Abstract
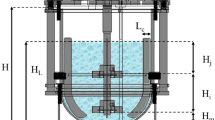
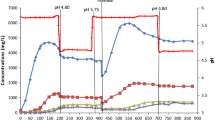
The influence of enhanced O2 concentration on growth and formation of secondary metabolites byStreptomyces griseoflavus (strain Tü 2880) was investigated in a stirred tank and in an air-lift fermentor. At a partial pressure of O2 po2 = 1880 mbar the growth was lowered by 50% compared to po2 = 210 mbar, whilst substrate consumption and O2 uptake rate increased markedly. Production of the colabomycin complex reached maximum values at po2 = 630 mbar. A similar increase of secondary metabolite formation was obtained when glycerol or acetate were fed at po2 = 220 mbar. The portion of the derivate colabomycin A in the product mixture rose from 43% at po2 = 210 mbar to 73% at po2 = 1260 mbar. Since dissolved O2 concentration has a significant influence on productivity and selectivity it may be used to regulate aerobic fermentation processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buse R (1992) Scale-down aerober Bioprozesse am Beispiel der fermentativen Herstellung von Gluconsäure und Ketogluconsäuren. Fortschritt-Berichte VDI-Reihe 17, VDI-Verlag Düsseldorf
Ceriotti G (1952) A microchemical determination of desoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem 198:297–303
Clark DS, Lentz CP (1961) Submerged citric acid fermentation of sugar beet molasses: effect of pressure and recirculation of oxygen. Can J Microbiol 7:447–453
Grote R, Zeeck A, Drautz H, Zähner H (1988a) Metabolic products of micro-organisms. 244 Colabomycins, new antibiotics of the manumycin group fromStreptomyces griseoflavus. I. Isolation, characterization and biological properties. J Antibiot 41:1178–1185
Grote R, Zeeck A, Beale M (1988b) Metabolic products of micro-organisms. 245 Colabomycins, new antibiotics of the manumycin group fromSreptomyces griseoflavus II. Structure of colabomycin A. J Antibiot 41:1186–1195
Kaiser D, Onken U, Sattler I, Zeeck A (1993) Influence of increased dissolved oxygen concentration on the formation of secondary metabolites by manumycin-producingStreptomyces parvulus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35:in press
Larsson G, Enfors EO (1988) Studies on insufficient mixing in bioreactors: effects of limiting oxygen concentration and short term oxygen starvation onPenicillium chrysogenum. Bioproc Eng 3:123–127
Liefke E (1988) Kultivierung aerober Bakterien bei erhöhtem Sauerstoffpartialdruck als verfahrenstechnische Möglichkeit zur Beeinflussung von Wachstum und Produktbildung. Ph.D. thesis. Universität Dortmund
Liefke E, Kaiser D, Onken U (1990) Growth and product formation of actinomycetes cultivated at increased total pressure and oxygen partial pressure. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 32:674–679
Onken U, Dick O (1993) Influence of increased oxygen concentration on microbial growth and formation of secondary metabolites. In: Anke T, Onken U (eds) Wege zu neuen Produkten und Verfahren der Biotechnologie (DECHEMA monograph, vol 129) VCH, Weinheim, pp 73–84
Onken U, Liefke E (1989) Effect of total and partial pressure (oxygen and carbon dioxide) on aerobic microbial processes. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 40: 137–169
Onken U, Kiese S, Jostmann T (1984) An airlift fermenter for continuous cultures at elevated pressures. Biotechnol Lett 6:283–288
Sattler I (1992) Voräufer-dirigierte Biosynthese und Fermentation unter erhöhtem Sauerstoffpartialdruck — Isolierung und Strukturaufklärung neuer Verbindungen aus der Manumycingruppe. Doctoral Thesis, University of Göttingen
Sattler I, Gröne C, Zeeck A (1993) New compounds of the manumycin group of antibiotics and a facilitated route for their structure elucidateion. J Org Chem 58:in press
Träger M, Müller U, Onken U (1987) Einfluss erhöhter Sauerstoffpartialdrücke auf die Bildung von Gluconsäure durchGluconobacter oxydans. Chem Ing Tech 59: 939–940
Vardar F, Lilly MD (1982) Effect of cycling dissolved oxygen concentrations on product formation in penicillin productions. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 14:203–211
Wesselmann E (1991) Einfluss der Gelöstsauerstoffkonzentration und der hydrodynamischen Bedingungen auf Wachstum und Sekundärmetabolismus von Ascomyceten und Basidiomyceten. Doctoral Thesis, University of Dortmund
Zeeck A, Schröder K, Grote R, Thiericke R (1987) The structure of manumycin. J Antibiot 40: 1530–1540
Zeeck A, Sattler I, Boddien C (1993) New manumycin-type compounds by precursor-directed biosynthesis and by cultivation under increased oxygen concentration. In: Anke T, Onken U (eds) Wege zu neuen Produkten und Verfahren der Biotechnologie (DECHEMA monograph, vol 129) VCH, Weinheim, pp 85–95
Zhou W, Holzhauer-Rieger K, Dors M, Schügerl K (1992) Influence of dissolved oxygen concentration on the biosynthesis of cephalosporin C. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 14:848–854
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dick, O., Onken, U., Sattler, I. et al. Influence of increased dissolved oxygen concentration on productivity and selectivity in cultures of a colabomycin-producing strain ofStreptomyces griseoflavus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 373–377 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00939022
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00939022