Abstract
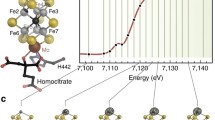
We have studied the molybdenum K-edge X-ray absorption spectra of Mo bound in the Mo-binding proteins Mop from Haemophilus influenzae, ModG from Azotobacter vinelandii and the Escherichia coli ModE transcriptional regulatory protein, and compared them with the absorption spectra of A. vinelandii ModA and monomeric molybdate. Pre-edge and extended fine structure data indicate that the Mo-binding proteins with molbindin-like domains bind tetrahedral molybdate with a Mo-O distance of 1.76 Å. The molbindin subunits or sub-domains represent a novel protein fold that is used by proteins with distinct functions to bind molybdate in the cytoplasm. The high specificity of the proteins for molybdenum does not depend on a change of coordination number or geometry.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 April 1999 / Accepted: 30 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duhme, AK., Meyer-Klaucke, W., White, D. et al. Extended X-ray absorption fine structure studies on periplasmic and intracellular molybdenum-binding proteins. JBIC 4, 588–592 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750050381
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750050381