Abstract
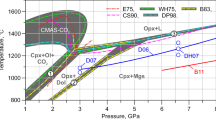
The model for the thermodynamic properties of multicomponent pyroxenes (Part I) is calibrated for ortho- and clinopyroxenes in the quadrilateral subsystem defined by the end-member components Mg2Si2O6, CaMgSi2O6, CaFeSi2O6, and Fe2Si2O6. This calibration accounts for: (1) Fe-Mg partitioning relations between orthopyroxenes and augites, and between pigeonites and augites, (2) miscibility gap features along the constituent binary joins CaMgSi2O6-Mg2Si2O6 and CaFeSi2O6-Fe2Si2O6, (3) calorimetric data for CaMgSi2O6-Mg2Si2O6 pyroxenes, and (4) the P-T-X systematics of both the reaction pigeonite=orthopyroxene+augite, and miscibility gap featurs, over the temperature and pressure ranges 800–1500°C and 0–30 kbar. The calibration is achieved with the simplifying assumption that all regular-solution-type parameters are constants independent of temperature. It is predicated on the assumptions that: (1) the Ca-Mg substitution is more nonideal in Pbca pyroxenes than in C2/c pyroxenes, and (2) entropies of about 3 and 6.5 J/K-mol are associated with the change of Ca from 6- to 8-fold coordination in the M2 site in magnesian and iron C2/c pyroxenes, respectively. The model predicts that Fe2+-Mg2+ M1-M2 site preferences in C2/c pyroxenes are highly dependent on Ca and Mg contents, with Fe2+ more strongly preferring M2 sites both in Ca-rich C2/c pyroxenes with a given Fe/(Fe+Mg) ratio, and in magnesian C2/c pyroxenes with intermediate Ca/(Ca+Fe+Mg) ratios.
The proposed model is internally consistent with our previous analyses of the solution properties of spinels, rhombohedral oxides, and Fe-Mg olivines and orthpyroxenes. Results of our calibration extend an existing database to include estimates for the thermodynamic properties of the C2/c and Pbca pyroxene end-members clinoenstatite, clinoferrosilite, hedenbergite, orthodiopside, and orthohedenbergite. Phase relations within the quadrilateral and its constitutent subsystems are calculated for temperatures and pressures over the range 800–1700°C and 0–50 kbar and compare favorably with experimental constraints.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atlas L (1952) The polymorphism of MgSiO3 and the solid-state equilibria in the system MgSiO3−CaMgSiO6. J Geol 60:125–147
Benna P, Tribaudino M, Zanini G, Bruno E (1990) The crystal structure of Ca0.8Mg1.2Si2O6 clinopyroxene (Di80En20) at T=-130°, 25°, 400°, and 700° C. Z Kristallogr 192:183–199
Berman RG (1988) Internally-consistent thermodynamic data for minerals in the system Na2O-K2O-CaO-MgO-FeO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-SiO2-TiO2-H2O-COn2. J Petrol 29:445–522
Berman RG, Brown TH (1985) Heat capacities of minerals in the system Na2O−K2O−CaO−MgO−FeO−Fe2O3−Al2O3−SiO2 −TiO2−H2O−CO2: representation, estimation, and high temperature extrapolation. Contrib Mineral Petrol 89:168–183
Biggar GM (1988) Protoenstatite composition from 1 bar to 5 kb (abstract). Chem Geol 70:3
Bowen NL, Schairer JF (1935) The system CaO-FeO-SiO2. Am J Sci 29:151–217
Brey G, Huth J (1984) The enstatite-diopside solvus to 60 kbar. Proc Third Int Kimberlite Conference vol 2, pp 257–264
Brown GE, Prewitt CT, Papike JJ, Sueno S (1972) A comparison of the structures of low and high pigeonite. J Geophys Res 77:5778–5789
Carlson WD (1986) Reversed phase equilibria in CaO-MgO-SiO2 at one atmosphere pressure. Contrib Mineral Petrol 92:218–224
Carlson WD (1988) Subsolidus phase equilibria on the forsteritesaturated join Mg2Si2O6−CaMgSi2O6 at atmospheric pressure. Am Mineral 73:232–241
Carlson WD, Lindsley DH (1988) Thermochemistry of pyroxenes on the join Mg2Si2O6−CaMgSi2O6. Am Mineral 73:242–252
Clark JR, Appelman DE, Papike JJ (1969) Crystal chemical characterization of clinopyroxenes based on eight new structure refinements. Mineral Soc Am Spec Pap 2:31–50
Davidson PM (1988) Phase separation in quadrilateral pyroxenes and olivines. In: Ghose S, Coey JMD, Salje E (eds) Structural and Magnetic phase transitions in minerals. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 39–59
