Abstract
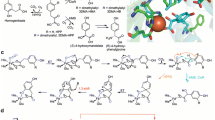
The intramolecular electron-transfer rate constant for the Cu(II)–topaNH2⇌ Cu(I)–topaSQ equilibrium in methylamine oxidase has been measured by temperature-jump relaxation techniques. At pH 7.0 the estimated kobs = 150±30 s–1 for both methylamine and benzylamine; assuming the equilibrium constant is ≈0.7–1 at pH 7.0 and 296 K, this would correspond to a forward electron-transfer rate constant kET≈ 60–75 s–1. Although substantially slower than the previously determined kET≈ 20 000 s–1 for pea seedling amine oxidase [5] steady-state kinetics measurements established that kET > kcat≈ 4–10 s–1. Thus the Cu(I)-semiquinone state is a viable intermediate in methylamine oxidase turnover.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 August 1995 / Accepted: 21 December 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dooley, D., Brown, D. Intramolecular electron transfer in the oxidation of amines by methylamine oxidase from Arthrobacter P1. JBIC 1, 205–209 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750050044
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007750050044