Summary
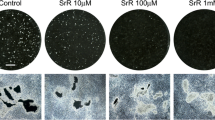
Morphologic effects of the ionophore A23187 were compared with those of PTH and 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D3 on fetal rat limb bone cultures. All three treatments resulted in loss of bone and the appearance of multinucleate osteoclasts. Only PTH caused proliferation of fibroblast-like cells within the marrow cavity. Cleanly dissected (“stripped”) bones were unresponsive to A23187 and exhibited many dead and dying cells after 48 h in culture with this agent; in contrast, stripped bones were responsive to PTH. All three treatments showed a similar time course of appearance of osteoclasts. The results indicate that all three agents promote osteoclast formation. There are several possible explanations for the differential effects of A23187 and PTH in stripped bones, including the possibility that the cells of the periosteum are required for the action of A23187 but not of PTH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dziak, R., Stern, P. H.: Parathyromimetic effects of the ionophore, A23187, on bone cells and organ cultures, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.65:1343–1349, 1975
Dziak, R., Stern, P. H.: Responses of fetal rat bone cells and bone organ cultures to the ionophore, A23187, Calcif. Tissue Res.22:137–147, 1976
Eilon, G., Raisz, L. G.: Comparison of the effects of stimulators and inhibitors of resorption on the release of lysosomal enzymes and radioactive calcium from fetal bone in organ culture, Endocrinology103:1969–1975, 1978
Hahn, T. J., Sharp, C. R., Richardson, C. A., Teitelbaum, S. L.: Comparison of PTH (1-34) and calcium ionophore A23187 (A) effects on resorption in cultured fetal rat bone, Endocrinol. Soc., 60th Annual Meeting, 1978, p. 320
Hahn, T. J., DeBartolo, T. F., Halstead, L. R.: Ouabain effects on hormonally-stimulated bone resorption and cyclic AMP content in cultured fetal rat bones, Endocrinol. Res. Commun.7:189–200, 1980
Lorenzo, J. A., Raisz, L. G.: Effects of calcium ionophores on bone resorption and DNA synthesis in cultured fetal rat bones, Am. Soc. Bone Min. Res., 2nd Annual Meeting, 1980, p. 3A
Raisz, L. G.: Bone resorption in tissue culture: factors influencing the response to parathyroid hormone, J. Clin. Invest.44:103–116, 1965
Brand, J. S., Raisz, L. G.: Effects of thyrocalcitonin and phosphate ion on the parathyroid stimulated resorption of bone, Endocrinology90:479–487, 1972
Raisz, L. G., Trummel, C. L., Holick, M. F., DeLuca, H. F.: 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol: a potent stimulator of bone resorption in tissue culture, Science175:768–769, 1972
Stern, P. H., Trummel, C. L., Schnoes, H. K., DeLuca, H. F.: Bone-resorbing activity of vitamin D metabolites and congenersin vitro: influence of hydroxyl substituents in the A ring, Endocrinology97:1552–1558, 1975
Mahgoub, A., Sheppard, H.: Effect of hydroxy-vitamin D3 derivatives on45Ca release from fetal rat bonein vitro, Endocrinology100:629–634, 1976
Stern, P. H.: Inhibition by steroids of parathyroid hormone-induced45Ca release from embryonic rat bonein vitro, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.168:211–217, 1969
Orr, M. F.: Tissue culture methods. In C. A. Smith, J. A. Vernon (eds.): Handbook of Auditory and Vestibular Research Methods, pp. 127–177. Charles Thomas, Springfield, Ill., 1976
McManus, J. F. A., Mowry, R. W.: Staining Methods, Histologic and Histochemical, pp. 55–64. Paul B. Hoeber, Inc., New York, 1960
Raisz, L. G., Brand, J. S., Au, W. Y. W., Niemann, I.: Interactions of parathyroid hormone and thyrocalcitonin on bone resorption in tissue culture. In R. V. Talmage, L. F. Belanger (eds.): Parathyroid Hormone and Calcitonin, Int. Congr. Ser. No. 159, pp. 370–380. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, 1968
Stern, P. H.: Ionophores: chemistry, physiology and potential applications to bone biology, Clin. Orthop.122:273–298, 1977
Reed, P. W., Lardy, H. A.: A23187: a divalent cation ionophore, Fed. Proc.31:432–436, 1972
Wollheim, C. B., Blondel, B., Trueheart, P. A., Renold, A. E., Sharp, A. W.: Calcium-induced insulin release in monolayer culture of endocrine pancreas studied with ionophore A23187, J. Biol. Chem.250:1354–1360, 1975
Cochrane, D. E., Douglas, W. W.: Calcium-induced extrusion of secretory granules (exocytosis) of mast cells exposed to 48/80 or the ionophores A23187 or X-537A, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.71:408–412, 1974
Butcher, F. R.: The role of calcium and cyclic nucleotides inα-amylase release from rat parotid: studies with the divalent cation ionophore A23187, Metabolism24:409–418, 1975
Garcia, A. G., Kirpekar, S. M., Prat, J. C.: A calcium ionophore stimulating the secretion of catecholamines from the cat adrenal, J. Physiol.244:253–262, 1975
Dziak, R., Stern, P. H.: Calcium treatment in isolated bone cells. III. Effects of parathyroid hormone and cyclic 3′,5′-AMP, Endocrinology97:1281–1287, 1975
Dziak, R.: Effects of vitamin D3 metabolites on bone cell calcium transport, Calcif. Tissue Res.26:65–70, 1978
Wong, G. L., Kent, G. N., Ku, K. Y., Cohn, D. V.: The interaction of parathormone and calcium on the hormone-regulated synthesis of hyaluronic acid and citric decarboxylation in isolated bone cells, Endocrinology103:2274–2282, 1978
Raisz, L. G., Trummel, C. L., Simmons, H.: Induction of bone resorption in tissue culture: prolonged response after brief exposure to parathyroid hormone or 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, Endocrinology90:744–751, 1972
Lucy, J. A.: Mechanisms of chemically induced cell fusion. In G. Poste, G. L. Nicholson (eds.): Membrane Fusion, pp. 268–304. North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1978
Ahkong, Q. F., Tampion, W., Lucy, J. A.: Promotion of cell fusion by divalent cation ionophores, Nature256:208–209, 1975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stern, P.H., Orr, M.F. & Brull, E. Ionophore A23187 promotes osteoclast formation in bone organ culture. Calcif Tissue Int 34, 31–36 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02411205
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02411205