Summary
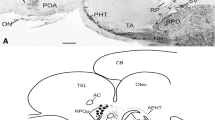
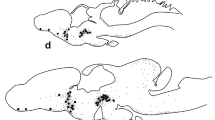
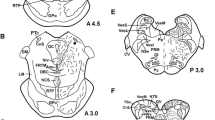
The presence and distribution of bombesin-like material were investigated in the brain of the cartilaginous fishScyliorhinus canicula using conventional immunocytochemical techniques. Perikarya containing bombesin-like immunoreactivity were identified in the hypothalamus, within the magnocellular component of the preoptic nucleus. Some immunopositive elements appeared to be of cerebrospinal fluid-contacting type. Beaded immunoreactive fibers were seen crossing the ventral telencephalon and the whole hypothalamus. An important tract of fibers was found in the infundibular floor and in the median eminence, in close contact with the vascular system of the pituitary portal plexus. A moderate number of positive fibers innervated the habenular complex and the dorsal wall of the posterior tuberculum. These findings indicate that a neuropeptide strictly related to amphibian bombesin is located in specific hypothalamic neurons ofS. canicula. The distribution of the immunoreactive fibers and terminals suggests that, in fish, this peptide, may be involved in neuroendocrine and neuromodulator functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anastasi A, Erspamer V, Bucci M (1971) Isolation and structure of bombesin and alytensin, two analogous active peptides from the skin of the European amphibiansBombina andAlytes. Experientia 27:166–167
Ball JN (1981) Hypothalamic control of the pars distalis in fish, amphibians and reptiles. Gen Comp Endocrinol 44:135–170
Bergmann W (1953) Über das Zwischenhirn-Hypophysensystem von Fischen. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 38:275–298
Bjenning C, Holmgren S (1988) Neuropeptides in the fish gut. An immunohistochemical study of evolutionary patterns. Histochemistry 88:155–163
Brown M, Rivier J, Vale W (1977a) Bombesin: potent effects on thermoregulation in the rat. Science 196:998–1000
Brown M, Rivier J, Vale W (1977b) Bombesin affects central nervous system to produce hyperglycaemia in rats. Life Sci 21:1729–1734
Buffa RT, Solovieva I, Fiocca R, Giorgino S, Rindi G, Solcia E, Mochizuchi T, Yanaihara C, Yanaihara N (1982) Localization of bombesin and GRP (gastrin-releasing peptide) sequences in gut nerves and endocrine cells. Histochemistry 76:457–467
Conlon JM, Henderson IW, Thim L (1987) Gastrin-releasing peptide from the elasmobranch fish,Scyliorhimus canicula (common dogfish). Gen Comp Endocrinol 68:415–420
Coons AH, Leduc EH, Conolly JM (1955) Studies on antibody production. I. Method for the histochemical demonstration of specific antibody and its application to the study of the hyperimmune rabbit. J Exp Med 102:49–59
Cutz E, Chaw W, Tract NS (1981) Bombesin, calcitonin and leuenkephalin immunoreactivity in endocrine cells of human lung. Experientia 37:765–767
Dockray CJ, Vaillant C, Walsh JH (1979) The neuronal origin of bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Neuroscience 4:1561–1568
El Salhy M (1984) Immunocytochemical investigation of the gastro-entero-pancreatic (GEP) neurohormonal peptides in the pancreas and gastrointestinal tract of the dogfish,Squalus acanthias. Histochemistry 80:193–205
Erspamer V (1983) Amphibian skin peptides in mammals-looking ahead. Trend Neurosci 6:200–201
Erspamer V, Melchiorri P (1980a) Amphibian skin peptides and mammalian neuropeptides. In: Pecile A, Muller E (eds) Growth hormone and other biologically active peptides. Excerpta Med, Amsterdam, pp 185–200
Erspamer V, Melchiorri P (1980b) Active polypeptides: from amphibian skin to gastrointestinal tract and brain of mammals. Trend Pharmacol Sci 1:391–395
Fasolo A, Franzoni MF, Mazzi V (1980) Evolution of the hypothalamo-hypophysial regulation in tetrapods. Boll Zool 47:127–147
Figlewicz DP, Lacour F, Sipols A, Porte D, Woods SC (1987) Gastroenteropancreatic peptides and the central nervous system. Am Rev Physiol 49:383–395
Gathei MA, Bloom SR, Langevin H, MacGregor GP, Lee YC, Adrian TE, O'Shaghnessy DJ, Blank MA, Uttenthal LO (1984) Regional distribution of bombesin and seven other regulatory peptides in the human brain. Brain Res 293:101–109
Gillati M, Moody TW (1984) The development of rat brain bombesin-like peptide and their receptors. Dev Brain Res 15:268–289
Gunion MW, Taché Y (1987) Bombesin microinfusion into the paraventricular nucleus suppressed gastric acid secretion in the rat. Brain Res 422:118–128
Holmgren S (1983) The effect of putative non-adrenergic, noncholinergic autonomic transmitters on isolated strips from the stomach of the rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri. Comp Biochem Physiol 74C:229–238
Holmgren S, Nilsson S (1983) Bombesin-, gastrin/CCK-, 5-hydroxytryptamine-, neurotensin-, somatostatin- and VIP-like immunoreactivity and catecholamine fluorescence in the gut of the elasmobranch,Scyliorhinus canicula. Cell Tissue Res 234:595–618
