Abstract
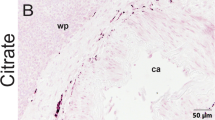
The opioidergic innervation of the mammalian spleen and possible species differences were investigated. Light-microscopic immunohistochemistry revealed that splenic nerves of bovine and porcine spleen, but not of rat, mouse, hamster and guinea-pig spleen contained proenkephalin-derived opioidergic innervation. Immunoreactivity to both prodynorphin and pro-opiomelanocortin was absent from splenic nerves. In bovine and porcine spleen, fibers immunoreactive for met-enkephalin, met-enkephalin-Arg-Phe, met-enkephalin-Arg-Gly-Leu, leu-enkephalin and peptide F formed perivascular plexus, traveled in trabecular connective tissue, and extended into the capsule. Spatial relationships with immune cells were apparent in the white and red pulp, excluding lymphoid follicles. Colocalization of enkephalin immunoreactivity with immunoreactivities for tyrosin hydroxylase, dopamin-β-hydroxylase, and neuropeptide Y, but not for substance P or calcitonin gene-related peptide were found. Our results provide evidence that opioid expression in splenic innervation is strongly species-dependent and exclusively proenkephalin-derived. Colocalization with marker enzymes of noradrenergic neurons indicates a mainly postganglionic sympathetic origin of proenkephalinergic splenic innervation. Opioidergic perivascular nerves probably control the splenic blood flow. A close interrelationship of opioidergic fibers with immune cells provides the anatomical basis for direct effects of neurally released opioids on splenic immune functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman KD, Felten SY, Bellinger DL, Livnat S, Felten DL (1987) Noradrenergic sympathetic innervation of spleen and lymph nodes in relation to specific cellular compartments. Prog Immunol 6:588–600
Baron R, Jänig W (1988) Sympathetic and afferent neurons projecting in the splenic nerve of the cat. Neurosci Lett 94:109–113
Behar O, Ovadia H, Polakiewicz RD, Rosen H (1994) Lipopolysaccharide induces proenkephalin gene expression in rat lymph nodes and adrenal glands. Endocrinology 134:475–481
Bellinger DL, Felten SY, Collier TJ, Felten DL (1987) Noradrenergic sympathetic innervation of the spleen. IV. Morphometric analysis in adult and aged F344 rats. J Neurosci Res 18:55–63
Bellinger DL, Lorton D, Hamill RW, Felten SY, Felten DL (1992) Acetylcholinesterase staining and choline acetyltransferase activity in the young adult rat spleen: lack of evidence for cholinergic innervation. Brain Behav Immun 7:191–204
Bette M, Schäfer MK-H, Fleischer B, Weihe E (1994) Superantigen stimulation in vivo induces opioid gene expression in mouse spleen. Neuropeptides 26[Suppl 1]:9
Blalock JE (1992) Production of peptide hormones and neurotransmitters by the immune system. Chem Immunol 52:1–24
Bryant HU, Holaday JW (1993) Opioids in immunologic processes. In: Herz A (ed) Handbook of experimental pharmacology, vol 104. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 361–392
Carr DJJ (1992) Neuroendocrine peptide receptors on cells of the immune system. Chem Immunol 52:84–105
Chevendra V, Weaver LC (1992) Distributions of neuropeptide Y, vasoactive intestinal peptide and somatostatin in populations of postganglionic neurons innervating the rat kidney, spleen and intestine. Neuroscience 50:727–743
Elfvin LG, Aldskogius H, Johansson J (1992) Splenic primary sensory afferents in the guinea-pig demonstrated with anterogradely transported wheat-germ agglutinin conjugated to horseradish peroxidase. Cell Tissue Res 269:229–234
Felten DL, Felten SY, Carlson SL, Olschowka JA, Livnat S (1985) Noradrenergic and peptidergic innervation of lymphoid tissue. J Immunol 135:755s-765s
