Abstract
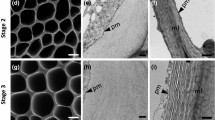
Freeze-fracturing of Glaucocystis nostochinearum Itzigsohn cells during cell-wall microfibril deposition indicates that unidirectionally polarized microfibril ends are localized in a “zone of synthesis” covering about 30% of the sarface area of the plasma membrane. Within this zone there are about 6 microfibril ends/μm2 cell surface. It is proposed that microfibrils are generated by the passage of their tips over the cell surface and that the pattern of microfibril organization at the poles of the cells, in which microfibrils of alternate layers are interconnected at 3 “rotation centres”, results directly from the pattern of this translation of microfibril tips. In a model of the deposition pattern it is proposed that the zone of synthesis may split into 3 sub-zones as the poles are approached, each sub-zone being responsible for the generation of one rotation centre. It is demonstrated that the microfibrillar component of the entire wall could be generated by the steady translation of the microfibril tips (at which synthesis is presumed to occur) over the cell surface at a rate of 0.25–0.5 μm min-1. Microcinematography indicates that the protoplast rotates during cell-wall deposition, and it is proposed that this rotation may play a role in the generation of the microfibril deposition pattern.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradley, D.E.: Replica and shadowing techniques. In: Techniques for Electron Microscopy, pp. 96–152, Kay, D.H., ed. Oxford: Blackwell 1965
Branton, D., Bullivant, S., Gilula, N.B., Karnovsky, M.J., Moor, H., Mühlethaler, K., Northcote, D.H., Packer, L., Satir, B., Satir, P., Speth, V., Staehelin, L.A., Steere, R.L., Weinstein, R.S.: Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science 190, 54–56 (1975)
Brown, R.M., Jr.: Pleurochrysis scherffelii (Chrysophyceae), vegetative development. Film E 1682. Göttingen: Irst. wiss. Film 1975
Brown, R.M., Jr., Willison, J.H.M.: Golgi apparatus and plasma membrane involvement in secretion and cell surface deposition, with special emphasis on cellulose biogenesis. In: International cell biology 1976–1977, pp. 267–283, Brinkley, B.R., Porter, K.R., eds. New York: Rockefeller Univ. Press 1977
Brown, R.M., Jr., Willison, J.H.M., Richardson, C.L.: Cellulose biosynthesis in Acetobacter xylinum: visualization of the site of synthesis and direct measurement of the in vivo process. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 73, 4565–4569 (1976)
Echlin, P.: The biology of Glaucocystis nostochinearum. I. The morphology and fine structure. Brit. Phycol. Bull. 3, 225–239 (1967)
Geitler, L.: Der Zellbau von Glaucocystis nostochinearum und Gloeochaete wittrockiana und die Chromatophoren-Symbiosetheorie von Mereschkovsky. Arch. Protistenk. 47, 1–24 (1924)
Griffiths, B.M.: On Glaucocystis nostochinearum Itzigsohn. Ann. Bot. 29, 423–432 (1919)
Heath, I.B.: A unified hypothesis for the role of membrane bound enzyme complexes and microtubules in plant cell wall synthesis. J. Theor. Biol. 48, 445–449 (1974)
Kantz, T., Bold, H.C.: Phycological studies. IX. Morphological and taxonomic investigations of Nostoc and Anabaena in culture. Univ. of Texas (Austin, Tex. USA), Publ. No. 6924 (1969)
Preston, R.D.: The Physical Biology of Plant Cell Walls. London: Chapman & Hall 1974
Robinson, D.G., Preston, R.D.: Studies on the fine structure of Glaudocystis nostochinearum Itzigs. I. Wall structure. J. Exp. Bot. 22, 635–643 (1971)
Schnepf, E.: Struktur der Zellwände und Cellulosefibrillen bei Glaucocystis. Planta 67, 213–224 (1965)
Schnepf, E., Koch, W., Diechgräber, G.: Zur Cytologie und taxonomischen Einordnung von Glaucocystis. Arch. Mikrobiol. 55, 149–174 (1966)
Schnepf, E., Röderer, G., Herth, W.: The formation of the fibrils in the lorica of Poteriochromonas stipitata: tip growth, kinetics, site, orientation. Planta 125, 45–62 (1975)
Roelofsen, P.A.: Cell-wall structure as related to surface growth. Acta Bot. Neerl 7, 77–89 (1958)
Roelofsen, P.A.: The Plant Cell Wall. Berlin: Borntraeger 1959
Willison, J.H.M., Brown, R.M., Jr.: Cell wall structure and deposition in Glaucocystis. J. Cell Biol., in press (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willison, J.H.M., Brown, R.M. A model for the pattern of deposition of microfibrils in the cell wall of Glaucocystis . Planta 141, 51–58 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387744
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387744