Abstract
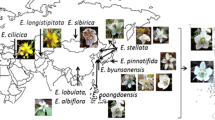
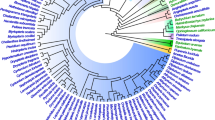
Restriction site and length variations of nrDNA were examined for 51 populations of seven species ofKrigia. The nrDNA repeat ranged in size from 8.7 to 9.6 kilobase (kb). The transcribed region, including the two ITSs, was 5.35 kb long in all examinedKrigia populations. In contrast, the size of the nontranscribed IGS varied from 3.35 to 4.25 kb. Eight different types of length-variations were identified among the 51 populations, including distinct nrDNA lengths in the tetraploid and diploid populations of bothK. biflora andK. virginica. However, a few variations were detected among populations of the same species or within a cytotype. All populations ofKrigia sect.Cymbia share a 600 bp insertion in IGS near the 18 S gene, and this feature suggests monophyly of the section. AllKrigia spp. had a conjugated type of subrepeat composed of approximately 75 basepairs (bp) and 125 bp. Base modifications in the gene coding regions were highly conserved among species. Forty-five restriction sites from 15 enzymes were mapped, 24 of which were variable among populations. Only four of the variable sites occurred in the rRNA coding region while 20 variable sites were detected in the noncoding regions. Collectively, 25 enzymes generated about 66 restriction sites in each nrDNA; this amounts to about 4.3% of the nrDNA repeat. A total of 50 restriction sites was variable, 28 of which were phylogenetically informative. Phylogenetic analyses of site mutations indicated that two sections ofKrigia, sect.Cymbia and sect.Krigia, are monophyletic. In addition, relationships among several species were congruent with other sources of data, such as cpDNA restriction site variation and morphology. Both length and restriction site variation supported an allopolyploid origin of the hexaploidK. montana. The average sequence divergence value inKrigia nrDNA was 40 times greater than that of the chloroplast DNA. The rapid evolution of nrDNA sequences was primarily due to changes of the IGS sequences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels, R., Dvorak, K., 1982: Relative rates of divergence of species and gene sequences within the rDNA region of species in theTriticeae: implications for the maintenance of homogeneity of a repeated gene family. — Theor. Appl. Genet.63: 361–365.
—, 1986: rDNA: evolution over a billion years. — InDutta, S. K., (Ed.): DNA systematics 2, pp. 81–135. — Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press.
Barker, R. F., Harberd, N. P., Jarvis, M. G., Flavell, R. B., 1988: Structure and evolution of the intergenic region in a ribosomal DNA repeat unit of wheat. — J. Mol. Biol.201: 1–17.
Chambers, C. L., 1965: An allopolyploidKrigia from the southern Appalachians. — Amer. J. Bot. (Abstr.)52: 654.
Chinnappa, C. C., 1981: Cytological studies inKrigia (Asteraceae). — Canad. J. Genet. Cytol.23: 671–678.
Choumane, W., Heizmann, P., 1988: Structure and variability of nuclear ribosomal genes in the genusHelianthus. — Theor. Appl. Genet.76: 481–489.
Doyle, J. J., Beachy, R. N., 1985: Ribosomal gene variation in soybean (Glycine) and its relatives. — Theor. Appl. Genet.70: 369–376.
—, —,Lewis, W. H., 1984: Evolution of rDNA inClaytonia polyploid complexes. — InGrant, W. F., (Ed.): Plant biosystematics, pp. 321–341. — Toronto: Academic Press.
—, 1988: A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. — Phytochem. Bull.19: 11–15.
Fedoroff, N. V., 1979: On spacers. — Cell16: 697–710.
Field, G. F., Olsen, G. L., Lane, D. J., Giovannoni, S. J., Ghiselin, M. T., Raff, E. C., Pace, N. R., Raff, R. A., 1988: Molecular phylogeny of the animal kingdom. — Science239: 748–753.
Ganal, M., Torves, R., Hemleben, V., 1988: Complex structure of the ribosomal DNA spacer ofCucumis sativus. — Mol. Gen. Genet.212: 548–554.
Gerlach, W. L., Bedbrook, J. R., 1979: Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat and barley. — Nucleic Acids Res.7: 1869–1885.
Grellet, F., Delcasso-Tremousaygue, D., Delseny, M., 1989: Isolation and characterization of unusual repeated sequences from the ribosomal intergenic spacer of the cruciferSisymbrium irio. — Pl. Mol. Biol.12: 695–707.
Hendy, M. D., Penny, D., 1982: Branch and bound algorithms to determine minimal evolutionary trees. — Math. Biosci.59: 227–290.
Jansen, R. K., Wallace, R. S., Kim, K.-J., Chambers, K. L., 1991: Systematic implications of chloroplast DNA variation in the subtribeMicroseridinae (Asteraceae:Lactuceae). — Amer. J. Bot.78 (in press).
