Abstract
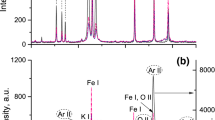
The effects of background gases on the optical emission of the excimer-laser-ablated plume from a brass target have been studied experimentally. It is found that the plume emission can be enhanced significantly in a proper gas ambient. In hydrogen, the highest peak intensity is detected, and in argon, there is a distinctive difference in the pressure-dependent emission between in He and in the other three gases, Ar, N2 and H2. Moreover, the monitored line peak intensity remains unchanged in Ar and N2 and increases in H2 within a distance above the target surface; but in He, the observed peak intensity decreases with distance like in vacuum. Furthermore, the emissions of several more atomic lines of Cu and Zn atoms from the plume are also found to be enhanced in the same manner in gas ambient. Some physical processes involved in the plume expansion and the possible mechanisms for the enhanced emission of the plume in backing gas are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.T. Chen, R.E. Russo: Spectrochim. Acta46B, 1471 (1991)
A. Quentmeier, W. Sdorra, K. Niemax: Spectrochim. Acta45B, 537 (1990)
K. Dittrich, R. Wennrich: Prog. Anal. Atom. Spectrosc.7, 139 (1984)
Y. Iida, A. Tsuge, Yoshinori, H. Maorikawa, T. Ishizuka: J. Anal. Atom. Spectrosc.6, 541 (1991)
Y. Iida: Spectrochim. Acta45B, 427 (1990)
Y. Iida: Appl. Spectrosc.43, 229 (1989)
Y. Iida: Spectrochim. Acta45B, 1353 (1990)
K. Kagawa, S. Yokoi, S. Nakajima: Opt. Commun.45, 261 (1983)
A.L. Lewes, II, E.H. Piepmeier: Appl. Spectrosc.37,523 (1983)
R.W. Dreyfus: J. Appl. Phys.69, 1721 (1991)
R. Kelly, R.W. Dreyfus: Surf. Sci.198, 263 (1988)
C.E. More:Atomic Energy Levels, vol. II (National Bureau of Standards, Washington, DC 1971)
Y.B. Zel'dovich, Y.P. Raizer:Physics of Shock Waves and High-Temperature Hydrodynamic Phenomena (Academic, New York 1967)
B.R. Finke, G. Simon: J. Phys. D23, 67 (1990)
A.D. Sappey, T.K. Gamble: J. Appl. Phys.72, 5095 (1992)
A.D. Sappey, T.K. Gamble: Appl. Phys. B53, 353 (1991)
R.M. Measures, P.G. Cardinal: Phys. Rev. A23, 804 (1981)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, H.P., Lou, Q.H., Cheung, N.H. et al. Experimental study of enhanced emission of the laser-ablated plume in backing gas. Appl. Phys. B 58, 143–148 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01082349
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01082349