Summary
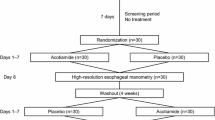
Nifedipine has been proven to be effective and safe in the treatment of primary oesophageal motility disorders which can cause angina-like chest pain and/or dysphagia. The effects of the calcium channel blockers nifedipine, nitrendipine, nimodipine and nisoldipine on oesophageal smooth muscle function in healthy male volunteers were studied by oesophageal manometry using the rapid pull-through-technique, in two randomized, double-blind crossover studies.
Lower oesophageal sphincter pressure, oesophageal contraction amplitude and duration after a wet swallow (measured 5 cm and 10 cm above the lower oesophageal sphincter) were determined 30 min before and at 10 minute intervals up to 90 min after the administration of nimodipine and up to 120 min after nifedipine, nitrendipine and nisoldipine. The plasma drug concentration was measured at baseline (−15 min) and in parallel with the manometric measurements.
Compared to placebo, lower oesophageal sphincter pressure was significantly decreased by 24% by nifedipine and 17% by nimodipine, whereas the effects of nitrendipine (decrease of 15%) and nisoldipine (9%) were not significant. Nifedipine significantly decreased by 17% the oral contraction amplitude compared to placebo and nimodipine by 11%. The duration of the contraction amplitudes was not altered. The decrease in sphincter pressure was correlated with the corresponding plasma drug levels of nifedipine r=0.92, nitrendipine r=0.80 and nisoldipine r=0.79. Nimodipine showed no such correlation.
It is concluded that among the calcium antagonists studied, nifedipine exerted the strongest effect on oesophageal smooth muscle function, so it appears to be the most suitable compound for the treatment of primary motor abnormalities of the oesophagus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mellow MH (1982) Effect on isosorbite and hydralazine in painful primary oesophageal motility disorders. Gastroenterology 83: 364–370
Swamy N (1977) Oesophageal spasm: clinical and manometric response to nitro-glycerine and long acting nitrates. Gastroenterology 72: 23–27
Weiser HF, Lepsien G, Golenhofen K, Schattenmann G, Siewert R (1977) Klinische und experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Wirkung von Nifedipin auf die glatte Muskulatur des Ösophagus. Z Gastroenterol 15: 691–698
Blackwell JN, Holt S, Heading RC (1981) Effect of nifedipine on oesophageal motility and gastric emptying. Digestion 21: 50–56
Baunack AR, Demol P, Weihrauch TR (1985) Placebo-controlled comparison of the efficacy of the calcium antagonists BAY 1 8201 and nifedipine on the lower oesophageal sphincter pressure in volunteers. Gastroenterology 88: 1319
Nasrallah SM, Backhaus E (1983) Manometric and clinical response to the oesophagus to nifedipine in oesophageal disorders. Gastroenterology 84: (abstr.) 1256
Richter JE, Dalton CB, Buice RG, Castell DO (1985) Nifedipine: a potent inhibitor of concentrations in the body of the human oesophagus. Studies in healthy volunteers and patients with nutcracker oesophagus. Gastroenterology 89: 549–554
Richter JE, Dalton CB, Bradley LA, Castell DO (1987) Oral nifedipine in the treatment of noncardiac chest pain in patients with the nutcracker oesophagus. Gastroenterology 93: 21–28
Ke MY, Oertel R, McCallum RW (1985) The effects of the calcium channel blocker nisoldipine (NS) and the calcium channel agonist BAY 8644 on oesophageal smooth muscle in the cat. Gastroeneterlogy 88: 1441
Weihrauch TR (1981) Oesophageal manometry. Methods and clinical practice. Urban and Schwarzenberg. Baltimore Munich, pp 64–67
Rämsch K-D, Graefe K-H, Scherling D, Sommer J, Ziegler R (1986) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of calcium-blocking agents nifedipine, nitrendipine and nimodipine. Am J Nephrol 6 [Suppl 1]: 73–80
van Harten J, Lodewijks MThM, Guyt-Scholten JW, van Brummelen P, Breimer DD (1987) Gas chromatographic determination of nisoldipine and one of its metabolites in plasma. J Chromatogr Biomed Appl 423: 327–333
Hongo M, Traube M, McAllister RG jr, McCallum RW (1984) Effects of Nifedipine on oesophageal motor function in humans: Correlation with plasma Nifedipine concentration. Gastroenterology 86: 8–12
Baunack AR, Weihrauch TR (1989) Comprehensive analysis of the efficacy of nifedipine in oesophageal motor disturbances causing angina-like chest pain and/or dysphagia. Hepato Gastroenterol 36: 296 (P26)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konrad-Dalhoff, I., Baunack, A.R., Rämsch, K.D. et al. Effect of the calcium antagonists nifedipine, nitrendipine, nimodipine and nisoldipine on oesophageal motility in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 41, 313–316 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314958
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00314958