Summary
Point-load tests were performed on three hard rocks of the Lake Superior district, ironformation, metadiabase, and ophitic basalt. More than 500 irregular, mine-run fragments ranging in diameter up to about 250 mm were tested in the field, using a specially designed, semi-portable test rig. Results were analyzed by multiple regression techniques, seeking a “best” expression for the point-load strength in terms of a size effect and shape effects. Standard unconfined compression tests and “Brazilian” tests were also performed on the metadiabase and the basalt, three core sizes of each, in order to determine their respective size effects. The size-effect exponents for compression were found to be a variable characteristic of rock type, as previously reported for other rocks by the senior author, whereas the size-effect exponent in the point-load test was constant over all three rocks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Load-bearing area of prismatic compression specimen, mm2
- α:
-
Probability level of a statistical significance test
- b, w :
-
Long and short prism dimensions, mm, in plane perpendicular to load
- c i ,c L :
-
Exponent in equation for strength (coefficient, in the log-linear form)
- d :
-
Diameter, mm
- D, H :
-
Initial and final (at rupture) distance between the load points, mm
- E :
-
Young's modulus, MPa
- F :
-
Axis of the fracture surface normal toD, mm, point-load test
- G, J :
-
Semiminor, semimajor, specimen axis, mm, perpendicular to direction of point load
- h :
-
Height of prismatic compression specimen, mm
- K :
-
Constant in linear regression model, basic rock strength parameter
- L, M, S :
-
Long, intermediate, and short axes, of point-load-test specimen
- log:
-
Natural (Napierian) logarithm
- n :
-
Number of tests
- v :
-
Poisson's ratio
- P :
-
Resistance of test specimen at rupture, Newtons
- Q :
-
Compressive strength, MPa, determined from unconfined compression test
- R :
-
Multiple correlation ratio for a multilinear regression analysis
- SE :
-
Standard error of estimate for a multilinear regression analysis
- T :
-
Tensile strength, MPa, determined from diametral compressive test of core
- t :
-
Thickness, mm
- U :
-
Geometric mean diameter, mm, of the minimum cross section through the load points=(DG)1/2
- V :
-
Geometric mean diameter, mm, of point-load specimen=(LMS)1/3
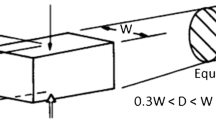
- W :
-
Geometric mean diameter, mm, of the specimen midsection perpendicular to the point-load direction=(GJ)1/2
- X, Y :
-
Geometric mean diameter, mm, of the fracture surface, estimated by (DF)1/2, by (HF)1/2
- Z LM ,Z RA , ...:
-
Differences between values of logK, used to express category effects, those attributed to specimen orientation and/or rock type
References
Broch, E., Franklin, J. A. (1972): The point-load strength test. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 9, 669–697.
Draper, N. R., Smith, H. (1981): Applied regression analysis. Second edn. J. Wiley, New York, 241.
Fannon, T. A. (1989): The effect of size on rock strength determined by point load tests on irregular shaped rock fragments, uniaxial compression tests, and Brazil tests. Project Report submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for M. S. degree in Mining Engineering, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, Michigan.
ISRM Commission on Standardization of Laboratory and Field Tests (1972): Suggested methods for determining the uniaxial compressive strength of rock materials and the point load strength index. ISRM, Lisbon.
ISRM Commission on Testing Methods (1985): Suggested method for determining point load strength (revised). Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 22, 51–60.
Panek, L. A. (1981): Estimating mine pillar strength from compression tests. Trans. AIME, 268, 1749–1761, and Discussion 272, 2005–2009.
Protodyakonov, M. M., Voblikov, V. S. (1957): Determining the strength of rock on samples of an irregular shape. Ugol 32 (4).
Villar, J. W., Dawe, G. A. (1985): The Tilden Mine — A new processing technique for iron ore. Mining Congress Journal 61 (10), 40–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panek, L.A., Fannon, T.A. Size and shape effects in point load tests of irregular rock fragments. Rock Mech Rock Engng 25, 109–140 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01040515
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01040515