Davidson PM, Lindsley DH (1985) Thermodynamic analysis of quadrilateral pyroxenes. Part II: Model calibration from experiments and applications to geothermometry. Contrib Mineral Petrol 91:390–404
Davidson PM, Grover JE, Lindsley DH (1982) (Ca, Mg)2Si2O6 clinopyroxenes: a solution model based on nonconvergent sitedisorder. Contrib Mineral Petrol 80:88–102
Dowty E, Lindsley DH (1973) Mössbauer spectra of synthetic hedenbergite-ferrosilite pyroxenes. Am Mineral 58:850–868
Fonarev VI, Graphcikov AA (1982) Experimental study of Fe−Mg- and Ca-distribution between coexisting ortho- and clinopyroxene at P=294 Mpa, T=750 and 800°C. Contrib Mineral Petrol 79:311–318
Francombe MH (1957) Lattice changes in spinel-type iron chromires. J Phys Chem Solids 3:37–43
Gasparik T (1990) A thermodynamic model for the enstatite-diopside join. Am Mineral 75:1080–1091
Ghiorso MS (1990) Thermodynamic properties of hematite-ilmenite-geikielite solid solutions. Contrib Mineral Petrol 104:645–667
Ghiorso MS, Sack RO (1991) Fe−Ti oxide geothermometry: thermodynamic formulation and the estimation of intensive variables in silicic magmas. Contrib Mineral Petrol 108:485–510
Grove TL, Juster TC (1989) Experimental investigations of low-Ca pyroxene stability and olivine-pyroxene-liquid equilibria at 1-atm in natural basaltic and andesitic liquids. Contrib Mineral Petrol 103:287–305
Haselton HT, Robic RA, Hemingway BS (1987) Heat capacities of synthetic hedenbergite, ferrobustamite, and CaFeSi2O6 glass. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 51:2211–2217
Helgeson HC, Delany JM, Nesbit HW, Bird DK (1978) Summary and critique of the thermodynamic properties of rock-forming minerals. Am J Sci 278A:1–299
Hirschmann M (1991) Thermodynamics of multicomponent olivines and the solution properties of (Ni, Mg, Fe)2SiO4 and (Ca, Mg, Fe)2SiO4 olivines. Am Mineral 76:1232–1248
Howells S, O'Hara MJ (1975) Paleogeotherms and the diopsideenstatite solvus. Nature 254:406–408
Kushiro I (1973) Incongruent melting of pure diopside. Carnegie Inst Washington Yearb 72:708–710
Kushiro I, Schairer JF (1963) New data on the system MgSiO3−CaMgSi2O6. Carnegie Inst Washington Yearb 62:95–103
Lange RA, De Yoreo JJ, Navrotsky A (1991) Scanning calorimetric measurement of heat capacity during incongruent melting of diopside. Am Mineral 76:904–912
Lindsley DH (1965) Ferrosilite. Carnegie Inst Washington Yearb 64:148–149
Lindsley DH (1981) The formation of pigeonite on the join hedenbergite-ferrosilite at 11.5 and 15 Kbar: experiments and a solution model. Am Mineral 66:1175–1182
Lindsley DH (1983) Pyroxene thermometry. Am Mineral 68:477–493
Lindsley DH, Andersen DJ (1983) A two-pyroxene thermometer. Proc 14th Lunar Planet Sci Conf, J Geophys Res 88 Supplement: A887-A906
Lindsley DH, Dixon SA (1976) Diopside-enstatite equilibria at 850°C to 1400°C, 5 to 35 kb. Am J Sci 276:1285–1301
Lindsley DH, Munoz JL (1969) Subsolidus relations along the join hedenbergite-ferrosilite. Am J Sci 267A:295–324
Lindsley DH, Munoz JL, Finger LW (1969) Unit cell parameters of clinopyroxenes along the join hedenbergite-ferrosilite. Carnegie Inst Washington Yearb 67:91–92
Lindsley DH, Grover JE, Davidson PM (1981) The thermodynamics of the Mg2Si2O6−CaMgSi2O6 join: a review and an improved model. In: Newton RC, Navrotsky A, Wood BJ (eds) Thermodynamics of minerals and melts. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 149–175
Longhi J, Boudreau AE (1980) The orthoenstatite liquidus field in the system forsterite-diopside-silica at one atmosphere. Am Mineral 65:563–573
McCallister RH, Finger LW, Ohashi Y (1976) Intracrystalline Fe2+−Mg equilibria in three natural Ca-rich clinopyroxenes. Am Mineral 61:671–676
Mori T (1978) Experimental study of pyroxene equilibria in the CaO−MgO−SiO2 system at high pressures and temperatures. J Petrol 19:45–65
Mori T, Green DH (1975) Pyroxenes in the system Mg2Si2O6−CaMgSi2O6 at high pressure. Earth Planet Sci Lett 26:277–286
Mori T, Green DH (1976) Subsolidus equilibria between pyroxene equilibria in the system CaO−MgO−FeO−SiO2. Am Mineral 61:616–625
Navrotsky A, Loucks D (1977) Calculation of subsolidus phase relations in carbonates and pyroxenes. Phys Chem Mineral 1:109–127
