Abstract
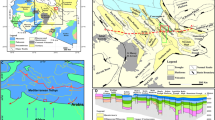
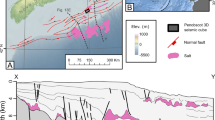
The Middle and Late Pleistocene succession on the glacier-fed fan at the mouth of Storfjorden trough was studied using high-resolution seismic data. Seven glacial advances to the shelf break during Middle and Late Pleistocene resulted in episodic high sediment input to the fan with real sedimentation rates of up to 172 cm/1000 years, separated by sediment-starved interstadials and interglacials. On the upper fan the high sediment input resulted in frequent slides and slumps, generating debris flows which dominate the mid-fan strata. Compared with the larger neighbouring Bear Island trough mouth fan, the Storfjorden trough mouth fan has a steeper fan gradient, narrower, thinner and shorter debris flow deposits and lower frequency of large scale sliding. Glacier-fed submarine fans receive their main sediment input from a glacier margin at the shelf break, as opposed to river-fed fans where sediment input occurs through a channel-levee complex. As a result, the depocentre of a river-fed fan is found on the mid-fan and the upper slope is mainly an area of sediment bypass, whereas the glacier-fed fan has an elongated depocentre across the uppermost fan. The river-fed fans are dominated by deposition from turbidity currents, whereas glacier-fed fans are dominated by debris flow deposits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksu AE, Hiscott RN (1992) Shingled Quaternary debris flow lenses on the north-east Newfoundland slope. Sedimentology 39:193–206
Alley RB, Blankenship DD, Rooney ST, Bentley CR (1989) Sedimentation beneath ice shelves — the view from Ice Stream B. Marine Geol 85:101–120
Andersen ES, Solheim A, Elverhøi A (1994) Development of a polar margin, exemplified by the western margin of Svalbard. In: Thurston DK, Fujita K (eds) Int Conf on Arctic Margins, Proc Anchorage, Alaska 1992. U.S. Dept of the Interior, Mineral Management Service, Alaska Outer Continental Shelf Region, OCS Study, MMS 94-0040, pp 155–160
Boulton GS (1979) Processes of glacier erosion on different substrata. J Glaciol 23:15–38
Bugge T (1983) Submarine slides on the Norwegian continental margin, with special emphasis on the Storegga area. Continental Shelf and Petroleum Technology Research Institute (IKU), Trondheim, Norway, Publication 110, 152 pp
Damuth JE (1978) Echo character of the Norwegian-Greenland Sea: relationship to Quaternary sedimentation. Marine Geol 28:1–36
Droz L, Bellaiche G (1985) Rhone Deep-sea fan: morphostructure and growth pattern. Am As Petrol Geol Bull 69:460–479
Hambrey MJ, Barrett PJ, Ehrmann WU, Larsen B (1992) Cenozoic sedimentary processes on the Antarctic continental margin and the record from deep drilling. Z Geomorphol N F 86:77–103
Hampton MA (1972) The role of subaqueous debris flow in generating turbidity currents. J Sedimentary Petrol 42:775–793
Hebbeln D (1992) Weichselian glacial history of the Svalbard area: correlating the marine and terrestrial records. Boreas 21:295–304
Hiscott RN, Aksu AE (1994) Submarine debris flows and continental slope evolution in front of Quaternary ice sheets, Baffin Bay, Canadian Arctic. Am As Petrol Geol Bull 78:445–460
Hjelstuen BO, Elverhøi A, Faleide JI (1996): Cenozoic erosion and sediment yield in the drainage area of the Storfjorden Fan. Global Plan Change 12:95–117
Kenyon NH (1986) Evidence from bedforms for a strong poleward current along the upper continental slope of northwest Europe. Marine Geol 72:187–198
Knutsen S-M, Richardsen G, Vorren TO (1993) Late Miocene-Pleistocene sequence stratigraphy and mass-movement on the western Barents Sea margin. In: Vorren TO, Bergsager E, Dahl-Stamnes ØA, Holter E, Johansen B, Lie E, Lund TB (eds) Arctic geology and petroleum potential. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 573–606
