Summary
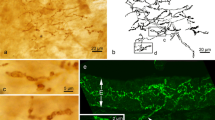
Sequential changes in the monoamine-contianing cell (MC cell) of the developing frog tongue has been studied by fluorescence histochemistry using uptake of 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine. At st. 16, a few yellow fluorescent cells, here called MC cells, appeared in random order at the uppermost layer of the dorsal epithelium. They were round or elliptical in shape. At st. 18 the MC cells, greatly transformed, were found at the periphery of the sensory disc primordium which first appears during this stage. The MC cell was made up of three parts: perikaryon, process and terminal portion. The perikaryon was located at the upper half of the epithelium and from it a single process stretched vertically toward the basal lamina, above which the dilated terminal portion was found. Thereafter the perikaryon gradually moved toward the basal layer while remaining at the periphery of the disc primordium. Meanwhile the terminal portion moved over the basal lamina toward the center of the disc primordium. At st. 22, the whole of the MC cell lay flat above the basal lamina. The perikaryon was localized at the periphery of the sensory disc and from there the process stretched toward the center. Thus, the morphology of MC cells resembled the adult state, except for smaller size. MC cells were never observed in the subepithelial connective tissue in the present study. This seems to suggest that the MC cell of the frog fungiform papilla is of epithelial origin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breathnach AS (1971a) Embryology of human skin. A review of ultrastructural studies. J Invest Dermatol 57:133–143
Breathnach AS (1971b) An atlas of the ultrastructure of human skin. J.A. Churchil, London, pp 76–77 and 388–389
Düring M v, Andres KH (1976) The ultrastructure of taste and touch receptors of the frog's taste organ. Cell Tissue Res 165:185–198
Falck B, Hillarp N-Å, Thieme G, Torp A (1962) Fluorescence of catecholamines and related compounds condensed with formaldehyde. J Histochem Cytochem 10:348–354
Farbman AI (1965) Electron microscope study of the developing taste bud in rat fungiform papilla. Dev Biol 11:110–135
Füjimoto S, Murray RG (1970) Fine structure of degeneration and regeneration in denervated rabbit vallate taste buds. Anat Rec 168:393–414
Hashimoto K (1972) The ultrastructure of the skin of human embryos. X. Merkel tactile cells in the finger and nail. J Anat 111:99–120
Hirata K, Nada O (1975) A monoamine in the gustatory cell of the frog's taste organ. A fluorescence histochemical and electron microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res 159:101–108
Hirata K, Nada O (1977) Cytoarchitecture of monoamine-containing cells in the frog's gustatory epithelium. Experientia 33:1223–1224
Kurosumi K, Kurosumi U, Suzuki H (1969) Fine structures of Merkel cells and associated nerve fibers in the epidermis of certain mammalian species. Arch Histol Jpn 30:295–313
Lyne AG, Hollis DE (1971) Merkel cells in sheep epidermis during fetal development. J Ultrastruct Res 34:464–472
Murray RG, Murray A, Fujimoto S (1969) Fine structure of gustatory cells in rabbit taste buds. J Ultrastruct Res 27:444–461
Nada O, Hirata K (1975a) The occurrence of the cell type containing a specific monoamine in the taste bud of the rabbit's foliate papilla. Histochemistry 43:237–240
Nada O, Hirata K (1975b) Specific effect of 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine on the monoamine fluorophore of the frog's gustatory cells. Histochemistry 45:121–127
Nada O, Hirata K (1977) The monoamine-containing cell in the gustatory epithelium of some vertebrates. Arch Histol Jpn 40 (Suppl):197–206
Reutter K (1971) Die Geschmacksknospen des Zwergwelses Amiurus nebulosus (Lesueur). Morphologische und histochemische Untersuchungen. Z Zellforsch 120:280–308
Reutter K (1978) Taste organ in the bullhead (Teleostei). Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 55:1–98
Taylor AC, Kollros JJ (1946) Stages in the normal development of Rana pipiens larvae. Anat Rec 94:7–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirata, K., Nada, O. A fluorescence histochemical study of the monoamine-containing cell in the developing frog taste organ. Histochemistry 67, 65–71 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00490088
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00490088