Abstract
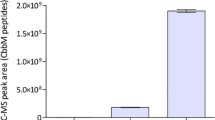
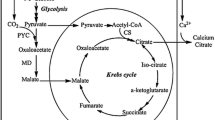
The methylotrophic yeast Hansenula polymorpha has been developed as an efficient production system for heterologous proteins. The system offers the possibility to cointegrate heterologous genes in anticipated fixed copy numbers into the chromosome. As a consequence coproduction of different proteins in stoichiometric ratios can be envisaged. This provides options to design this yeast as an industrial biocatalyst in procedures where several enzymes are required for the efficient conversion of a given inexpensive compound into a valuable product. To this end recombinant strains have been engineered with multiple copies of expression cassettes containing the glycolate oxidase (GO) gene from spinach and the catalase T (CTT1) gene from S. cerevisiae. The newly created strains produce high levels of the peroxisomal glycolate oxidase and the cytosolic catalase T. The strains efficiently convert glycolate into glyoxylic acid, oxidizing the added substrate and decomposing the peroxide formed during this reaction into water and oxygen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 31 October 1995/Received last revision: 23 February 1996/Accepted: 4 March 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gellissen, G., Piontek, M., Dahlems, U. et al. Recombinant Hansenula polymorpha as a biocatalyst: coexpression of the spinach glycolate oxidase (GO) and the S. cerevisiae catalase T (CTT1) gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46, 46–54 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530050781
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530050781