Kristoffersen Y, Sand M, Beskow B, Otha Y (1989) Western Barents Sea bathymetry. Scale 1:1500000. Norsk Polarinstitutt
Laberg JS, Vorren TO (1993) A Late Pleistocene submarine slide on the Bear Island trough mouth fan. Geo-Marine Lett 13:227–234
Laberg JS, Vorren TO (1995) Late Weichselian submarine debris flow deposits on the Bear Island trough mouth fan. Marine Geol 127:45–72
Laberg JS, Vorren TO (1996) The Middle and Late Pleistocene evolution of the Bear Island trough mouth fan. Glob Plan Change 12:309–330
Mangerud J, Svendsen JI (1992) The last interglacial—glacial period on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. Quaternary Sci Rev 11:633–664
Myhre AM, Eldholm O (1988) The Western Svalbard margin (74°–80° N). Marine Petrol Geol 5:134–156
Norem H (1994) MAST II — sediment pathways, processes and fluxes. Flow behaviour of glacigenic submarine slides. Report No. 933015-1, Norwegian Geotechnical Institute, Oslo, 33 pp
North American Commission on Stratigraphic Nomenclature (NACSN) (1983) North American Stratigraphic Code. Am As Petrol Geol Bull 67:841–875
Perry RK, Fleming HS, Cherkis NZ, Feden RH, Vogt PR (1980) Bathymetry of the Norwegian-Greenland and western Barents Sea. Naval Research Laboratory-Acoustics Division, Environmental Sciences Branch, Washington DC
Pickering KT, Hiscott RN, Hein FJ (1989) Deep marine environments: clastic sedimentation and tectonics. Unwin Hyman, London, pp 416
Quadfasel D, Rudels B, Kurz K (1988) Outflow of dense water from a Svalbard fjord into the Fram Strait. Deep-Sea Res 35:1143–1150
Reading HG, Richards M (1994) Turbidite systems in deep-water basin margins classified by grain size and feeder system. Am As Petrol Geol Bull 78:792–822
Schlüter H-U, Hinz K (1978) The continental margin of west Spitsbergen. Polarforschung 48:151–169
Sigmond EMD (1992) Bedrock map of Norway and adjacent ocean areas. Scale 1:3 million. Geological Survey of Norway
Solheim A (1991) The depositional environment of surging subpolar tidewater glaciers. Norsk Polarinstitutt Skrifter 194:1–97
Solheim A, Kristoffersen Y (1984) Distribution of sediments above bedrock and glacial history in the western Barents Sea. Norsk Polarinstitutt Skrifter 179B: 1–26
Stow DA (1986) Deep clastic seas. In: Reading HG (ed) Sedimentary environments and facies. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 399–444
Sættem J, Poole DAR, Ellingsen KL, Sejrup HP (1992) Glacial geology of outer Bjørnøyrenna, southwestern Barents Sea. Marine Geol 103:15–51
Talwani M et al. (1976) Site 344 of the Deep Sea Drilling Project. In: Talwani M, Udintsev G et al. (eds) Initial reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, vol 38. Washington (U.S. Government Printing Office), pp 389–401
Vogt PR, Crane K, Sundvor E (1993) Glacigenic mudflows on the Bear Island submarine fan. EOS, Trans Am Geophys Union 74:449, 452–453
Vorren TO, Hald M, Lebesbye E (1988) Late Cenozoic environment in the Barents Sea. Paleoceanography 3:601–612
Vorren TO, Lebesbye E, Andreassen K, Larsen K -B (1989) Glacigenic sediments on a passive continental margin as exemplified by the Barents Sea. Marine Geol 85:251–272
Vorren TO, Richardsen G, Knutsen S-M, Henriksen E (1991) Cenozoic erosion and sedimentation in the western Barents Sea. Marine Petrol Geol 8:317–340
Williams DF, Thunell RC, Tappa E, Rio D, Raffi I (1988) Chronology of the Pleistocene oxygen isotope record: 0–1.88 m.y. B.P. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 64:221–240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laberg, J.S., Vorren, T.O. The glacier-fed fan at the mouth of Storfjorden trough, western Barents Sea: a comparative study. Geol Rundsch 85, 338–349 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02422239
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02422239