Abstract
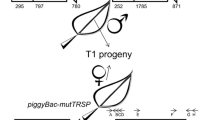
A reverse genetic system for studying excision of the transposable elementDs1 in maize plants has been established previously. In this system, theDs1 element, as part of the genome of maize streak virus (MSV), is introduced into maize plants via agroinfection. In the presence of theAc element, excision ofDs1 from the MSV genome results in the appearance of viral symptoms on the maize plants. Here, we used this system to study DNA sequences requiredin cis for excision ofDs1. TheDs1 element contains theAc transposase binding motif AAACGG in only one of its subterminal regions (defined here as the 5′ subterminal region). We showed that mutation of these motifs abolished completely the excision capacity ofDs1. This is the first direct demonstration that the transposase binding motifs are essential for excision. Mutagenesis with oligonucleotide insertions in the other (3′) subterminal region resulted in elements with either a reduced or an increased excision efficiency, indicating that this subterminal region also has an important function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker B, Schell J, Lörz H, Fedoroff N (1986) Transposition of the maize controlling element “Activator” in tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4844–4848
Coen ES, Robbins TP, Almeida J, Hudson A, Carpenter R (1989) Consequences and mechanisms of transposition inAntirrhinum majus. In: Berg DE, Howe MM (eds) Mobile DNA. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 413–436
Coupland G, Baker B, Schell J, Starlinger P (1988) Characterization of the maize transposable elementAc by internal deletions. EMBO J 7:3653–3659
Coupland G, Plum C, Chatterjee S, Post A, Starlinger P (1989) Sequences near the termini are required for transposition of the maize transposonAc in transgenic tobacco plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:9385–9388
Dennis ES, Finnegan EJ, Taylor BH, Peterson TA, Walker AR, Peacock WJ (1988) Maize transposable elements: structure, function, and regulation. In: Nelson, O (ed) Plant transposable elements. Plenum Press, New York, pp 101–113
Feldmar S, Kunze R (1991) The ORFa protein, the putative transposase of maize transposable elementAc, has a basic DNA binding domain. EMBO J 10:4003–4010
Frey M, Reinecke J, Grant S, Saedler H, Gierl A (1990) Excision of theEn/Spm transposable element ofZea mays requires two element-encoded proteins. EMBO J 9:4037–4044
Gerlach WL, Dennis ES, Peacock WJ, Clegg MT (1987) TheDs1 controlling element family in maize andTripsacum. J Mol Evol 26:329–334
Grimsley N, Hohn T, Davies JW, Hohn B (1987)Agrobacterium-mediated delivery of infectious maize streak virus into maize plants. Nature 325:177–179
Grimsley N, Ramos C, Hein T, Hohn B (1988) Meristematic tissues of maize plants are most susceptible to agroinfection with maize streak virus. Bio/Technology 6:185–189
Kunze R, Starlinger P (1989) The putative transposase of transposable elementAc fromZea mays L. interacts with subterminal sequences ofAc. EMBO J 8:3177–3185
Laufs J, Wirtz U, Kammann M, Matzeit V, Schaefer S, Schell J, Czernilofsky AP, Baker B, Gronenborn B (1990) Wheat dwarf virusAc/Ds vectors: expression and excision of transposable elements introduced into various cereals by a viral replicon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:7752–7756
Masson P, Strem M, Fedoroff N (1991) The tnpA and tnpD gene products of theSpm element are required for transposition in tobacco. Plant Cell 3:73–85
McClintock B (1947) Cytogenetic studies of maize and Neurospora. Carnegie Inst Wash Yearbook 46:146–152
McClintock B (1951) Chromosome organization and gene expression. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 16:13–47
Müller-Neumann M, Yoder JI, Starlinger P (1984) The DNA sequence of the transposable elementAc ofZea mays L. Mol Gen Genet 198:19–24
Mullineaux PM, Donson J, Morris-Krsiiiinich BAM, Boulton MI, Davies JW (1984) The nucleotide sequence of maize streak virus DNA. EMBO J 3:3063–3068
Murai N, Li Z, Kawagoe Y, Hayashimoto A (1991) Transposition of the maizeActivator element in transgenic rice plants. Nucleic Acids Res 19:617–622
Nevers P, Shepherd N, Saedler H (1986) Plant transposable elements. Adv Bot Res 12:103–203
Peacock WJ, Dennis ES, Gerlach WL, Sachs MM, Schwartz D (1984) Insection and excision ofDs controlling elements in maize. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 49:347–354
Pisabarro AG, Martin WF, Peterson PA, Saedler H, Gierl A (1991) Molecular analysis of theUbiquitous (Uq) transposable element system ofZea mays. Mol Gen Genet 230:201–208
Pohlman RF, Fedoroff N, Messing J (1984a) The nucleotide sequence of the maize controlling elementActivator. Cell 37: 635–643
Pohlman RF, Fedoroff N, Messing J (1984b) Correction: nucleotide sequence ofAc. Cell 39:417
Sachs MM, Peacock WJ, Dennis ES, Gerlach WL (1983) Maize Ac-Ds controlling elements—a molecular view-point. Maydica 28:289–303
Saedler H, Nevers P (1985) Transposition in plants: a molecular model. EMBO J 4:585–590
Shen W-H, Hohn B (1991) Mutational analysis of the small intergenic region of Maize Streak Virus. Virology 183:721–730
Shen W-H, Hohn B (1992) Excision of a transposable element from a viral vector introduced into maize plants by agroinfection. Plant J 2:35–42
Shen W-H, Hohn B (1994) Amplification and expression of the β-glucuronidase gene in maize plants by vectors based on maize streak virus. Plant J 5:227–236
Shen W-H, Das S, Hohn B (1992) Mechanism ofDs1 excision from the genome of maize streak virus. Mol Gen Genet 233:388–394
Sugimoto K, Otsuki Y, Saji S, Hirochika H (1994) Transposition of the maizeDs element from a viral vector to the rice genome. Plant J 5:863–871
Sutton WD, Gerlach WL, Schwartz D, Peacock WJ (1984) Molecular analysis ofDs controlling element mutations at theAdh1 locus of maize. Science 223:1265–1268
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. Saedler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bravo-Angel, A.M., Becker, HA., Kunze, R. et al. The binding motifs forAc transposase are absolutely required for excision ofDs1 in maize. Molec. Gen. Genet. 248, 527–534 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02423447
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02423447