Newton RC, Charlu TV, Anderson PAM, Kleppa OJ (1979) Thermochemistry of synthetic clinopyroxenes on the join CaMgSi2O6−Mg2Si2O6. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 43:55–60
Nickel KG, Brey G (1984) Subsolidus orthopyroxene-clinopyroxene systematics in the system CaO−MgO−SiO2 to 60 kb: a re-evaluation of the regular solution model. Contrib Mineral Petrol 87:35–42
O'Leary MJ, Sack RO (1987) Fe−Zn exchange reaction between tetrahedrite and sphalerite in natural environments. Contrib Mineral Petrol 96:415–425
Ottenello G (1992) Interactions and mixing properties in the (C2/c) clinopyroxene quadrilateral. Contrib Mineral Petrol 111:53–60
Perkins D III, Newton RC (1980) The composition of coexisting pyroxenes and garnet in the system CaO−MgO−Al2O3−SiO2 at 900–1100°C and high pressures. Contrib Mineral Petrol 75:291–300
Podpora C, Lindsley DH (1979) Fe-rich pigeonites: minimum temperatures of stability in the Ca−Ng−Fe quadrilateral (abstract). EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 60:420–421
Prewitt CT, Brown GE, Papike JJ (1971) Apollo 12 clinopyroxenes: high temperature X-ray diffraction studies. Proc Second Lunar Sci Conf vol 1. MIT Press, pp 59–68
Robbins M, Wertheim GK, Sherwood RC, Buchanan DNE (1971) Magnetic properties and site distributions in the system FeCr2O4−Fe3O4(Fe2+Cr2-xFe 3+x O4). J Phys Chem Solids 32:717–729
Rossi G, Oberti R, Dal Negro A, Molin GM, Mellini M (1987) Residual electron density at the M2 site in C2/c clinopyroxenes: relationships with bulk chemistry and subsolidus exsolution. Phys Chem Mineral 14:514–520
Sack RO (1992) Thermochemistry of tetrahedrite-tennantite fahlores. In: Ross NL, Price GD (eds) The stability of minerals. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 243–266
Sack RO, Ghiorso MS (1989) Importance of considerations of mixing properties in establishing an internally consistent thermodynamic database: thermochemistry of minerals in the system Mg2SiO4−Fe2SiO4−SiO2. Contrib Mineral Petrol 102:41–68
Sack RO, Ghiorso MS (1991 a) An internally consistent model for the thermodynamic properties of Fe−Mg-titanomagnetite-aluminate spinels. Contrib Mineral Petrol 106:474–505
Sack RO, Ghiorso MS (1991 b) Chromian spinels as petrogenetic indicators: thermodynamics and petrological applications. Am Mineral 76:827–847
Sack RO, Ghiorso MS (1994) Thermodynamics of multicomponent pyroxenes. I. Formulation of a general model. Contrib Mineral Petrol (in press)
Sack RO, Ebel DS, O'Leary MJ (1987) Tennahedrite thermochemistry and metal zoning. In: Helgeson HC (ed) Chemical transport in metasomatic processes. D Reidel, Dordrecht Boston Lancaster Tokyo, pp 701–731
Saxena SK, Ghose S, Turnock AC (1974) Cation distributions in low-calcium pyroxenes: dependence on temperature and calcium content and the thermal history of lunar and terrestrial pigeonites. Earth Planet Sci Lett 21:194–200
Schwcitzer E (1982) The reaction pigeonite=diopsidess+enstatitess at 15 kbar. Am Mineral 67:54–58
Spiridonov EM (1984) Species and varieties of fahlore (tetrahedrite-tennantite) minerals and their rational nomenclature. Dok Akad Nauk SSSR 279:166–172
Smyth JR (1969) Orthopyroxene-high-low clinopyroxene inversions. Earth Planet Sci Lett 6:406–407
Sueno S, Cameron M, Papike JJ, Prewitt CT (1973) The high temperature crystal chemistry of tremolite. Am Mineral 58:649–664
Tribaudino M, Benna P, Bruno E (1989) Average structure and the M2 site configurations in C2/c clinopyroxenes along the Di-En join. Contrib Mineral Petrol 103:452–456
Turnock AC, Lindsley DH (1981) Experimental determination of pyroxene solvi for P ⇐ 1 kb, 900 and 1000°C. Can Mineral 19:255–267
Warner RD, Luth WC (1974) The diopside-clinoenstatite two-phase region in the system CaMgSi2O6−Mg2Si2O6. Am Mineral 59:98–109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sack, R.O., Ghiorso, M.S. Thermodynamics of multicomponent pyroxenes: II. Phase relations in the quadrilateral. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 116, 287–300 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306498
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306498