Abstract
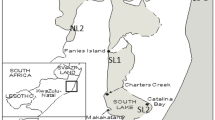
The concentrations of heavy metals and radionuclides in the sediments and water of Great Bear Lake were determined during 1978 near an operating silver mine and an abandoned uranium mine. Additional information on the level of mercury in fish tissues were also collected. The mines, situated on the same site, deposited tailings and other waste material directly into the lake. The concentrations of mercury, lead, manganese, and nickel in the sediments were highest near the tailings deposit and decreased significantly as the distance from the mine increased. Although there were also significant positive correlations between these metals and the organic content of the sediments, water depth and slope of the bottom had no impact on metal distribution. Since the concentrations of arsenic, cobalt, copper,226radium,210lead and230thorium varied inconsistently throughout the study area, the distribution of these substances could not be related to any of the environmental factors that were measured. There were, however, significant negative correlations between the concentrations of232thorium and228thorium and distance from the mine and organic content of the sediments. Heavy metal and radionuclide levels in water were generally below detectable limits, reflecting the strong chemical bonding characteristics of the sediments. The low concentrations of mercury in the tissues of lake troutSalvelinus namaycush were probably related to low uptake rates and the ability of this species to move into uncontaminated areas of the lake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiard, J. C-, and C. Amiard-Triquett: Distribution of cobalt 60 in a mollusc, a crustacean, and a freshwater teleost: Variations as a function of the source of pollution and during elimination. Environ. Pollut.18, 199 (1979).
Beinninger, L. K., D. M. Lewis, and K. K. Turekian: The use of natural 210Pb as a heavy metal tracer in a river-estuarine system. In T. M. Church (ed): Marine chemistry in the coastal environment, p. 201. Am. Chem. Soc. Symp. Ser.18. (1975).
Cartwright, R., R. A. Griffin, and R. H. Gilkeson: Migration of landfill leachate through glacial tills. Ground Wat.15, 294 (1977).
Edgington, D. N., and J. A. Robbins: Patterns of deposition of natural and fallout radionuclides in the sediments of Lake Michigan and their relation to limnological processes. In. J. O. Nriagu (ed.): Environmental biogeochemistry, Vol. 2. Ann Arbor Sci, Ann Arbor (1977).
Goldberg, E. D.: Geochronology with210Pb. In: Radioactive dating, p. 121. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna (1963).
Hakanson, L., and T. Ahl: The distribution of heavy metals in the surficial sediments of Lake Vattern, Sweden. Internat. Conf. Heavy Metals in the Environment, Vol. II, 765 (1975).
Hendzel, M. R., and D. M. Jamieson: Determinations of mercury in fish. Anal. Chem.48, 926 (1976).
Jackson, T. A.: Sources of heavy metal contamination in a river-lake system. Environ. Pollut.18, 131 (1979).
Johnson, L.: Physical and chemical characteristics of Great Bear Lake, Northwest Territories. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can.32, 1971 (1975).
Jonasson, I. R., and M. H. Timperley: Field observations on the transport of heavy metals in sediments, pp. 97–101. In P. A. Krenkel (ed.): Heavy metals in the aquatic environment. Toronto: Pergamon Press (1973).
Kemp, A. L. W., J. D. H. Williams, R. L. Thomas, and M. L. Gregory: Impact of man's activities on the chemical composition of the sediments of Lakes Superior and Huron. Water, Air, Soil Pollut.10, 38, (1978).
Krishnaswami, S., and D. Lal: Radionuclide limnochronology pp. 153–177. In A. Lerman (ed.): Lakes, chemistry, geology, physics. New York: Springer-Verlag (1978).
Kudo, A., R. D. Townsend, and D. R. Miller: Prediction of mercury distribution in river sediments. J. Environ. Div.103, 605 (1977).
Lewis, D. M.: The geochemistry of manganese, iron, uranium, Pb-210, and major ions in the Susquehanna River. PhD thesis, Yale University (1976).
Lund, L. J., A. L. Page, and C. O. Nelson: Movement of heavy metals below sewage disposal ponds. J. Environ. Qual.5, 330 (1976).
Moore, J. W.: Distribution and transport of heavy metals in the sediments of a small northern eutrophic lake. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.24, 828 (1980).
Moore, J. W., D. J. Sutherland, and V. A. Beaubien: Comparison of methods and concepts used in assessing the extent of water pollution in a Canadian Shield Lake. Wat. Pollut. Res. Canada14, 35 (1979).
Nathwani, J. S., and C. R. Phillips: Rate controlling processes in the release of radium-226 from uranium mill tailings. I. Leaching study. Water, Air, Soil Pollut.11, 301 (1979a).
—, —: Rate controlling processes in the release of radium-226 from uranium mill tailings II. Kinetic study. Water, Air, Soil Pollut.11, 309 (1979b).
Ottawa River Project Group: Mercury in the Ottawa River. Environ. Res.19, 231 (1979).
Sarkka, J., M. J. Hattula, J. Janatuinen, and J. Paasivirta: Mercury in sediments of Lake Parjanne, Finland. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.20, 332 (1978).
Skei, J. M.: Serious mercury contamination of sediments in a Norwegian semi-enclosed bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull.9, 191 (1978).
Stumm, W., and P. Baccini: Man-made chemical perturbation of lakes. In A. Lerman (ed): Lakes, chemistry, geology, physics, p. 91. New York: Springer-Verlag (1978).
Suzuki, M., T. Yamada, T. Miyazaki, and K. Kawazoe: Sorption and accumulation of cadmium in the sediment of the Tama River. Wat. Res.13, 57 (1979).
Thomas, R. L.: The distribution of mercury in the sediments of Lake Ontario. Can. J. Earth Sci.9, 636 (1972).
Wagemann, R., N. B. Snow, D. M. Rosenberg, and A. Lutz: Arsenic in sediments, water, and aquatic biota from lakes in the vicinity of Yellowknife, Northwest Territories, Canada. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.7, 169 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, J.W., Sutherland, D.J. Distribution of heavy metals and radionuclides in sediments, water, and fish in an area of Great Bear Lake contaminated with mine wastes. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 10, 329–338 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055634
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055634