Summary
Influence of food on the serum concentration and kinetics ambenonium chloride (AMBC) has been examined in thirteen patients with myasthenia gravis (MG).
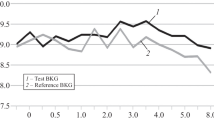
Mean serum concentrations and Cmax during fasting were higher than those in the non-fasting state. The AUC (0–3 h) was also about four-times larger.
The drug effects versus the serum concentration were observed to be anti-clockwise or clockwise. The effective range of the Cmax varied between patients. The unexpected increase in Cmax led to adverse muscarinic actions of AMBC, when the condition was changed from the non-fasting to the fasting state.
It is recommended that the dose be changed during non-fasting treatment when adjusting the optimum regimen for patients myasthenia gravis. Patients must be advised to keep to the dosing and dietary schedule in order to avoid unexpected adverse actions to AMBC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohtsubo K, Higuchi S, Aoyama T, Fujii N, Goto I (1989) Sensitive determination of ambenonium chloride in serum from patients with myasthenia gravis using ion-exchange resin extraction and reversed-phase ion-pair chromatography. J Chromatogr 496: 397–406
Yamaoka K, Nakagawa T, Uno T (1978) Statistical moments in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 6: 547–558
Aquilonius SM, Eckenrnas SA, Hartvig P, Lindstrom B, Osterman PO (1980) Pharmacokinetics and oral bioavailability of pyridostigmine in man. Eur J Pharmacol 18: 423–428
Sorensen PS, Flachs H, Friis ML, Hvidberg EF, Paulson O (1984) Steady state kinetics of pyridostigmine in myasthenia gravis. Neurology 34: 1020–1024
Breyer-Pfaff U, Maier U, Brinkmann AM, Schumm F (1985) Pyridostigmine kinetics in healthy subjects and patients with myasthenia gravis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 37: 495–501
Levine RR, Blair MR, Clark BB (1955) Factors influencing the intestinal absorption of certain monoquaternary anticholinergic compounds with special reference to benzomethamin [N-diethylaminoethyl-N′-methyl-benzilamide methobromide]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 114: 78–86
Levine RR (1966) Mechanism of intestinal absorption, as they relate to quaternary ammonium compounds. Arzneimittel-Forsch 16: 1373–1375
Saitoh H, Hasegawa N, Kawai S, Miyazaki K, Arita T (1986) Interaction of tertiary amines and quaternary ammonium compounds with gastrointestinal mucin. J Pharmacobio-Dyn 9: 1008–1014
Saitoh H, Kawai S, Miyazaki K, Arita T (1988) Transport characteristics of propantheline across rat intestinal brush border membrane. J Pharm Pharmacol 40: 176–180
Chan K, Calvey TN (1987) Plasma concentration of pyridostigmine and effecsin myasthenia gravis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 22: 596–601
Davison SC, Hyman NM, Dehghan A, Chan K (1981) The relationship of plasma levels of pyridostigmine to clinical effect in patients with myasthenia gravis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 44: 1141–1145
Aquilonius SM, Eckernas SA, Hartvig P, Lindstrom B, Osterman P, Stalberg E (1983) Clinical pharmacology of pyridostigmine and neostigmine in patients with myasthenia gravis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46: 929–935
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohtsubo, K., Fujii, N., Higuchi, S. et al. Influence of food on serum ambenonium concentration in patients with myasthenia gravis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 42, 371–374 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280120
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280120