Abstract
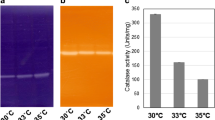
The latency phase, growth rate, cell yield and end-products of Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis CB1 were affected by oxygen and the supply of 225 μM Mn2+. Mn2+ was especially related to the highest substrate consumption. Aerobiosis and Mn2+ supply were responsible for the highest superoxide dismutase activity. An auto-inhibitory accumulation of H2O2 meant that the survival of air-grown cells supplied with Mn2+ rapidly decreased during the stationary phase. As shown by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, Mn2+ supply influenced protein expression. As shown by non-denaturating zymograms, Lb. sanfranciscensis CB1 expressed an approximately 12.5-kDa superoxide dismutase, which is probably Mn-dependent. The enzyme was insensitive to H2O2 treatment, was not induced by the presence of paraquat under aerobic conditions and was relatively stable at pH 4.0. Sourdoughs that contained high levels of oxygen enhanced cell growth, acidification and acetic acid production by Lb. sanfranciscensis CB1.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 July 1998 / Received last revision: 11 November 1998 / Accepted: 13 November 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Angelis, M., Gobbetti, M. Lactobacillus sanfranciscensis CB1: manganese, oxygen, superoxide dismutase and metabolism. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51, 358–363 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051402
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051402