Summary
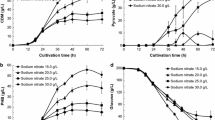
Agrobacterium radiobacter NCIB 11 883 does not produce gluconate under conditions of glucose excess in batch or continuous culture. However, the addition of micromolar concentrations of pyrrolo quinoline quinone (PQQ) to fermentation media resulted in rapid excretion of gluconate by batch and continuous cultures. This rapid dehydrogenation of glucose was found in cells grown under carbon and nitrogen limitation and is constitutive which suggests that the only reason why this activity is not normally expressed is due to the inability of the organism to synthesize the prosthetic group (PQQ) of the glucose dehydrogenase enzyme.
Although the addition of PQQ to batch and continuous cultures caused a very rapid specific rate of gluconate production (0.6–1.1 g gluconate g-1 dry wt. h-1) the rate of exopolysaccharide production remained unaltered. Indeed, when the rates of substrate and oxygen uptake are corrected for the rate of gluconate production in the presence of PQQ there appears to be little physiological consequence as a result of this oxidation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bont JAM de, Dokter P, van Schie BJ, Frank J, Duine J, Keunen JG (1984) Role of quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase in gluconic acid production by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. J Microbiol Serol 50:76–77
Duine JA, Frank J (1981) Quinoproteins a novel class of dehydrogenases. Trends Biochem Sci 6:278–280
Hommes RWJ, Postma PW, Neijssel OM, Tempest DW, Dokter P, Duine JA (1984) Evidence of a quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase apoenzyme in several strains Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 24:329–333
Hommes RWJ, van Hell B, Postma PW, Neijssel OM, Tempest DW (1985) The functional significance of glucose dehydrogenase in Klebsiella aerogenes. Arch Microbiol 143:163–168
Linton JD, Austin RM, Haugh DE (1984) The kinetics and physiology of stipitatic acid and gluconate production by carbon sufficient cultures of Penicillium stipitatum growing in continuous culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 26:1455–1464
Midgley M, Daws EA (1973) The regulation of glucose and methyl-glucoside in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem J 132:141–154
van Schie BJ, van Dijken JP, Kuenen JG (1984) Non-coordinated synthesis of glucose dehydrogenase and its prosthetic group PQQ in Acinetobacter and Pseudomonas species. FEMS Microbiol Lett 24:133–138
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linton, J.D., Woodard, S. & Gouldney, D.G. The consequence of stimulating glucose dehydrogenase activity by the addition of PQQ on metabolite production by Agrobacterium radiobacter NCIB 11883. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 25, 357–361 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252547
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252547