Abstract
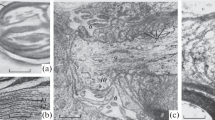
We investigated function and ultrastructure of sciatic nerves isolated from wood frogs (Rana sylvatica) endemic to the Northwest Territories, Canada, following freezing at −2.5 °C, −5.0 °C, or −7.5 °C. All frogs frozen at −2.5 °C, and most frogs (71%) frozen at −5.0 °C, recovered within 14 h after thawing began; however, frogs did not survive exposure to −7.5 °C. Sciatic nerves isolated from frogs frozen at −7.5 °C were refractory to electrical stimulation, whereas those obtained from frogs surviving exposure to −2.5 °C or −5.0 °C generally exhibited normal characteristics of compound action potentials. Frogs responded to freezing by mobilizing hepatic glycogen reserves to synthesize the cryoprotectant glucose, which increased 20-fold in the liver and 40-fold in the blood. Ultrastructural analyses of nerves harvested from frogs in each treatment group revealed that freezing at −2.5 °C or −5.0 °C had little or no effect on tissue and cellular organization, but that (lethal) exposure to −7.5 °C resulted in marked shrinkage of the axon, degeneration of mitochondria within the axoplasm, and extensive delamination of myelin sheaths of the surrounding Schwann cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 28 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costanzo, J., Allenspach, A. & Lee Jr., R. Electrophysiological and ultrastructural correlates of cryoinjury in sciatic nerve of the freeze-tolerant wood frog, Rana sylvatica. J Comp Physiol B 169, 351–359 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003600050231
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003600050231