Abstract
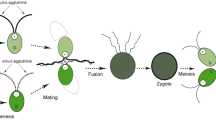
A new study of sexual agglutination between Chlamydomonas eugametos gametes and between vis-à-vis pairs has been made using techniques that allow one to distinguish between the flagella or cell bodies of individual mating types (mt+ or mt-). It is shown that before mt+ and mt- gametes fuse in pairs, their flagella, which adhere over their whole length, are maintained in a particular conformation around the mt- cell body. In clumps of agglutinating gametes the cells are asymmetrically distributed with the mt+ gametes constituting the outer surface of the clumps with the mt- gametes on the inside. The flagella are then all directed towards the middle of the clump. This orientation of the flagella is maintained for approx. 8 min after cell fusion before the vis-à-vis pair becomes motile. At this stage, all the flagellar tips are activated. The original mt+ flagellar tips then deactivate and swimming is resumed. The original mt- flagella remain immotile and activated after cell fusion and eventually shorten by a third, but only 30 min or more after fusion. Motile vis-à-vis pairs eventually settle to the substrate when the gamete bodies fuse completely to form a zygote. Settling vis-à-vis pairs are attracted to those that have already settled, to glutaraldehyde-fixed pairs and to flagella isolated from mt- gametes. They are not chemotactically attracted, rather they are weakly agglutinated. Living vis-à-vis pairs can be shown to aggregate in rows with the cell bodies lying side by side. It is argued that the flagellar agglutination sites involved in gamete recognition are also involved in vis-à-vis pair aggregation
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- mt+/- :
-
mating type plus or minus
- FTA:
-
flagellar tip activation
References
Bloodgood, R.A. (1977) Motility occurring in association with the surface of the Chlamydomonas flagellum. J. Cell Biol. 75, 983–989
Bloodgood, R.A., Levin, E.N. (1983) Transient increase in calcium efflux accompanies fertilization in Chlamydomonas. J. Cell Biol. 97, 397–404
Brown, R.M., Johnson, O.P., Bold, H.C. (1968) Electron and phase contrast microscopy of sexual reproduction in Chlamydomonas moewusii. J. Phycol. 4, 100–120
Crabbendam, K.J., Nanninga, N., Musgrave, A., van den Ende, H. (1984) Flagellar tip activation in vis-à-vis paris of Chlamydomonas eugametos. Arch. Microbiol. 138, 220–223
Elzenga, J.T.M., Nanninga, N., Lens, P.F. van den Ende, H. (1982) Flagellar tip activation in Chlamydomonas eugametos. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 15, 279–283
Goodenough, U.W., Jurivich, D. (1978) Tipping and mating structure activation induced in Chlamydomonas gametes by flagellar membrane antisera. J. Cell Biol. 79, 680–693
Homan, W.L., Musgrave, A., Molenaar, E.M., van den Ende, H. (1980) Isolation of monovalent sexual binding components from Chlamydomonas eugametos flagellar membranes. Arch. Microbiol. 128, 120–125
Hyams, J.S., Borisy, G.G. (1978) Isolated flagellar apparatus of Chlamydomonas: characterisation of forward swimming and alteration of wave form and reversal of motion by calcium ions in vitro. J. Cell Sci. 33, 235–253
Lens, P.F., van den Briel, W., Musgrave, A., van den Ende, H. (1980) Sex-specific glycoproteins in Chlamydomonas flagella. An immunological study. Arch. Microbiol. 126, 77–81
Lens, P.F., Olofson, F., Nederbragt, A., Musgrave, A., van den Ende, H. (1982) An antiserum against a glycoprotein functional in flagellar adhesion between Chlamydomonas eugametos gametes. Arch. Microbiol. 131, 241–246
Lewin, R.A. (1952) Studies on the flagella of algae. 1. General observations on Chlamydomonas moewusii. Gerloff. Biol. Bull. 102, 74–79
Mesland, D.A.M. (1976) Mating in Chlamydomonas eugametos. A scanning electron microscopical study. Arch. Microbiol. 109, 31–35
Mesland, D.A.M., Hoffman, J.L., Caligor, E., Goodenough, U.W. (1980) Flagellar tip activation stimulated by membrane adhesions in Chlamydomonas eugametos. J. Cell Biol. 84, 599–617
Pijst, H.L.A., Ossendorp, F.A., van Egmond, P., Kamps, A.M.I.E., Musgrave, A., van den Ende, H. (1984) Sex-specific binding and inactivation of agglutination factor in Chlamydomonas eugametos. Planta 160, 529–535
Snell, W.J., Roseman, S. (1979) Kinetics of adhesion and deadhesion of Chlamydomonas gametes. J. Biol. Chem. 254, 10820–10829
Triemer, R.E., Brown, R.M. (1975) The ultrastructure of fertilization in Chlamydomonas meewusii. Protoplasma 84, 315–325
Witman, G.B., Carlson, K., Berliner, J., Rosenbaum, J.L. (1972) Chlamydomonas flagella. I. Isolation and electrophoretic analysis of microtubules, matrix, membranes and mastigonemes. J. Cell Biol. 54, 507–539
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Musgrave, A., de Wildt, P., Schuring, F. et al. Sexual agglutination in Chlamydomonas eugametos before and after cell fusion. Planta 166, 234–243 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397354
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397354