Abstract
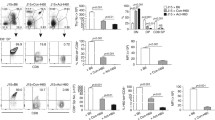
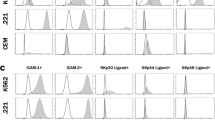
Previously we have reported that two sublines of the YAC lymphoma selected for reduced expression of H-2a and Moloney-virus determined cell-surface (MCSA) antigens are, in contrast to YAC, allotransplantable in H-2-incompatible recipients, and resistant to rejection by preimmunized semisyngeneic hosts. A third YAC variant with reduced MCSA but unchanged H-2-antigen expression, was not allotransplantable and showed only a slight decrease in its immunosensitivity in preimmunized semisyngeneic hosts in vivo. This suggested that H-2-antigen expression may be more important than MCSA expression for recognition and rejection by semisyngeneic mice. We have now tested the sublines expressing low H-2a for their in vitro sensitivity to humoral and cell-mediated lysis. — The variants were more resistant than YAC to complement lysis by anti-H-2a, anti-MCSA, anti-Thy 1.2 and antispecies sera. Absorption tests with antispecies serum indicated that the decreased cytolytic sensitivity of the variants was not related to the concentration of the relevant antigens, which was similar to that of the original YAC tumor. As expected from the low amount of H-2a the variants showed a decreased sensitivity to the killing effect of allogeneic cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL). They were also lysed to a lesser extent than YAC by semisyngeneic CTL, probably directed against virally determined antigens. However, they were also less sensitive to lysis by natural killer (NK) cells, although NK lysis is probably unrelated to MHC expression. In conclusion, our selection for reduced H-2-expression appears to have resulted in the isolation of variants with a generally increased resistance to various humoral and cell-mediated lytic functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ährlund-Richter, L., Klein, E., and Masucci, G.: Somatic hybrids between a high NK-sensitive lymphoid (YACIR) and several low sensitive sarcoma or L-cell-derived mouse lines exhibit low sensitivity.Somatic Cell Gen. 6: 89–99, 1980
Becker, S., Fenyö, E. M., and Klein, E.: The “natural killer” cell in the mouse does not require H-2 homology and is not directed against type or group specific antigens of murine C viral proteins.Eur. J. Immunol. 6: 882–885, 1976
Becker, S., Kiessling R., Lee, N., and Klein, G.: Modulation of sensitivity to natural killer cells lysis after in vitro explanation of a mouse lymphoma.J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 61: 1495–1498, 1978
Dalianis, T., Klein, G., and Andersson, B.: Column selection of antigenic variants from tumors. YAC (Moloney) lymphoma variants with reduced antigen expression.Immunogenetics 9: 465–475, 1979
Fenyö, E. M., Klein, E., Klein, G., and Swiech, K.: Selection of an immunoresistent Moloney lymphoma subline with decreased concentration of tumor-specific antigens.J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 40: 69–89, 1968
Klein, E. and Klein, G.: Antigenic properties of lymphoma induced by the Moloney agent.J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 32: 547–568, 1964
Klein, P. A.: Anomalous reactions of mouse alloantisera with cultured tumor cells. I. Demonstration of widespread occurence using typing sera.J. Immunol. 115: 1254–1260, 1975
Lerner, R. A., Oldstone, M. B. A., and Cooper, N. R.: Cell cycle-dependent immune lysis of Moloney virus transformed lymphocytes: Presence of viral antigen, accessibility to antibody and complement activation.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 68: 2584–2588, 1971
Meruelo, D.: A role for elevated H-2 antigen expression in resistance to neoplasia caused by radiation-induced leukemia virus.J. Exp. Med. 149: 898–909, 1979
Nowinski, R. C. and Klein, P. A.: Anomalous reactions of mouse alloantisera with cultured tumor cells. II. Cytotoxicity caused by antibodies to leukemia viruses.J. Immunol. 115: 1261–1268, 1975
Witz, I. P., Lee, N., and Klein, G.: Serologically detectable and cross-reactive antigens on the membrane of a polyoma virus induced murine tumor.Int. J. Cancer. 18: 243–249, 1976
Zinkernagel, R. M. and Doherty, P. C.: H-2 compatibility requirement for T-cell mediated lysis of target cells injected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Different cytotoxic T-cell specificities are associated with structures, coded for in H-2K or H-2D.J. Exp. Med. 149: 898–909, 1975
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
On leave from Instituto Venezolano de Investigaciones Cientificas (IVIC), Caracas, Venezuela.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalianis, T., Ährlund-Richter, L., Merino, F. et al. Reduced humoral and cellular cytotoxic sensitivity in major histocompatibility variants of the YAC (Moloney) lymphoma. Immunogenetics 12, 371–380 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01561677
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01561677