Summary
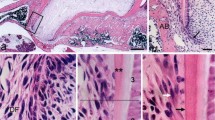
The present study describes the formative process of the initiation of cellular intrinsic fiber cementum (CIFC) in still growing human teeth. From 29 premolars and molars with incomplete roots developed to 60–90% of their final length, 8 premolars (with roots formed to three quarters of their final length) were selected for electron-microscopic investigation. All teeth were clinically intact and prefixed in Karnovsky's fixative immediately after extraction. Most of them were decalcified in ethylene diaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and the apical part of the roots was divided axially into mesial and distal portions that were subdivided in about 5 slices each. Following osmication and embedding in Epon, these blocks were cut for light- and electron-microscopic examination. In addition, 5 teeth with incomplete roots were freed from organic material and processed for scanning electron microscopy. It was found that CIFC-initiation commenced very close to the advancing root edge and resulted in a rapid cementum thickening. Thereafter, appositional growth continued on the already established cementum surface. Large, basophilic and rough endoplasmic reticulum-rich cementoblasts, some of which became cementocytes, were responsible for both fast and slow CIFC-formation. The CIFC-matrix was free of Sharpey's fibers and composed of more or less organized intrinsic collagen fibrils, in part fibril bundles, that ran roughly parallel to the root surface. Initially, the cementum fibrils intermingled with those of the dentinal collagen fibrils, which were not yet mineralized. This boundary subsequently underwent calcification. The development of collagen fibril bundles and their extracellular arrangement were associated with cytoplasmic processes probably involved in fibril formation and fibril assembly. Many cementoblasts contained intracytoplasmic, membrane-bounded collagen fibrils, which probably were related to fibril formation rather than degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beertsen W, Everts V (1990) Formation of acellular root cementum in relation to dental and non-dental hard tissues in the rat. J Dent Res 69:1669–1673
Birk DE, Trelstad RL (1984) Extracellular compartments in matrix morphogenesis: collagen fibril, bundle, and lamellar formation by corneal fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 99:2024–2033
Birk DE, Trelstad RL (1986) Extracellular compartments in tendon morphogenesis: collagen fibril, bundle, and macroaggregate formation. J Cell Biol 103:231–240
Bosshardt DD, Schroeder HE (1990) Evidence for rapid multipolar and slow unipolar production of human cellular and acellular cementum matrix with intrinsic fibers. J Clin Periodontol 17:663–668
Bosshardt DD, Schroeder HE (1991 a) Initiation of acellular extrinsic fiber cementum on human teeth. A light- and electron-microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res 263:311–324
Bosshardt DD, Schroeder HE (1991 b) Establishment of acellular extrinsic fiber cementum on human teeth. A light- and electronmicroscopic study. Cell Tissue Res 263:325–336
Bosshardt DD, Luder HU, Schroeder HE (1989) Rate and growth pattern of cementum apposition as compared to dentine and root formation in a fluorochrome-labelled monkey (Macaca fascicularis). J Biol Buccale 17:3–13
Carneiro J, Fava de Moraes F (1965) Radioautographic visualization of collagen metabolism in the periodontal tissue of the mouse. Arch Oral Biol 10:833–848
Cho MI, Garant PR (1981 a) Sequential events in the formation of collagen secretion granules with special reference to the development of segment-long-spacing-like aggreagates. Anat Rec 199:309–320
Cho MI, Garant PR (1981 b) Role of microtubules in the organization of the Golgi complex and the secretion of collagen secretory granules by periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Anat Rec 199:459–471
Cho MI, Garant PR (1985) Mirror symmetry of newly divided rat periodontal ligament fibroblasts in situ and its relationship to cell migration. J Periodont Res 20:185–200
Deporter DA, Ten Cate AR (1980) Collagen resorption by periodontal ligament fibroblasts at the hard tissue-ligament interfaces of the mouse periodontium. J Periodontol 51:429–432
Freyfuss F, Frank R (1964) Microradiographie et microscopie électronique du cément humain. Bull Group Int Rech Sc Stomat 7:167–181
Frank RM, Frank P (1969) Autoradiographie quantitative de l'losteogenèse en microscopie électronique à l'aide de la proline tritiée. Z Zellforsch 99:121–133
