Abstract
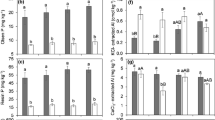
A field study was conducted to determine the influence of a short-term (2 year) cessation of fertiliser applications, liming, and sheep-grazing on microbial biomass and activity in a reseeded upland grassland soil. The cessation of fertiliser applications (N and NPK) on a limed and grazed grassland had no effect on microbial biomass measurements, enzyme activities, or respiration. Withholding fertiliser and lime from a grazed grassland resulted in significant reductions in both microbial biomass C (P<0.05) and dehydrogenase activity (P<0.05) by approximately 18 and 21%, respectively. The removal of fertiliser applications, liming, and grazing resulted in even greater reductions in microbial biomass C (44%, P<0.001) and dehydrogenase activity (31%, P<0.001), and significant reductions in microbial biomass N (P<0.005), urease activity (P<0.05), phosphatase activity (P<0.001), and basal respiration (P<0.05). The abundance of culturable bacteria and fungi and the soil ATP content were unaffected by changes in grassland managements. With the cessation of liming soil pH fell from 5.4 to 4.7, and the removal of grazing resulted in a further reduction to pH 4.5. A significant negative linear relationship (r 2=0.97; P<0.01) was found between increasing soil acidity and dehydrogenase activity. Possible mechanisms influencing these changes are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander M (1977) Introduction to soil microbiology. Wiley, New York
Arnebrant K, Bååth E (1991) measurement of ATP in forest humus. Soil Biol Biochem 23:501–506
Bardgett RD (1990) The effects of changes in sheep grazing intensity on faunal—fungal interactions related to nutrient cycling in upland soils. PhD thesis, University of Lancaster
Bardgett RD (1991) The use of the membrane filter technique for comparative measurements of hyphal lengths in different grassland sites. Agric Ecosyst Environ 35:115–119
Bardgett RD, Frankland JC, Whittaker JB (1993a) The effects of agricultural management on the soil biota of some upland grasslands. Agric Ecosyst Environ 45:25–45
Bardgett RD, Whittaker JB, Frankland JC (1993b) The diet and food preferences of Onychiurus procampatus (Collembola) from upland grassland soils. Biol Fertil Soils 16:296–298
Bardgett RD, Whittaker JB, Frankland JC (1993c) The effect of collemboland grazing on fungal activity in differently managed upland pastures: A microcosm study. Biol Fertil soils 16: 255–262
Beyer L, Wachendorf C, Elsner DC, Knabe R (1993) Suitability of dehydrogenase activity assay as an index of soil biological activity. Biol Fertil Soils 16:52–56
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: A rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842
Burns RG (1978) Soil enzymes. Academic Press, New York
Carter MR (1986) Microbial biomass and mineralizable nitrogen in solonetzic soils: Influence of gypsum and lime amendments. Soil Biol Biochem 18:531–537
Cepeda MCT, Carballas T, Sortes FG, de Blas E (1991) Liming and the phosphatase activity and mineralization of phosphorus in an acidic soil. Soil Biol Biochem 23:209–215
Chander K, Brookes PC (1991) Is the dehydrogenase assay invalid to estimate microbial activity in copper-contaminated soils? Soil Biol Biochem 23:909–915
Curl EA, Truelove B (1986) The rhizosphere. Springer, Berlin
Davies A (1992) Extensification and pasture productivity. AFRC—Institute of Grassland and Environmental Research Annual Report, Aberystwyth, Dyfed, 1992, pp 72–73
Eiland F (1983) A simple method for quantitative determination of ATP in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 15:665–670
Eiland F (1985) Determination of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenylate energy charge (AEC) in soil and use of adenine nucleotides as measures of soil microbial biomass and activity. Dan J Plant Soil Sci 1777:1–193
Frankland JC, Dighton J, Boddy L (1990) Methods for studying fungi in soil and forest litter. In: Norris JR, Grigorova r (eds) Methods in microbiology. Academic Press, London, pp 343–404
Halstead RL (1964) Phosphatase activity of soils as influenced by lime and other treatments. Can J Soil Sci 44:137–144
Hanlon RD (1981) Influence of grazing by Collembola on the activity of senescent fungal colonies grown on media of different nutrient contents. Oikos 36:336–363
Haynes RJ, Swift RS (1988) Effects of lime and phosphate additions on changes in enzyme activities, microbial biomass and levels of extractable nitrogen, sulphur and phosphorus in an acid soil. Biol Fertil Soils 6:153–158
Illmer P, Schinner F (1991) Effects of lime and nutrient salts on the microbiological activities of forest soils. Biol Fertil Soils 11: 261–266
