Abstract
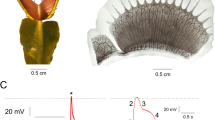
A superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) multichannel magnetometer was used to measure the temporal and spatial evolution of the magnetic field accompanying stimulation by burning and/or cutting of Vicia faba plants. These magnetic fields are caused by ionic currents that appear after injury in different parts of the plant. All measured V. faba plants responded to the burning stimulation with detectable quasi-d.c. magnetic signals. In order to measure these signals, a suitable modulation had to be used. The covariance method was applied to analyse the measured data. The results demonstrate a dipolar-like magnetic signal, exponentially decreasing in time, above the cutting type of injury. After the burning stimulation, the magnetically detected activity was concentrated predominantly above the leaves/petioles and less above the stem. Possible mechanisms for this behaviour are suggested. A comparison with previously known electrical measurements of plant injury is given.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Revised version: 16 August 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jazbinsek, V., Thiel, G., Müller, W. et al. Magnetic detection of injury-induced ionic currents in bean plants. Eur Biophys J 29, 515–522 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002490000105
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002490000105