Abstract
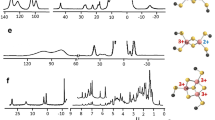
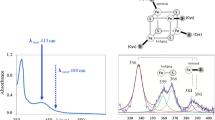
The oxidized Fe7S8 ferredoxin from Bacillus schlegelii, containing both [Fe3S4]+ and [Fe4S4]2+ clusters, has been investigated by 1H NMR spectroscopy. An extensive sequence-specific assignment of the hyperfine-shifted resonances has been obtained by making use of a computer-generated structural model. The pattern and the temperature dependence of the hyperfine shifts of the β-CH2 protons of the cysteines coordinating the [Fe3S4]+ cluster are rationalized in terms of magnetic interactions between the iron ions. The same approach holds for the hyperfine coupling with 57Fe. It is shown that the magnetic interactions are more asymmetric in Fe7S8 ferredoxins than in Fe3S4 ferredoxins. The NMR non-observability of the β-CH2 protons of coordinated cysteines in the one-electron-reduced form has been discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 19 June 1996 / Accepted: 2 August 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aono, S., Bertini, I., Cowan, J. et al. 1H NMR studies of the Fe7S8 ferredoxin from Bacillus schlegelii: a further attempt to understand Fe3S4 clusters. JBIC 1, 523–528 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750050087
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750050087