Jenkinson DS, Powlson DS (1976) The effects of biocidal treatments on metabolism in soil. V. A method for measuring soil biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 8:209–213
Lynch JM, Panting LM (1980) Variations in the size of the soil biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 12:547–550
Macduff JH, Jackson SB (1992) Influx and efflux of nitrate and ammonium in Italian ryegrass and white clover roots: Comparisons between effects of darkness and defoliation. J Exp Bot 43:525–535
Martens R (1990) Contribution of rhizodeposits to the maintenance and growth of the soil microbial biomass. Soil Biol Biochem 22:141–147
Mersi W von, Schinner F (1991) An improved and accurate method for determining the dehydrogenase activity of soils with iodonitrotetrazolium chloride. Biol Fertil Soils 11:216–220
Milton WEJ (1940) The effect of manuring, grazing and cutting on the yield, botanical and chemical composition of natural hill pastures. I. Yield and botanical section. J Ecol 28:326–356
Nannipieri P, Johnson RL, Paul EA (1978) Criteria for measurement of microbial growth and activity in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 10:223–229
Nannipieri P, Grego S, Ceccanti B (1990) Ecological significance of biological activity in soil. Soil Biochem 6:293–355
Newbould P (1985) Improvement of native grasslands in the uplands. Soil Use Manage 1:43–49
Newman EI (1985) The rhizosphere-C sources and microbial populations. In: Fitter AH (ed) Ecological interactions in soil. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 107–121
Perrott KW, Sarathchandra SU, Waller BW (1990) Seasonal storage and release of phosphorus and potassium by organic matter and microbial biomass in a high-producing pastoral soil. Aust J Soil Res 28:593–608
Perrott KW, Sarathchandra SU, Dow BW (1992) Seasonal and fertilizer effects on the organic cycle and microbial biomass in a hill country soil under pasture. Aust J Soil Res 30:383–394
Sarathchandra SU, Upsdell MP (1981) Nitrogen mineralization and the activity and populations of microflora in a high-producing yellow-brown loam under pasture. NZ J Agric Res 24:171–176
Sarathchandra SU, Perrott KW, Boase MR, Waller JE (1988) Seasonal changes and the effects of fertiliser on some chemical, biochemical and microbiological characteristics of high-producing pastoral soil. Biol Fertil Soils 6:328–335
Sparling GP, West AW (1988a) A direct extraction method to estimate soil microbial C: Calibration in situ using soil microbial respiration and 14C labelled cells. Soil Biol Biochem 20: 337–343
Sparling GP, West AW (1988b) Modifications to the fumigation-extraction technique to permit simultaneous extraction of soil microbial C and N. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 19: 327–344
Sparling GP, West AW, Feltham CW, Reynolds J (1990) Estimation of soil microbial C by a fumigation-extraction method: Use on soils of high organic matter content and reassessment of the k ec-factor. Soil Biol Biochem 22:301–307
Speir TW, Ross DJ (1978) Soil phosphatase and sulphatase. In: Burns RG (ed) Soil enzymes. Academic Press, London, pp 197–250
Speir TW, Ross DJ, Orchard VA (1984) Spatial variability of biochemical properties in a taxonomically-uniform soil under grazed pasture. Soil Biol Biochem 16:153–160
Sydes C, Miller GR (1988) Range management and nature conservation in the British uplands. In: Usher MB, Thompson DBA (eds) Ecological change in the uplands. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 323–337
Tabatabai MA, Bremner JM (1969) The use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assya of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol Biochem 1:303–307
Tate KR, Ross DJ, Feltham CW (1988) A direct method to estimate soil microbial biomass C: Effects of experimental variable and some different calibration procedures. Soil Biol Biochem 20:329–335
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987a) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987b) Microbial biomass measurements in forest soils: The use of the chloroform fumigation-incubation technique in strongly acid soils. Soil Biol Biochem 19:697–702
Wardle DA (1992) A comparative assessment of factors which influence microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen levels in soil. Biol Rev 67:321–358
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bardgett, R.D., Leemans, D.K. The short-term effects of cessation of fertiliser applications, liming, and grazing on microbial biomass and activity in a reseeded upland grassland soil. Biol Fertil Soils 19, 148–154 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336151
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336151