Abstract
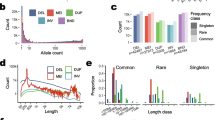
The distribution of deletion breakpoints in the dystrophin gene was studied in a series of subjects belonging to different European populations. The data, obtained from the literature or directly from the present study, refer to population samples from France, Finland, Germany, Italy, Netherland, Switzerland, and U.K. (England, Scotland, Wales). In total, 1516 breakpoints were assigned to different introns, 359 in the region encompassing the first 40 exons and 1157 (76%) in the distal part of the gene. Intron 7 appears to be equally involved as the starting or ending breakpoint, whereas intron 44 is involved mostly as a starting breakpoint. Breakpoint distribution by intron seems to differ in different populations, reaching statistical significance in the case of introns 44, 49, and 53. This finding suggests that some intronic sequences might contain preferential breakpoints that might vary in different populations, possibly as a consequence of genetic drift.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akita Y, Ohno S, Goto J, Nakano I, Takatsu M, Sugita H, Suzuki K (1987) Diagnosis of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies by DNA polymorphism. Jpn J Hum Genet 32:71–82
Barbujani G, Sokal R (1990) Zones of sharp genetic change in Europe are also linguistic boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1816–1819
Blonden LAJ, et al (1991) 242 Breakpoints in the 200-kb deletionprone P20 region of the DMD gene are widely spread. Genomics 10:631–639
Cooke A, Lanyon WG, Wilcox DE, Dornan ES, Kataki A, Gillard EF, McWhinnie AJM, Morris A, Ferguson-Smith MA, Connor JM (1990) Analysis of Scottish Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy families with dystrophin cDNA probes. J Med Genet 27:292–297
Cooper DN, Krawczak M (1990) The mutational spectrum of single base-pair substitutions causing human genetic disease: patterns and predictions. Hum Genet 85:55–74
Cooper DN, Krawczak M (1991) Mechanism of insertional mutagenesis in human genes causing genetic disease. Hum Genet 87:409–415
Covone AE, Lerone M, Romeo G (1991) Genotype-phenotype correlation and germline mosaicism in DMD/BMD patients with deletions of the dystrophin gene. Hum Genet 87:353–360
Darras BT, Blattner P, Harper JF, Spiro AJ, Alter S, Francke U (1988) Intragenic deletions in 21 Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)/Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) families studied with the dystrophin cDNA: location of breakpoints on HindIII and BglII exon-containing fragment maps, meiotic and mitotic origin of the mutations. Am J Hum Genet 43:620–629
Den Dunnen JT, Bakker E, Klein-Breteler EG, Pearson PL, Ommen GJB van (1987) Direct detection of more than 50% of muscular dystrophy mutations by field inversion gels. Nature 329:640–642
Den Dunnen JT, Grootscholten PM, Bakker E, Blonden LAJ. Ginjaar HB, Wapenaar MC, Passen HMB van, Broeckhoven C van, Pearson PL, Ommen GJB van (1989) Topography of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene: FIGE and cDNA analysis of 194 cases reveales 115 deletions and 13 duplications. Am J Hum Genet 45:835–847
Forrest SM, Cross GS, Speer A, Gardner-Medwin D, Burn J, Davies K (1987) Preferential deletion of exons in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. Nature 329:638–640
Gilgenkrantz H, Chelly J, Lambert M, Recan D, Barbot JC, Ommen GJB van, Kaplan JC (1989) Analysis of molecular deletions with cDNA probes in patients with Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. Genomics 5:574–580
Gillard EF, Chamberlain JS, Murphy EG, Duff CL, Smith B, Burghes AHM, Thomsom MW, Sutherland J, Oss I, Bodrug SE, Klamut HJ, Ray PN, Worton RG (1989) Molecular and phenotypic analysis of patients with deletions within the deletion-rich region of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene. Am J Hum Genet 45:507–520
Hodgson S, Hart K, Abbs S, Heckmatt J, Rodillo E, Bobrow M, Dubowitz V (1989) Correlation of clinical and deletion data in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet 26:683–693
Koenig M, Hoffman EP, Bertelson CJ, Monaco AP, Feener C, Kunkel LM (1987) Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell 50:509–517
Koenig M, et al (1989) The molecular basis for Duchenne versus Becker muscular dystrophy: correlation of severity with type of deletion. Am J Hum Genet 45:498–506
Krawczak M, Cooper DN (1991) Gene deletions causing human genetic disease: mechanism of mutagenesis and the role of local DNA sequence environment. Hum Genet 86:425–441
Liechti-Gallati S, Koenig M, Kunkel LM, Frey D, Boltshauser E, Schneider V, Braga S, Moser H (1989) Molecular deletion patterns in Duchenne and Becker type muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet 81:343–348
Lindlof M, Kiuru A, Kaariainen H, Kalimo H, Lang H, Pihko H, Rapola J, Somer H, Somer M, Savontaus ML, Chapelle A (1989) Gene deletions in X-linked muscular dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet 44:496–503
Love DR, et al. (1991) Sequence of junction fragments in the deletion-prone region of the dystrophin gene. Genomics 10:56–67
Lucotte G, David F, Levy C (1989) Molecular deletion patterns in Duchenne muscular dystrophy patients. Ann Genet 32:214–219
Pizzuti A, Pieretti M, Blonden LAJ, Civitello AB, Ommen GJB van, Caskey CT (1991) Sequence analysis of the dystrophin gene deletion hot-spot. Am J Hum Genet 49 [Suppl]:416A
Ruley HE, Fried M (1983) Clustered illegitimate recombination events in mammalian cells involving very short sequence homologies. Nature 304:181–184
Upadhyaya M, Smith RA, Thomas NST, Norman AM, Harper PS (1990) Intragenic deletions in 164 boys with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) studied with dystrophin cDNA. Clin Genet 37:456–462
Vitiello L, Mostacciuolo ML, Oliviero S, Schiavon F, Nicoletti L, Angelini C, Danieli GA (1992) Screening for mutations in the uscle promoter region and for exonic deletions in a series of 115 DMD and BMD patients. J Med Genet 29:127–130
Xu X, Ray PN, Worton RG (1991) Mechanisms of tandem duplication in the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene include both homologous and non-homologous intrachromosomal recombination. EMBO J 10:2471–2477
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonio Danieli, G., Mioni, F., Müller, C.R. et al. Patterns of deletions of the dystrophin gene in different European populations. Hum Genet 91, 342–346 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217354
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217354