situ and isolated fromPetunia hybrida L. andNicotiana tabacum L. Ann Bot 71: 161–167
—, Scali M, Moscatelli A, Del Casino C, Cai G, Tiezzi A, Cresti M (1994) Confocal image analysis of spatial variations in immunocytochemically identified calmodulin during pollen hydration, germination and pollen tube tip growth inNicotiana tabacum L. Zygote 2: 63–68
—, Kranz E, Cresti M (1995) Characterisation of isolated egg cells, in vitro fusion products and zygotes ofZea mays L. using the technique of image analysis and confocal laser microscopy. Zygote 3: 57–64
Ueda K, Tanaka I (1994) The basic proteins for male gametic nuclei isolated from pollen grains ofLilium longiflorum. Planta 192: 446–452
Van der Maas HM, Zaal MACM, De Jong ER, Van Went JL (1993a) Optimization of isolation and storage of sperm cells from the pollen of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Sex Plant Reprod 6: 64–70
— — —, Krens FA, Van Went JL (1993b) Isolation of viable egg cells of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Protoplasma 173: 86–89
Webb MC, Gunning BES (1994) Embryo sac development inArabidopsis thaliana. II. The cytoskeleton during megagametogenesis. Sex Plant Reprod 7: 153–163.
Wu H-M, Wang H, Cheung AY (1995) A pollen tube growth stimulatory glycoprotein is deglycosyled by pollen tubes and displays a glycosylation gradient in the flower. Cell 82: 395–403
Yanagimachi R (1978) Calcium requirement for sperm-egg fusion in mammals. Biol Reprod 19: 949–958
Yu H-S, Russell SD (1994) Occurrence of mitochondria in the nuclei of tobacco sperm cells. Plant Cell 6: 1477–1484
—, Huang B-Q, Russell SD (1994) Transmission of male cytoplasm during fertilization inNicotiana tabacum. Sex Plant Reprod 7: 313–323
Zhang G, Campenot MK, McGann LE, Cass DD (1992a) Flow cytometric characteristics of sperm cells isolated from pollen ofZea mays L. Plant Physiol 99: 54–59
—, Williams CM, Campenot MK, McGann LE, Cass DD (1992b) Improvement of longevity and viability of sperm cells isolated from pollen ofZea mays L. Plant Physiol 100: 47–53
—, Gifford DJ, Cass DD (1993) RNA and protein synthesis in sperm cells isolated fromZea mays L. Pollen. Sex Plant Reprod 6: 239–243
- Williams CM, Campenot MK, McGann LE, Cutler AJ, Cass DD (1995) Effects of calcium, magnesium, potassium, and boron on sperm cells isolated from pollen ofZea mays L. Sex Plant
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. Dr. Dr. h.c. Eberhard Schnepf on the occasion of his retirement
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faure, J.E., Aldon, D., Rougier, M. et al. Emerging data on pollen tube growth and fertilization in flowering plants, 1990–1995. Protoplasma 193, 132–143 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01276641
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01276641