Frank RM, Fellinger E, Steuer P (1976) Ultrastructure du ligament alvéolo-dentaire du rat. J Biol Buccale 4:295–313
Frasca JM, Parks VR (1965) A routine technique for double-staining ultrathin sections using uranyl and lead salts. Cell Biol 25:157–161
Furseth R (1967) A microradiographic and electron microscopic study of the cementum of human deciduous teeth. Acta Odontol Scand 25:613–645
Furseth R (1969) The fine structure of the cellular cementum of young human teeth. Arch Oral Biol 14:1147–1158
Garant RP (1976 a) An electron microscopic study of the periodontal tissue of germfree rats and rats monoinfected with Actinomyces naeslundii. J Periodont Res 11 [Suppl 15]:9–79
Garant PR (1976 b) Collagen resorption by fibroblasts. A theory of fibroblastic maintenance of the periodontal ligament. J Periodontol 47:380–390
Garant PR, Cho MI (1979) Cytoplasmic polarization of periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Implication for cell migration and collagen secretion. J Periodont Res 14:95–106
Herting HC (1962) Elektronemikroskopische Untersuchungen über das Zahnwurzelzement des Menschen. Arch Oral Biol [Suppl] ORCA:303–312
Karnovsky MJ (1965) A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolarity for use in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 27:137A-138A
Marks SC, Popoff SN (1988) Bone cell biology: The regulation of development, structure, and function in the skeleton. Am J Anat 183:1–44
Melcher AH, Chan J (1981) Phagocytosis and digestion of collagen by gingival fibroblasts in vivo: a study of serial sections. J Ultrastruct Res 77:1–36
Nalbandian J (1978) The microscopic pattern of tetracycline fluorrescence in the cementum of human teeth. J Biol Buccale 6:27–41
Paynter KJ, Pudy G (1958) A study of the structure, chemical nature, and development of cementum in the rat. Anat Rec 131:233–251
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212
Rohr H (1965) Die Kollagensynthese in ihrer Beziehung zur submikroskopischen Struktur des Osteoblasten. Elektronenmikroskopisch-autoradiographische Untersuchung mit Tritium-markiertem Prolin. Virchows Arch [A] 338:342–354
Ross R (1968) The connective tissue fiber forming cell. In: Gould BS (ed) Treatise on collagen, vol 2, part A. Academic Press, New York, p 2
Schellens JPM, Everts V, Beertsen W (1982) Quantitative analysis of connective tissue resorption in the supra-alveolar region of the mouse incisor ligament. J Periodont Res 17:407–422
Schroeder HE (1986) The periodontium. Handbook of microscopic anatomy, vol V/5. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 47–64
Schroeder HE, Rossinsky K, Müller W (1980) An established routine method for differential staining of epoxy-embedded tissue sections. Microsc Acta 83:111–116
Selvig KA (1965) The fine structure of human cementum. Acta Odontol Scand 23:423–441
Shore RC, Berkovitz BKB (1979) An ultrastructural study of periodontal ligament fibroblasts in relation to their possible role in tooth eurption and in intracellular collagen degradation in the rat. Arch Oral Biol 24:155–164
Ten Cate AR (1972) Morphological studies of fibrocytes in connective tissue undergoing rapid remodeling. J Anat 112:401–414
Ten Cate AR, Deporter DA (1974) The role of the fibroblasts in collagen turnover in the functioning periodontal ligament of the mouse. Arch Oral Biol 19:339–340
Ten Cate AR, Deporter DA, Freeman E (1976) The role of fibroblasts in the remodeling of periodontal ligament during physiological tooth movement. Am J Orthod 69:155–168
Weinstock M (1975) Elaboration of precursor collagen by osteoblasts as visualized by radioautography after 3H-proline administration. In: Slavkin HC, Greulich RC (ed) Extracellular matrix influences on gene expression. Academic Press, New York, pp 119–128
Weinstock M, Leblond CP (1974) Synthesis, migration, and release of precursor collagen by odontoblasts as visualized by radioautography after (3H) proline administration. J Cell Biol 60:92–127
Wright GM, Leblond CP (1981) Immunohistochemical localization of procollagens. III. Type I procollagen antigenicity in osteoblasts and prebone (osteoid). J Histochem Cytochem 29:791–804
Yamasaki A, Rose GG, Mahan CJ (1981) Collagen degradation by human gingival fibroblasts. I. In vivo phagocytosis. J Periodont Res 16:309–322
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bosshardt, D.D., Schroeder, H.E. Initial formation of cellular intrinsic fiber cementum in developing human teeth. Cell Tissue Res 267, 321–335 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00302971
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00302971