Summary
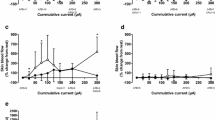
The effect of captopril on skin response to intradermal injection of bradykinin was investigated by laser Doppler flowmetry (LDF) and weal and flare measurements in this randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over balanced study. Intradermal injections of 1 and 2.5 µg of bradykinin and normal saline were made into the forearm skin of six healthy volunteers between 1 and 2 h (t1) and between 3 and 4 h (t2) after either 25 mg captopril or placebo. Skin blood flow outside the induced weal was monitored continuously by LDF for 15 min and the mean LDF values over the last 15 s were used for analysis. Weal and flare sizes were measured at 15 min.
On the placebo days, the mean LDF output, weal volume and flare area increased with incremental bradykinin dose. Pre-treatment with captopril significantly increased LDF output following intradermal bradykinin at t1 but not at t2. At both t1 and t2, captopril significantly increased weal volume. There was no significant difference between treatments in flare areas. Skin response following intradermal normal saline, measured by the above parameters, was not affected by captopril.
This study showed that captopril potentiated the effects of intradermal bradykinin both with respect to blood flow changes and weal formation. The non-invasive technique of LDF can be used to detect the skin blood flow changes induced by intradermal bradykinin and the potentiation of this effect by captopril. It appears to be a useful and more objective method of quantifying local cutaneous blood flow changes than measurement of flare area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferner RE, Simpson JM, Rawlins MD (1987) Effects of intradermal bradykinin after inhibition of angiotensin converting enzyme. Br Med J 294: 1119–1120
Fuller RW, Warren JB, McCusker M, Dollery CT (1987) Effect of enalapril on the skin response to bradykinin in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 23: 88–90
Soter NA, Lewis RA, Corey EJ, Austen KR (1983) Local effects of leukotrienes (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4 and LTB4) in human skin. J Invest Dermatol 80: 115–119
Stern M (1975) In vivo evaluation of microcirculation by coherent light scattering. Nature 254: 56–58
Holloway GA, Watkins DW (1977) Laser Doppler measurement of cutaneous blood flow. J Invest Dermatol 69: 306–309
Bisgaard H, Kristensen JK (1984) Quantitation of microcirculatory blood flow changes in human cutaneous tissue induced by inflammatory mediators. J Invest Dermatol 83: 184–187
Serup J, Staberg B (1985) Quantification of weal reactions with laser Doppler flowmetry. Allergy 40: 233–237
Hovell CJ, Beasley CRW, Mani R, Holgate ST (1987) Laser Doppler flowmetry for determining changes in cutaneous blood flow following intradermal injection of histamine. Clin Allergy 17: 469–479
Almond NE (1987) A fibre-optic laser Doppler flowmeter system and its application to the study of the skin microcirculation in humans. Ph. D. thesis; University of London, Faculty of Science
Cook J, Shuster S (1980) Histamine weal formation and absorption in man. Br J Pharmacol 69: 579–585
Regoli D, Barabe J (1980) Pharmacology of bradykinin and related peptides. Pharmacol Rev 32: 1–46
Serup J (1984) Diameter, thickness, area and volume of skin prick histamine weals. Measurement of skin thickness by 15 MHz A-mode ultrasound. Allergy 39: 359–364
Johnson MG, Hay JB, Movat HZ (1976) The modulation of enhanced vascular permeability by prostaglandins through alterations in blood flow (hyperemia). Agents Actions 6: 705–711
Holloway GA (1980) Cutaneous blood flow responses to injection trauma measured by laser Doppler velocimetry. J Invest Dermatol 74: 1–4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li Kam Wa, T.C., Almond, N.E., Cooke, E.D. et al. Effect of captopril on skin blood flow following intradermal bradykinin measured by laser Doppler flowmetry. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 37, 471–475 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558126
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558126