Holmgren S, Vaillant C, Dimaline R (1982) VIP-, substance P-, gastin/CCK-, bombesin-, somatostatin- and glucagon-like immunoreactivity in the gut of the rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri. Cell Tissue Res 223:141–153
Holstein B, Humphrey CS (1980) Stimulation of gastric acid secretion and suppression of VIP-like immunoreactivity by bombesin in the Atlantic codfish,Gadus morhua. Acta Physiol Scand 109:217–223
Lundin K, Holmgren S, Nilsson S (1984) Peptidergic functions in the dogfish rectum. Acta Physiol Scand 121:46A
Mazzi V (1952) I fenomeni neurosecretori nel nucleo magnocellulare preottico dei Selaci e dei Ciclostomi. Riv Biol XLIV:429–449
McDonald TJ, Jornvall J, Nilson G, Vagne M, Gathei M, Bloom SR, Mutt V (1979) Characterization of a gastrin releasing peptide from porcine non-antral gastric tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 90:227–233
McDonald TJ, Jornvall H, Gathei M, Mutt V (1980) Characterization of an avian (proventricular) peptide having sequence homology with porcine gastrin-releasing peptide and the amphibian peptides bombesin and alytensin. FEBS Lett 122:45–48
Merali Z, Johnston S, Zalcman S (1983) Bombesin-induced behavioural changes: antagonism by neuroleptics. Peptides 4:693–697
Minamino N, Kangawa K, Matsuo H (1983) A novel bombesin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 114:541–548
Minamino N, Kangawa K, Matsuo H (1984) Neuromedin C: a bombesin-like peptide identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 119:14–20
Moody TW, Pert CB, Rivier J, Brown MR (1978) Bombesin: specific binding to rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:5372–5376
Panula P (1986) Histochemistry and function of bombesin-like peptides. Med Biol 64:177–192
Panula P, Yang HY, Costa E (1982) Neuronal localization of the bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of rat. Regul Pept 4:275–283
Pert A, Moody TW, Pert C, Dewald L, Rivier J (1980) Bombesin receptor distribution in brain and effects on nocireception and locomotory activity. Brain Res 193:209–220
Polak JM, Gathei MA, Wharton J, Bishop AE, Bloom SR, Solcia E, Brown MR, Pearse AGE (1978) Bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the gastrointestinal tract, lung, and central nervous system. Scand J Gastroenterol 13S:149–156
Pontiroli AE, Scarpignato C (1986) Effects of bombesin on basal and stimulated secretion of some pituitary hormones in humans. Hormone Res 23:129–135
Porreca F, Fulginiti JT, Burks M (1985) Bombesin stimulates small intestinal motility after intracerebroventricular administration to rats. Eur J Pharmacol 114:167–173
Reeve J, Walsh J, Chew P, Clark B, Hawke D, Shively J (1983) Amino acid sequence of three bombesin-like peptides from canine intestine extracts. J Biol Chem 258:5582–5588
Rivier C, Rivier J, Vale W (1978) The effect of bombesin and related peptides on prolactin and growth hormone secretion in the rat. Endocrinology 102:519–522
Roth KA, Weber E, Barchas JD (1982) Distribution of gastrinreleasing peptide-bombesin-like immunostaining in rat brain. Brain Res 251:277–282
Scharrer E (1952) Das Hypophysen-Zwischenhirnsystem vonScyllium stellare. Z Zellforsch 37:196–204
Smeets WJAJ, Nieuwenhuys R, Roberts BL (1983) The central nervous system of cartilaginous fishes. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry. 2nd ed, Wiley, New York, pp 104–169
Vallarino M, Danger JM, Fasolo A, Pelletier G, Saint-Pierre S, Vaudry H (1988) Distribution and characterization of neuropeptide Y in the brain of an elasmobranch fish. Brain Res 448:67–76
Vallarino M, Tranchand Bunel D, Delbende C, Ottonello I, Vaudry H (1989) Distribution of the pro-opiomelanocortin-derived peptides, alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and beta-endorphin in the brain of the dogfishScyliorhinus canicula. An immunocytochemical study. J Exp Zool (in press)
Van de Kamer J, Zandbergen MA (1981) The hypothalamic-hypophyseal system and its evolutionary aspects inScyliorhinus caniculus. Cell Tissue Res 214:575–582
Vigh-Teichman I, Vigh B, Röhlich P, Olsson R (1980) Phylogenetic aspects of the sensory neurons of the wall of the diencephalon. In: Rakic L, Mrsulja BB (eds) Circulatory and developmental aspects of brain metabolism. Plenum, New York, pp 415–428
Walsh J, Lechago J, Wong H, Rosenquist G (1982) Presence of renatensin-like and bombesin-like peptides in amphibian brain. Regul Pept 3:1–13
Westendorf JM, Schonbrun A (1982) Bombesin stimulates prolactin and growth hormone release by pituitary cells in culture. Endocrinology 110:352–358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vallarino, M., D'Este, L., Negri, L. et al. Occurrence of bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the brain of the cartilaginous fish,Scyliorhinus canicula . Cell Tissue Res. 259, 177–181 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571441
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00571441