Abstract
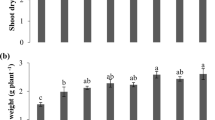
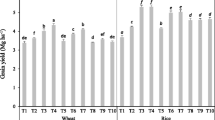
We evaluated the effect of agricultural-grade (AG) pyrites (total sulfur 22%) varying in water-soluble sulfur (1–8%) and gypsum on the soil properties and yields of rice and wheat in alkali soils during the years 1993–1995 at the Gudha and Saraswati experimental farms at the Central Soil Salinity Research Institute, Karnal, India. Gypsum and pyrites were applied on the basis of gypsum requirement (GR) of the soils. Results showed that the efficiency of AG pyrites in decreasing soil pH and exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) and increasing crop yields was dependent on their water-soluble sulfur content at the time of application to the field. Pyrites with 5.5% and 8% soluble sulfur were as effective as gypsum. The freshly mined pyrite (water-soluble S 1%) was found to be inefficient in reclaiming alkali soils. We also explored the possibility of increasing the water-soluble sulfur content of pyrite by optimizing its storage conditions. When pyrite (1% water-soluble S) was stored under moist conditions by sprinkling water over the bags under a rain shelter, there was an enrichment of indigenous iron- and sulfur-oxidizing bacteria of pyrite, and the water-soluble sulfur increased to 5% within a period of 6 months. However no such increase occurred when pyrite was stored dry. We conclude that the soluble sulfur content of pyrite increased during its storage under moist conditions and should be between 6% and 8% at the time of its application to the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrol IP, Bhumbla DR (1979) Crop responses to differential gypsum applications in a highly sodic soil and the tolerance of several crops to exchangeable soidum under field conditions. Soil Sci 127:79–85
Grishin SI, Tuovinen OH (1988) Fast kinetics of Fe(II) oxidation in packed bed reactors. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:3092–3100
Harrison AP Jr (1984) The acidophilic thiobacilli and other acidophilic bacteria that share their habitat. Annu Rev Microbiol 38:265–292
Jackson ML (1967) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi
Jaggi TN (1978) Use of Amjhore pyrites as alkali soil amendment. In: Singh R (ed) Proceedings of Seminar “Use of sedimentary pyrites in reclamation of alkali soil”. Fertiliser Association of India. Phosphates and Pyrites Chemical Limited. Government of India, New Delhi, pp 34–37
Kovda VA (1965) Alkaline soda-saline soils. Agrochem Talajt 14 (Suppl):15–48
Minhas PS, Gupta RK (1992) Quality of irrigation water-assessment and management. Information and Publication Section. Indian Council of Agriculture Research, New Delhi, pp 1–123
Oster JD (1982) Gypsum use in irrigated agriculture — a review. Fert Res 3:73–89
Puhaaka J, Hiltunen P, Tuovinen OH (1985) Patterns of substrate utilization from sulfide ore material by mixed cultures of microorganisms enriched from mine waters. System Appl Microbiol 6:302–307
Sharma P, Swarup A (1995) Microbial oxidation of pyrites in relation to its efficiency in alkali soil reclamation. In: Huang PM, Berthelin J, Bollag JM, McGill WP, Page AL (eds) Environmental impact of soil component interactions — natural and anthropogenic organics, vol 1. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, pp 97–104
Sharma OP, Gupta RK (1986) Comparative performance of gypsum and pyrites in sodic vertisols. Indian J Agric Sci 56:423–429
Sharma P, Varma AK (1991) Microbial reclamation of metals from ores and industrial waste waters. Indian J Microbiol 31:1–26
Sharma DR, Sharma DK, Minhas PS (1993) Feasibility studies on the use of saline/sodic waters in conjunction with canal water and amendments. In: Tyagi NK, Kamra SK, Minhas PS, Singh NT (eds) Proceedings of national workshop on “Sustainable irrigation in saline environment”. CSSRI, Karnal, India, pp 110–117
Singh NT, Hira GS, Singh R (1978) Comparative effects of pyrites and gypsum on physicochemical properties of a sodic soil. In: Singh R (ed) Proceedings of Seminar on “Use of Sedimentary pyrites in reclamation of alkali soil”. Fertiliser Association of India. Phosphates and Pyrites Chemical Limited, New Delhi, pp 69–80
Singh NT, Hira GS, Bajwa MS (1981) Use of amendments in reclamation of alkali soils in India. Agrochem Talajt 30:158–177
Swarup A (1981) Effect of presubmergence and amendments on the growth of rice and wheat on a sodic soil. Z Acker Pflanzenbau 150:333–338
Swarup A (1985) Yield and nutrition of rice as influence by presubmergence and amendments in a highly sodic soil. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 33:352–357
Tiwari KN, Dwivedi BS, Upadhyay GP, Pathak AN (1984) Sedimentary pyrites as amendment for sodic soils and carrier of iron and sulfur - a review. Fert News 29:31–41
United States Department of Agriculture (1975) Soil taxonomy. Handbook No. 436, Washington DC
Verma KS, Abrol IP (1980) Effects of gypsum and pyrites on soil properties in a highly sodic soil. Indian J Agric Sci 50:844–851
Vogel AI (1961) A textbook of quantitative inorganic analysis, 3rd edn. The English Language Book Society and Langman Group, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, P., Swarup, A. Comparison of pyrites varying in water-soluble sulfur with gypsum for the reclamation of alkali soils under a rice-wheat rotation. Biol Fert Soils 24, 96–101 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01420227
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01420227