Summary
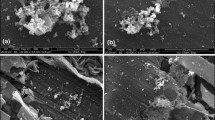
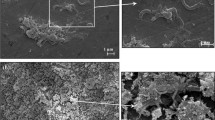
This communication reports the presence of polysaccharides in biofilms formed by pure and mixed cultures of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans and Pseudomonas fluorescens on mild and stainless steel surfaces. The results of colorimetric assays, indicating significant differences between the amounts of neutral sugars present in these biofilms, were supported by gas chromatographic (GC)-mass spectrophotometric and GC-flame ionisation detection analyses. Neutral sugars in biofilms grown on mild steel surfaces were identified and quantified, revealing glucose as a major carbohydrate followed by mannose and galactose in all types of biofilm. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) precipitated from bacterial cultures grown with and without steel surfaces were also analysed for their carbohydrate content. The influence of the surfaces present in the cultures on the amount and type of sugars released into the bulk phase was established. There was significantly more carbohydrate in EPS harvested from pure and mixed cultures of D. desulfuricans incubated mild and stainless steel coupons than in EPS obtained from coupon-free cultures. No significant difference in sugar quantities was observed in EPS precipitated from cultures of P. fluorescens grown under different conditions (absence or presence of steel surfaces). The main carbohydrates identified in all types of EPS samples were mannose, glucose and galactose in order of prevalence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beech IB, Gaylarde CC (1989) Adhesion of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans and Pseudomonas fluorescens to mild steel surfaces. J Appl Bacteriol 67:201–207
Blumenkrantz N, Asboe-Hansen G (1973) New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem 54:484–489
Corpe WA (1970) An acid polysaccharide produced by a primary film-forming marine bacterium. Dev Ind Microbiol 2:402–412
Corpe WA (1975) Metal binding properties of surface materials from marine bacteria. Dev Ind Microbiol 16:249–259
Costerton JW (1987) Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol 41:435–464
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:1151–1159
Fazio SA, Uhlinger DJ, Parker JH, White DC (1982) Estimations of uronic acids as quantitative measures of extracellular and cell wall polysaccharide polymers from environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:1151–1159
Ford TE, Maki JS, Mitchell R (1988) Involvement of bacterial expolymers in biodeterioration of metals. In: Houghton DR, Smith RN, Eggins HOW (eds) Biodeterioration 7, Proceedings of the Seventh International Biodeterioration Symposium, Cambridge, June 1987. Elsevier Applied Science, Barking, UK, pp 378–384
Gaylarde CC, Beech IB (1989) Bacterial polysaccharides and corrosion. In: Gaylarde CC, Morton LHG (eds) Biocorrosion: Biodeterioration Society, Kew, UK, pp 85–98
Gaylarde CC, Johnston JM (1980) The importance of microbial adhension in anaerobic metal corrosion. In: Berkeley RCW, Lynch JM, Melling J, Rutter PR, Vincent B (eds) Microbial adhesion to surfaces. Ellis Horwood, Chichester, pp 511–513
Gaylarde CC, Videla HA (1987) Localised corrosion induced by a marine vibrio. Int Biodeterior 23:91–104
Geesey GG, Jang L, Jolley JG, Hankins MR, Iwaoka T, Griffiths PR (1988) Binding of metal ions by extracellular polymers of biofilm bacteria. Water Sci Technol 20:161–165
Hamilton WA (1985) Sulfate reducing bacteria and anaerobic corrosion. Annu Rev Microbiol 39:195–217
Iverson WP (1987) Microbial corrosion of metals. Adv Appl Microbiol 32:1–36
Jolley JG, Geesey GG, Hankins MR, Wright RB, Wichlacz PL (1988) Auger electron spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of the biocorrosion of copper by gum arabic, bacterial culture supernatant and Pseudomonas atlantica exopolymer. Surface Interface Anal 11:371–376
Kennedy AFD, Sutherland IW (1987) Analysis of bacterial ecopolysaccharides. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 9:12–19
Moreno DA, Ibars JR, Beech IB, Gaylarde CC (1990) Biofilm formation on mild steel coupons by Pseudomonas fluorescens and Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Biofouling (in press)
Ochynski FW, Postgate JR (1963) Some biological differences between fresh water and salt water strains of sulphate-reducing bacteria. In: Oppenheimer CH (ed) Marine microbiology. Thomas, Springfield, Ill., pp 426–441
Postgate JR (1984) The sulphate-reducing bacteria. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Quintero E, Ishida K, Gordon G, Geesey GG (1990) Comparison of reduction methods for gas chromatographic/mass spectrinetric identification and quantification of uronic acids in acid polysaccharides. J Microbiol Methods 9:309–322
Read RR, Costerton JW (1987) Purification and characterisation of adhesive exopolysaccharides from Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Can J Microbiol 33:1080–1090
Tiller AK (1983) Electrochemical aspects of corrosion: an overview. In: Microbial corrosion. Metals Society, London, UK, pp 54–65
White DC, Nivens DE, Nichols PD, Kerger BD, Henson JM, Geesey GG, Clarke CK (1985) The role of extracellular polymers in microbial adhesion and corrosion. In: Proceedings of the International Workshop on Biodeterioration, University of La Plata, Argentina, March 1985. Aquatec Quimica, São Paulo, pp 73–86
White DC, Nivens DE, Nichols PD, Mikell AT, Kerger BD, Henson JM, Geesey GG, Clarke CK (1986) Role of aerobic bacteria and their extracellular polymers in the facilitation of corrosion; use of fourier transforming infrared spectroscopy and ‘signature’ fatty acid analysis. In: Biologically induced corrosio n. National Assoc. of Corrosion Engineers-8, Houston, Tex., pp 233–243
York WS, Darvill AG, McNeil M, Stevenson TT, Albersheim P (1985) Isolation and characterisation of plant cell walls and cell wall components. Methods Enzymol 118:3–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: I. B. Beech
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beech, I.B., Gaylarde, C.C., Smith, J.J. et al. Extracellular polysaccharides from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans and Pseudomonas fluorescens in the presence of mild and stainless steel. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 35, 65–71 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180638
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180638