Summary
The effects on renal hemodynamics and salt-water handling of equipotent doses of the cardioselective β-blocker metoprolol (M, 100 mg) and of the non-selective (intrinsic sympathetic activity) β-antagonist pindolol (P, 10 mg) were compared in 30 WHO Grade 1–2 hypertensive men.
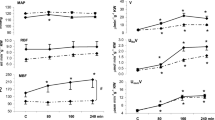
M lowered pulse rate more than P. Systolic pressure was equally reduced by both agents, and diastolic and mean pressures were decreased only after P. Glomerular filtration rate was not significantly altered by either antagonist, and renal blood flow decreased by approximately 11% both after M and P. Renal vascular resistance was unchanged after P, and was increased by 10% after M.
It is concluded that, like the effects on central haemodynamics, ISA is more important in the renal response to β-adrenoceptor blockade than is β-receptor selectivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atterhög JH, Duner H, Pernow B (1977) Haemodynamic effects of pindolol in hypertensive patients. Acta Med Scand 606 [Suppl]: 55–62
Brater DC, Anderson SA, Kaplan NM, Ram CVS (1983) Effects of atenolol, nadolol and propranolol on renal hemodynamics. NZ Med J 96: 833–836
Britton KE, Nimmon CC, Nawaz MK, Gruenewald SM (1983) Intrarenal blood flow in essential hypertension. NZ Med J 96: 839–841
Koch G, Franz J-W, Gubba A, Lohmann FW (1983) Beta-adrenoceptor blockade and physical activity: Cardiovascular and metabolic aspects. Acta Med Scand 672 [Suppl]: 55–62
Ljungman S, Aurell M, Hartford M, Wikstrand J, Berglund G (1982) Blood pressure in relation to the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Acta Med Scand 211: 351–60
Lund-Johansen P (1983) Central hemodynamic effects of β-blockers in hypertension. A comparison between atenolol, metoprolol, timolol, penbutolol, alprenolol, pindolol and bunitrolol. Eur Heart J 4 [Suppl]: D1-D12
Malini PL, Strocchi E, Negroni S, Ambrosioni E, Magnani B (1982) Renal hemodynamics after chronic treatment with labetalol and propranolol. Br J Clin Pharmacol 13 [Suppl 1]: 123S-126S
Malini PL, Strocchi E, Ambrosioni E (1983) Comparison of the effects of timilol and propranolol on renal hemodynamics. NZ Med J 96: 892–893
Malini PL, Strocchi E, Ambrosioni E (1983) The effects of mepindolol on renal hemodynamics. NZ Med J 96: 893–895
Malini PL, Strocchi E, Ambrosioni E, Magnani B (1983) The effects of a beta-blocker (propranolol), and alpha-/beta-blocker (labetalol) and a beta-blocker with vasodilating activity (prizidolol) on renal hemodynamics at rest and during exercise. NZ Med J 96: 890–891
Snedecor GW (1967) Statistical methods, 6th edn. The Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa
Thurau K (1964) Renal hemodynamics. Am J Med 36: 698–719
Wainer E, Boner G, Rosenfeld JB (1980) Effects of pindolol on renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther 28: 575–580
Weber MA, Drayer JIM (1980) Renal effects of beta-adrenoceptor blockade. Kidney Int 18: 686–699
Wilkinson R (1982) β-blockers and renal function. Drugs 23: 195–206
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koch, G., Fransson, L., Karlegärd, L. et al. Responses of glomerular filtration, renal blood flow and salt-water handling to acute cardioselective and non-selective β-adrenoceptor blockade in essential hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 36, 343–345 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558292
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00558292