Abstract
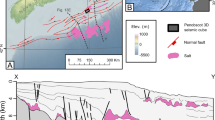
Bathymetric charts of the continental slope of the northwestern Gulf of Mexico reveal the presence of over 90 intraslope basins with relief in excess of 150 m. The evolution and the general configuration of the basins are a function of halokinesis of allochthonous salt. Intraslope-interlobal and intraslope-superlobal basins occupy the upper and lower continental slope, respectively. Other structures on the slope associated with salt tectonics are the Sigsbee Escarpment, the seaward edge of the Sigsbee salt nappe, and the Alaminos and Keathley canyons. Major erosional features are the Mississippi Canyon and portions of a submarine canyon on the southern extreme of the Sigsbee Escarpment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouma AH, Chancey O, Merkel O (1972) Alaminos Canyon area. In: Rezak R, Henry VJ (eds) Contributions on the Geological Oceanography of the Gulf of Mexico. Texas A&M University Oceanographic Studies, v. 3. Gulf Publishing Co., Houston, pp 153–179
Bouma AH, Coleman JM, Meyer A, and others (1986) Initial Reports Deep Sea Drilling Project Leg 96. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC, 824 pp
Buffler RT, Worzel J (1978) Deformation and origin of the Sigsbee Scarp—Lower continental slope, northern Gulf of Mexico. Offshore Technology Conference #3217, pp 1425–1434
Buffler RT (1983) Structure of the Sigsbee Scarp, Gulf of Mexico. In: Bally AW (ed) Seismic Expression of Structural Styles—A Picture and Work Atlas. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Studies in Geology 15, v. 2, pp 2.3–2.50
Coleman JM, Prior DB, Lindsay JF (1983) Deltaic influences on shelf edge instability processes. In: Stanley DJ, Moore GT (eds) The Shelfbreak: Critical Interface on Continental Margins. Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists Special Publication 33:121–137
Garrison LE, Martin RG Jr (1973) Geologic structure in the Gulf of Mexico. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 773, 85 pp
Gealy BL (1955) Topography of the continental slope, northwest Gulf of Mexico. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 66:203–227
Hardin NS (1989) Salt distribution and emplacement processes, northwest Gulf of Mexico lower slope: A suture between two provinces. Gulf Coast Section Society of Economics Paleontologists and Mineralogists Foundation 10th Annual Research Conference Program and Abstracts, pp 55–59
Humphries CC Jr (1978) Salt movement on continental slope, northern Gulf of Mexico. In: Bouma AH, Moore GT, Coleman JM (eds) Framework, Facies, and Oil Trapping Characteristics of the Upper Continental Margin. American Association Petroleum Geologists Studies in Geology 7:69–85
Jackson MPA, Talbot CJ (1989) Salt canopies, Gulf Section. In: Society of Society of Economics Paleontologists and Mineralogists Foundation 10th Annual Research Conference Program Abstracts, pp 72–78
Lee GH, Bryant WR, Watkins JL (1989) Salt structures and sedimentary basins in the Keathley Canyon area, northwestern Gulf of Mexico. Gulf Coast Section Society of Economics Paleontologists and Mineralogists Foundations 10th Annual Research Conference, pp 90–93
Lehner P (1969) Salt tectonic and Pleistocene stratigraphy on continental slope of northern Gulf of Mexico. American Association Petroleum Geologists Bulletin 53:2431–2479
Martin RG Jr (1980) Distribution of salt structures in the Gulf of Mexico. Map and descriptive text. U.S. Geological Survey, Map MF-1213
Martin RG, Bouma AH Jr (1978) Physiography of Gulf of Mexico. In: Bouma AH, Moore GT, Coleman JM (eds) Framework, Facies, and Oil Trapping Characteristics of the Upper Continental Margin. American Association Petroleum Geologists Studies in Geology 7:3–19
Moore DG, Curray JR (1963) Structural framework of the continental terrace, northwest Gulf of Mexico. Journal Geophysical Research 68:1725–1747
Shaub FJ, Buffler RT, Parsons JG (1984) Seismic stratigraphic framework of the deep central Gulf of Mexico basin. American Association Petroleum Geologists Bulletin 11:1–14
Watkins JS, Ladd JW, Buffler RT, Shaub FJ, Houston MH, Worzel JL (1978) Occurrence and evolution of salt in the deep Gulf of Mexico. In: Bouma AH, Moore GT, Coleman JM (eds) Framework, Facies, and Oil Trapping Characteristics of the Upper Continental Margin. American Association Petroleum Geologists Studies in Geology 7:43–65
Winker CD, Edwards MB (1983) Unstable progradational elastic shelf margins. Society Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists Special Publication 33:139–157
Worrall DM, Snelson S (1989) Evolution of the northern Gulf of Mexico, with emphasis on Cenozoic growth faulting and the role of salt. In: Bally AW, Palmer AR (eds) The Geology of North America—An Overview. Geological Society of America, Boulder, Colorado, pp 97–138
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bryant, W.R., Bryant, J.R., Feeley, M.H. et al. Physiographic and bathymetric characteristics of the continental slope, northwest Gulf of Mexico. Geo-Marine Letters 10, 182–199 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02431065
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02431065