Abstract
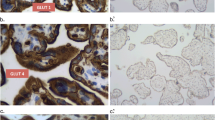
GLUT1 is an isoform of facilitated-diffusion glucose transporters and has been shown to be abundant in cells of blood-tissue barriers. Using antibodies against GLUT1, we investigated the immunohistochemical localization of GLUT1 in the rat placenta. Rat placenta is of the hemotrichorial type. Three cell layers (from the maternal blood side inward) cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblasts I and II, lie between the maternal and fetal bloodstreams. GLUT1 was abundant along the invaginating plasma membrane facing the cytotrophoblast and the syncytiotrophoblast I. Also, the infolded basal plasma membrane of the syncytiotrophoblast II was rich in GLUT1. Apposing plasma membranes of syncytiotrophoblasts I and II, however, had only a small amount of GLUT1. Numerous gap junctions were seen between syncytiotrophoblasts I and II. Taking into account the localization of GLUT1 and the gap junctions, we suggest a possible major transport route of glucose across the placental barrier, as follows: glucose in the maternal blood passes freely through pores of the cytotrophoblast. Glucose is then transported into the cytoplasm of the syncytiotrophoblast I via GLUT1. Glucose enters the syncytiotrophoblast II throught the gap junctions. Finally glucose leaves the syncytiotrophoblast II via GLUT1 and enters the fetal blood through pores of the endothelial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Aoki A, Metz J, Forssmann WG (1978) Studies on the ultrastructure and permeability of the hemotrichorial placenta. II. Fetal capillaries and tracer administration into the fetal blood circulation. Cell Tissue Res 192:409–422
Bell GI, Kayano T, Buse JB, Burant CF, Takeda J, Lin D, Fukumoto H, Seino S (1990) Molecular biology of mammalian glucose transporters. Diabetes Care 13:198–208
Benirschke K, Kaufmann P (1990a) Basic structure of the villous trees. In: Pathology of the human placenta, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 22–70
Benirschke K, Kaufmann P (1990b) Placental types. In: Pathology of the human placenta, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 1–12
DeMay J (1984) Colloidal gold as marker and tracer in light and electron microscopy. EMSA Bulletin 14:54–66
Ezaki O, Kasuga M, Akanuma Y, Takata K, Hirano H, Fujita-Yamaguchi Y, Kasahara M (1986) Recycling of the glucose transporter, the insulin receptor, and insulin in rat adipocytes. Effect of acidtropic agents. J Biol Chem 261:3295–3305
Forssmann WG, Metz J, Heinrich D (1975) Gap junctions in the hemotrichorial placenta of the rat. J Ultrastruct Res 53:374–381
Harik SI, Kalaria RN, Andersson L, Lundahl P, Perry G (1990a) Immunocytochemical localization of the erythroid glucose transporter: abundance in tissues with barrier functions. J Neurosci 10:3862–3872
Harik SI, Kalaria RN, Whitney PM, Andersson L, Lundahl P, Ledbetter SR, Perry G (1990b) Glucose transporters are abundant in cells with “occluding” junctions at the blood-eye barriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4261–4264
James DE, Strube M, Mueckler M (1989) Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature 338:83–87
Jollie WP (1964) Fine structural changes in placental labyrinth of the rat with increasing gestational age. J Ultrastruct Res 10:27–47
Kasahara M, Inui K, Takano M, Hori R (1985) Distinction of three types of D-glucose transport systems in animal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 132:490–496
Loewenstein WR (1979) Junctional intercellular communication and the control of growth. Biochim Biophys Acta 560:1–65
Metz J (1980) On the developing rat placenta. I. Differentiation and junctional alterations of labyrinthine layers II and III. Anat Embryol (Berl) 159:289–305
Metz J, Heinrich D, Forssmann WG (1976a) Ultrastructure of the labyrinth in the rat full-term placenta. Anat Embryol (Berl) 149:123–148
Metz J, Heinrich D, Forssmann WG (1976b) Gap junctions in hemodichorial and hemotrichorial placentae. Cell Tissue Res 171:305–315
Metz J, Aoki A, Forssmann WG (1978) Studies on the ultrastructure and permeability of the hemotrichorial placenta. I. Intercellular junctions of layer I and tracer administration into the maternal compartments. Cell Tissue Res 192:391–407
Mueckler M, Caruso C, Baldwin SA, Panico M, Blench I, Morris HR, Allard WJ, Lienhard GE, Lodish HF (1985) Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science 229:941–945
Pitts JD, Finbow ME (1986) The gap junction. J Cell Sci [Suppl] 4:239–266
Risek B, Gilula NB (1991) Spatiotemporal expression of three gap junction gene products involved in fetomaternal communication during rat pregnancy. Development 113:165–181
Sase S, Takata K, Hirano H, Kasahara M (1982) Characterization and identification of the glucose transporter of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 693:253–261
Silverman M (1991) Structure and function of hexose transporters. Ann Rev Biochem 60:757–794
Simionescu N, Simionescu M (1976) Galloylglucoses of low molecular weight as mordant in electron microscopy. I. Procedure and evidence for mordanting effect. J Cell Biol 70:608–621
Slot JW, Geuze HJ (1985) A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol 38:87–93
Spray DC, Bennett MVL (1985) Physiology and pharmacology of gap junctions. Ann Rev Physiol 47:281–303
Takata K, Hirano H (1990) Use of fluorescein-phalloidin and DAPI as a counterstain for immunofluorescence microscopic studies with semithin frozen sections. Acta Histochem Cytochem 23:679–683
Takata K, Singer SJ (1988) Phosphotyrosine-modified proteins are concentrated at the membranes of epithelial and endothelial cells during tissue development in chick embryos. J Cell Biol 106:1757–1764
Takata K, Kasahara T, Kasahara M, Ezaki O, Hirano H (1990) Erythrocyte/HepG2-type glucose transporter is concentrated in cells of blood-tissue barriers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 173:67–73
Takata K, Kasahara T, Kasahara M, Ezaki O, Hirano H (1991) Ultracytochemical localization of erythrocyte/HepG2-type glucose transporter (GLUT1) in the ciliary body and iris of the rat eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 32:1659–1666
Takata K, Kasahara T, Kasahara M, Ezaki O, Hirano H (1992a) Localization of erythrocyte/HepG2-type glucose transporter (GLUT1) in human placental villi. Cell Tissue Res 267:407–412
Takata K, Kasahara T, Kasahara M, Ezaki O, Hirano H (1992b) Ultracytochemical localization of the erythrocyte/HepG2-type glucose transporter (GLUT1) in cells of the blood-retinal barrier in the rat. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 33:377–383
Takata K, Kasahara M, Oka Y, Hirano H (1993) Mammalian sugar transporters: their localization and link to cellular functions. Acta Histochem Cytochem 26:165–178
Tokuyasu KT (1986) Application of cryoultramicrotomy to immunocytochemistry. J Microsc 143:139–149
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takata, K., Kasahara, T., Kasahara, M. et al. Immunolocalization of glucose transporter GLUT1 in the rat placental barrier: possible role of GLUT1 and the gap junction in the transport of glucose across the placental barrier. Cell Tissue Res 276, 411–418 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00343939
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00343939