Summary
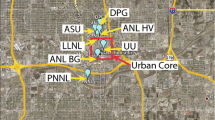
A description of the Argonne Boundary Layer Experiments (ABLE) facility, located in southern Kansas, USA, to study the planetary boundary layer on a continuous basis is given. The use and role of the minisodars in these studies is shown to be important and necessary in the study of surface boundary layers, extension of wind profiles to the surface, and estimates of convergence/divergence over 50–100 km scales over this site. A description of the site and location and description of the instrument systems is given; products available through internet access are briefly described. Use of the site by cooperative investigations is also described and invited.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received October 12, 1998 Revised January 29, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coulter, R., Klazura, G., Lesht, B. et al. The Argonne Boundary Layer Experiments Facility: Using Minisodars to Complement a Wind Profiler Network. Meteorol Atmos Phys 71, 53–59 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007030050043
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007030050043