Abstract
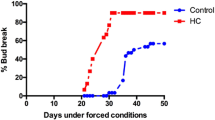
Axillary and apical buds of in-vitro-propagated cuttings of Cedrus libani are unable to burst at 24 °C, but this inhibition was overcome at 30 °C. Here we have used cedar microcuttings to investigate whether the levels of endogenous hormones vary with bud dormancy and temperature. We analysed the levels of abscisic acid, indole-3-acetic acid, zeatin, isopentenyladenine and their major metabolites using HPLC purification and fractionation of the samples coupled to an ELISA method for hormonal quantitation involving several antibodies elicited against each hormonal family. Abscisic acid levels in microcuttings with dormant buds were higher than those in microcuttings with growing buds. At 24 °C, needles accumulated more abscisic acid than at 30 °C. In addition, when needles were removed, but growth release was achieved at 24 °C. Abscisic acid supplied at 30 °C induced the formation of dormant buds. These results suggest that abscisic acid accumulation in the needles can explain the bud dormancy of cedar microcuttings at 24 °C.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 November 1997 / Revision received: 16 January 1998 / Accepted: 5 May 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piola, F., Label, P., Vergne, P. et al. Effects of endogenous ABA levels and temperature on cedar (Cedrus libani Loudon) bud dormancy in vitro. Plant Cell Reports 18, 279–283 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050571
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050571