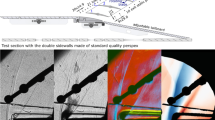
Abstract
The Flow Visualization Gun (FVG), a novel time line visualization technique, has been used to investigate the flow field of a helicopter rotor with swept back tip shape in hover flight condition. After introducing the FVG-technique, the paper presents some visualization photographs of the rotor blade tip vortices and the rotor downwash. Using orthogonal sets of flow photographs and digital image analysis, the 3-dimensional time line displacement within the flow and the tip vortex structure are determined. The data of 16 time line experiments are interpolated in space and time to obtain velocity data on an evenly spaced 3-dimensional grid. Vorticity contour plots of the flow field show the complex arrangement of the tip vortices of the blade itself and of the preceding blade and some additional vorticity in the direct wake which may form a secondary vortex. Understanding and control of this vorticity distribution is important for the design of new efficient tip shapes. While the FVG technique has been used so far for qualitative investigation of complex flow patterns at local velocities of up to 20 m/s, a good comparison to laser velocimetry data validates the technique as an interesting tool for both qualitative and quantitative investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohn IL; Nadig FH; Simmons WF (1964) Acceleration of small particles by means of exploding wires. Exploding Wires 3: New York: Plenum Press: 339–351
Chace WG (1959) Liquid behavior of exploding wires. The Physics of Fluids 2: 230–235
Favier D; Maresca C; Berton E; Plantin de Huges P (1991) Investigation of the tip shape influence on the flowfield around hovering rotor blades. AIAA 22nd Fluid Dynamics, Plasma Dyn. and Laser Conference, Honolulu, pp.
Lorber PF; Stauter RC; Landgrebe AJ (1989) A comprehensive hover test of the airloads and airflow of an extensively instrumented model helicopter rotor. Proceedings of the 45th AHS Annual Forum
Lorber PF; Stauter RCh; Haas RJ; Anderson TJ (1994) Techniques for comprehensive measurement of model helicopter rotor aerodynamics. Presented at the AHS 50th Annual Forum, Washington DC
Lusseyran D; Rockwell D (1988) Estimation of velocity eigenfunction and vorticity distributions from the time line visualization technique. Exp Fluids 6: 228–236
Müller RHG; Staufenbiel R (1987) The influence of winglets on rotor aerodynamics. Vertica 11: 601–618
Müller RHG; Steinhoff JS (1990) Application of a new visualization method to helicopter rotor flow. 8th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference, Portland, Oregon
Müller RHG (1990a) Visualization and measurement of helicopter rotor flow using projected smoke filaments and digital image processing. 16th European Rotorcraft Forum, Glasgow, Scotland
Müller RHG (1990b) Special vortices at a helicopter rotor blade. J Amer Helicopter Soc
Müller RHG; Favier D; NSI MBA M; Maresca C; Berton E (1994) Tip vortex development and structure at BVI for a hovering rotor with swept back tip shapes using the flow visualization gun technique. 20th European Rotorcraft Forum, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Philippe JJ; Roesch P; Dequin AM; Cler A (1985) A survey of recent development in rotor aerodynamics. AGARD LS 139, Braunschweig, Rome, St. Louis
Scherrer VE (1962) An exploding wire hypervelocity projector. Exploding Wires 2: New York: Plenum Press 235–244
Silva M; Favier D; Ramos J; Nsi Mba M; Berton E (1993) An experimental investigation of the drag mechanisms of a helicopter rotor in hovering flight. 19th European Rotorcraft Forum, Cernobbio (Como), Italy
Steinhoff JS (1985) A simple efficient method for flow measurement and visualization. Flow visualization III (Yang W, editor) Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, Springer-Verlag, pp. 19–24
Thompson TL; Kwon OJ; Kemnitz JL; Komerath NM; Gray RB (1987) Tip vortex core measurements on a hovering model rotor. AIAA 25th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, Nevada
Tsung FL; Liou SG; Komerath NM; Sankar LN (1990) Computation and measurement of the flowfield near a swept rotor blade tip in hover. 46th Annual Forum of the American Helicopter Society, Washington, DC
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was supported by a “Poste Rouge” grant by the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (C.N.R.S.). The authors would like to thank all members of the IRPHE for their help concerning the mechanical and electronical set up of the experiments.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, R.H.G., Mba, M.N., Aymard, E. et al. Visualization and measurement of helicopter rotor flow with swept back tip shapes at hover flight using the “flow visualization gun” time line technique. Experiments in Fluids 21, 161–169 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191687
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00191687