Jorgensen, R. A., Cluster, P. D., 1988: Modes and tempos in evolution of nuclear ribosomal DNA: new characters for evolutionary studies and new markers for genetic and population studies. — Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard.75: 1238–1247.
—, 1987: Structure and variation in ribosomal RNA genes of pea. — Pl. Mol. Biol.8: 3–12.
Kato, A., Yakura, K., Tanifuji, S., 1985: Repeated DNA sequences found in the large spacer ofVicia faba rDNA. — Biochem. Biophys. Acta825: 411–415.
Kim, K.-J., 1989: A systematic study of the genusKrigia (Asteraceae, Lactuceae), emphasizing chloroplast DNA and nuclear ribosomal DNA variations. — Ph.D. Dissertation, The University of Texas at Austin.
-Turner, B. L., 1991: Systematic overviews ofKrigia (Asteraceae:Lactuceae). — Brittonia (submitted).
-Jansen, R. K., Turner, B. L., 1991a: Evolutionary implications of intraspecific chloroplast DNA variation among the species of dwarf dandelions (Krigia—Asteraceae). — Amer. J. Bot. (submitted).
-Turner, B. L., Jansen, R. K., 1991b: Phylogenetic and evolutionary implications of interspecific chloroplast-DNA variation in dwarf dandelion (Krigia—Lactuceae—Asteraceae). — Syst. Bot. (submitted).
King, L. M., Schaal, B. A., 1989: Ribosomal-DNA variation and distribution inRudbeckia missouriensis. — Evolution43: 1117–1119.
Lake, A. J., 1985: Evolving ribosome structure: domains in archaebacteria, eubacteria, eocytes and eukaryotes. — Ann. Rev. Biochem.54: 507–530.
Learn, G. A. Jr.,Schaal, B. A., 1987: Population subdivision for ribosomal DNA repeat variants inClematis fremontii. — Evolution41: 433–438.
McClelland, M., Nelson, M., 1985: The effect of site specific methylation on restriction endonuclease digestion. — Nucleic Acids Res.13: s201-s207.
Nei, M., Li, W.-H., 1979: Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. — Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.76: 5268–5273.
Nelson, M., McClelland, M., 1987: The effect of site-specific methylation on restriction-modification enzymes. — Nucleic Acids Res.15: s219-s230.
Palmer, J., 1986: Isolation and structural analysis of chloroplast DNA. — Methods Enzym.118: 167–186.
Raue, H. A., Klootwijk, J., Musters, W., 1988: Evolutionary conservation of structure and function of higher molecular weight ribosomal RNA. — Prog. Biophys. Molec. Biol.51: 77–129.
Reddy, P., Apples, R., Baum, B. R., 1990: Ribosomal DNA spacer-length variation inSecale spp. (Poaceae). — Pl. Syst. Evol.171: 205–220.
Rogers, S. O., Bendich, A. J., 1987: Ribosomal RNA genes in plants: variability in copy number and in the intergenic spacer. — Pl. Mol. Bol.9: 509–520.
Saghai-Maroof, M. A., Soliman, K. M., Jorgensen, R. A., Allard, R. W., 1984: Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. — Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.81: 8014–8018.
Schaal, B. A., Leverich, W. J., Nieto-Sotelo, J., 1987: Ribosomal DNA variation in the native plant,Phlox divaricata. — Mol. Biol. Evol.4: 611–621.
—,Learn, G. H. Jr., 1988: ribosomal DNA variation within and among plant populations. — Ann. Missouri Bot. Gard.75: 1207–1216.
Schmidt-Puchta, W., Gunther, I., Sanger, H. L., 1989: Nucleotide sequence of the intergenic spacer (IGS) of the tomato ribosomal DNA. — Pl. Mol. Biol.13: 251–253.
Siegel, A., Kolacz, K., 1983: Heterogeneity of pumpkin ribosomal DNA. — Pl. Physiol.72: 166–171.
Sytsma, K. J., Schaal, B. A., 1985: Phylogenetics of theLisianthius skinneri (Gentianaceae) species complex in Panama utilizing DNA restriction fragment analysis. — Evolution39: 594–608.
Tomb, S., Chambers, K. L., Hyhos, D. W., Powell, A. M., Raven, P. H., 1978: Chromosome numbers in theCompositae XIV.Lactuceae. — Amer. J. Bot.65: 717–721.
Yakura, K., Kato, A., Tanifuji, S., 1984: Length heterogeneity in the large spacer ofVicia faba rDNA is due to differing number of 325 bp repetitive elements. — Mol. Gen. Genet.139: 400–405.
Zimmer, E. A., Jupe, E. R., Walbot, V., 1988: Ribosomal gene structure, variation and inheritance in maize and its ancestors. — Genetics120: 1125–1136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, K.J., Mabry, T.J. Phylogenetic and evolutionary implications of nuclear ribosomal DNA variation in dwarf dandelions (Krigia, Lactuceae, Asteraceae). Pl Syst Evol 177, 53–69 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00937826
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00937826