Summary
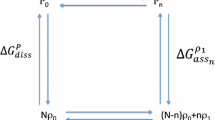
The theoretical basis of the quantitative subunit hybridization technique and its ability to measure evolutionary amino acid substitutions is examined. Homospecific:heterospecific enzyme ratios found after subunit reassociation depend upon K1.2, the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the heterospecific enzyme. It is shown that if this constant is near the geometric mean of the two homospecific enzyme dissociation constants, as it should be in enzymes whose subunits pair isologously, the quantitative subunit hybridization method will not detect most changes in the subunit contact regions of homologous proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Collier, G.E., MacIntyre, R.J. (1977). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., U.S.A.74, 684–688
Collier, G.E., MacIntyre, R.J. (1978). J. Mol. Evol.12, 173–182
MacIntyre, R.J. (1971). Brookhaven Symp. Biol.23, 144–184
MacIntyre, R.J., Dean, M.R. (1978). J. Mol. Evol.12, 143–171
Matthews, B.W., Bernhard, S.A. (1973). Ann. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng.2, 257–317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Collier, G.E., Moffat, K. & MacIntyre, R.J. Theoretical considerations of the sensitivity of quantitative subunit hybridization. J Mol Evol 12, 183–188 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01733266
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01733266