Felten SY, Olschowka JA (1987) Noradrenergic sympathetic innervation of the spleen. II. Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive nerve terminals form synaptic-like contacts on lymphocytes in the splenic white pulp. J Neurosci Res 18:37–48
Felten SY, Olschowka JA, Ackerman KD, Felten DL (1988) Catecholaminergic innervation of the spleen: are lymphocytes targets of noradrenergic nerves? In: Dahlström A, Belmarker RH, Sandler M (eds) Progress in catecholamine research, part A: basic aspects and peripheral mechanisms. Liss. New York, pp 525–531
Felten SY, Felten DL, Bellinger DL, Olschowka JA (1992) Noradrenergic and peptidergic innervation of lymphoid organs. Chem Immunol 52:25–48
Fillenz M (1970) The innervation of the cat spleen. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 174:459–468
Fink T, Weihe E (1988) Multiple neuropeptides in nerves supplying mammalian lymph nodes: messenger candidates for sensory and autonomic neuroimmunomodulation? Neurosci Lett 90:39–44
Fried G, Terenius L, Brodin E, Efendic S, Dockray G, Fahrenkrug J, Goldstein M, Hökfelt T (1986) Neuropeptide Y, enkephalin and noradrenaline coexist in sympathetic neurons innervation the bovine spleen. Cell Tissue Res 243:495–508
Geppetti P, Maggi CA, Zecchi-Orlandini S, Santicioli P, Meli A, Frilli S, Soillantini MG, Amenta F (1987) Substance P-like immunoreactivity in capsaicin-sensitive structures of the rat thymus. Regul Pept 18:321–329
Gillespie JS, Kirpekar SM (1965) The localization of endogenous and infused noradrenaline in the spleen. J Physiol 179:46P
Hartschuh W, Weibe E, Yanaihara N (1989) Immunohistochemical analysis of chromogranin A and multiple peptides in the mammalian Merkel cell: further evidence for its paraneuronal functions? Arch Histol Cytol 152:423–431
Hörsch D, Fink T, Büchler M, Weihe E (1993) Regional specificities in the distribution, chemical phenotypes, and coexistence patterns of neuropeptide containing nerve fibres in the human anal canal. J Comp Neurol 335:381–401
Illes P, Bettermann R, Brod I, Bucher B (1987) Beta-endorphin-sensitive opioid receptors in the rat tail artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs arch Pharmacol 335:420–427
Klein RL, Wilson SP, Dzielak DJ, Yang WH, Viveros OH (1982) Opioid peptides and noradrenaline co-exist in large densecored vesicles from sympathetic nerve. Neuroscience 7:1161–1170
Kondo H, Yamamoto M, Yanaihara N, Nagatsu I (1988) Transient involvement of enkephalins in both the sympathetic and parasympathetic innervations of the submandibular gland of rats. Light-and electron-microscopic immunocytochemical study. Cell Tissue Res 253:529–537
Kurkowski R, Kummer W, Heym C (1990) Substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in tracheobronchial lymph nodes of the guinea pig: origin, ultrasrtucture and coexistence with other peptides. Peptides 11:13–20
Livnat S, Felten SY, Carlson SL, Bellinger DL, Felten DL (1985) Involvement of peripheral and central catecholamine systems in neural-immune interactions. J Neuroimmunol 10:5–30
Lorton D, Bellinger DL, Felten SY, Felten DL (1991) Substance P innervation of spleen in rats: nerve fibers associate with lymphocytes and macrophages in specific compartments of the spleen. Brain Behav Immun 5:29–40
Lundberg JM, Änggård A, Pernow J, Hökfelt T (1985) Neuropeptide Y-, substance P-and VIP-immunoreactive nerves in cat spleen in relation to autonomic vascular and volume control. Cell Tissue Res 239:9–18
Lundberg JM, Rudehill A, Sollevi A, Fried G, Wallin G (1989) Co-release of neuropeptide Y and noradrenaline from pig spleen in vivo: importance of subcellular storage, nerve impulse frequency and pattern, feedback regulation and resupply by axonal transport. Neuroscience 28:474–486
Mechanick JI, Levin N, Roberts JL, Autelitano DJ (1992) Proopiomelanocortin gene expression in a distinct population of rat spleen and lung leukocytes. Endocrinology 131:518–525
Michel S, Weihe E (1991) Zur Innervation der Rattenmilz: Eine neuroimmune Funktionskomponente? In: Kühnel W (ed) Verhandlungen der Anatomischen Gesellschaft, 86. Versammlung in Szeged. Fischer, Jena, p 192
Müller S, Weihe E (1991) Interrelation of peptidergic innervation with mast cells and ED1 positive cells in rat thymus. Brain Behav Immun 5:55–72
Nance DM, Burns J (1989) Innervation of the spleen in the rat: evidence for absence of afferent innervation. Brain Behav Immun 3:281–290
Nohr D, Weihe E (1991) The neuroimmune link in the mammalian bronchus associated lymphoid tissue (BALT): peptides and neural markers. Brain Behav Immun 5:84–101
Persson S, Schäfer M K-H, Nohr D, Ekström G, Post C, Nyberg F, Weihe E (1994) Spinal prodynorphin gene expression in collagen-induced arthritis: influence of the glucocoticosteroid budesonide. Neuroscience 63:313–326
Przewlocki R, Hassan AH, Lason W, Epplen C, Herz A, Stein C (1992) Gene expression and localization of opioid peptides in immune cells of inflamed tissue: functional role in antinociception. Neuroscience 48:491–500
Reilly FD (1985) Innervation and vascular pharmacodynamics of the mammalian spleen. Experientia 41:187–192
Romeo HE, Fink T, Yanaihara N, Weihe E (1995) Distribution and relative proportions of neuropeptide Y-and proenkephalin-containing noradrenergic neurons in rat superior superior cervical ganglion: separate projections to submaxillary lymph nodes. Peptides 15:1479–1487
Sharp B, Linner K (1993) Editorial: What do we know about the expression of pro-opiomelanocortin transcripts and related peptides in lymphoid tissue? Endocrinology 133:1921A-1921B
Sibinga NE Goldstein A (1988) Opioid peptides and opioid receptors in cells of the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 6:219–249
Van Epps DE, Kutvirt SL (1987) Modulation of human neutrophil adherence by β-endorphin and met-enkephalin. J Neuroimmunol 15:219–228
Weber E, Evans CJ, Barchas JD (1983) Multiple endogenous ligands for opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci 8:336
Weihe E, Nohr D, Hartschuh W, Gauweiler B, Fink T (1988) Multiplicity of opioidergic pathways related to cardiovascular innervation: differential contribution of all three opioid precursors. In: Stumpe KO, Kraft K, Faden AL (eds) Opioid peptides and blood pressure control. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 27–49
Weihe E, Müller S, Fink T, Zentel HJ (1989) Tachykinins, calcitonin gene-related peptides and neuropeptide Y in nerves of the mammalian thymus: interactions with mast cells in autonomic and sensory neuroimmunomodulation? Neurosci Lett 100:77–82
Weihe E, Nohr D, Michel S, Müller S, Zentel HJ, Fink T, Krekel J (1991) Molecular anatomy of the neuro-immune connection. Int J Neurosci 59:1–23
Williams JM, Peterson RG, Shea PA, Schmidtje FC, Bauer DC, Felten DL (1981) Sympathetic innervation of murine thymus and spleen: evidence for a functional link between the nervous and immune systems. Brain Res Bull 6:83–94
Zentel HJ, Weihe E (1991) The neuro-B cell link of peptidergic innervation in the bursa Fabricii. Brain Behav Immun 5:132–147
Zurawski G, Benedik M, Kamb BJ, Abrams JS, Zurawski SM, Lee FD (1986) Activation of mouse T-helper cells induces abundant preproenkephalin mRNA synthesis. Science 232:772–775
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nohr, D., Michel, S., Fink, T. et al. Pro-enkephalin opioid peptides are abundant in porcine and bovine splenic nerves, but absent from nerves of rat, mouse, hamster, and guinea-pig spleen. Cell Tissue Res 281, 143–152 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307968
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307968