Summary
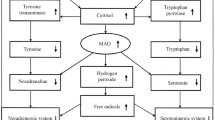
Investigations with an irreversible monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor were performed in man in order to correlate biochemical, pharmacological, and clinical changes during and after MAO inhibition. — Six healthy volunteers were treated with the hydrazine MAO inhibitor benmoxine (1-α-methylbenzyl-2-benzoyl hydrazine) in a dosage of either 75 mg/day for 4 weeks, or with 75 mg/day for 2 weeks, and 100 mg and 125 mg per day during the 3rd and 4th week respectively. — 1. Inhibition of plasma MAO occurred rapidly and was almost complete after one week of treatment with 75 mg/day benmoxine. After discontinuation of the treatment, there was rapid normalization of enzyme activity (within one week) and a subsequent rebound. — 2. Inhibition of blood platelet MAO was also rapid and almost total, but the return to normal did not occur earlier than 3 weeks after cessation of the drug. — 3. The serotonin content of blood platelets increased cumulatively and dose-dependently during the treatment period. Normal serotonin levels were found 2–3 weeks after treatment was discontinued. — 4. Urinary tryptamine excretion was not increased when the lower benmoxine dose was given. An immediate threefold rise was observed with the higher dosage. This effect disappeared after about one week. — 5. Due to progressive MAO inhibition, the blood pressure rising effect of intravenously infused tyramine also increased cumulatively. This effect was dose-dependent: three- and fivefold potentiation were found after 4 weeks of treatment with the two different dosage schedules. — The mydriatic response to tyramine instilled into the conjunctival sac was also enhanced after 4 weeks of treatment. 6. Cardiovascular dysregulation could be detected (Schellong test, after exercise) only when the higher doses of inhibitor were given, i.e., after 4 weeks, when the pressure response to tyramine was increased to about 5 fold. — It is concluded that only the combined application of several methods (biochemical, pharmacological and clinical investigation procedures) permit definite conclusions to be drawn about the time course and extent of MAO inhibition in man.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertalanffy, D.F.: Mitotic rates and renewal times of the digestive tract epithelia in the rat. Acta anat. (Basel)40, 130–148 (1960).
—— Cell renewal in the gastrointestinal tract of man. Gastroenterology43, 472–475 (1962).
Biel, J.H., Horita, A., Drukker, A.E.: Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (hydrazines). In: Psychopharmacological agents, vol. I, ed. M. Gordon, p. 359–443. New York and London: Academic Press 1964.
Bogdanski, D.F., Pletscher, A., Brodie, B.B., Udenfriend, S.: Identification and assay of serotonin in brain. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.117, 82–88 (1956).
Brunner, H.: Personal communication (1970).
Buffoni, F.: Histaminase and related amine oxidases. Pharmacol. Rev.18, 1163–1199 (1966).
Carlsson, A., Lindqvist, M., Fuxe, K., Hamberger, B.: The effect of (+)-amphetamine on various central and peripheral catecholamine-containing neurons. J. Pharm. (London)18, 128 130 (1966).
—— Waldeck, B.: Effects of amphetamine, tyramine, and protryptyline on reserpine-resistant amine concentrating mechanisms of adrenergic nerves. J. Pharm. (London)18, 252–253 (1966).
Davey, M.J., Farmer, J.B., Reinert, H.: The effect of nialamide on adrenergic functions. Brit. J. Pharmacol.20, 121–134 (1963).
Derlath, S.: Die direkte phasenoptische Thrombozyten- und Reticulozytenzählung. Ärztl. Forsch.10, 552–555 (1957).
Fischbach, R., Harrer, G., Harrer, H.: Verstärkung der Noradrenalin-Wirkung durch Psychopharmaka beim Menschen. Arzneimittelforsch.16, 263–265 (1966).
Holtz, P., Büchsel, H.: Über die Substratspezifität und -affinität der d-Aminosäurenoxydase und Aminoxydase. Hoppe-Seyler's Zschr. physiol. Chem.272, 201–211 (1942).
—— Palm, D.: Pharmacological aspects of vitamin B6. Pharmacol. Rev.16, 113–178 (1964).
—— —— Brenzcatechinamine und andere sympathicomimetische Amine (Biosynthese und Inaktivierung, Freisetzung und Wirkung). Ergebn. Physiol.58, 1–580 (1966).
Horwitz, D., Goldberg, L.J., Sjoerdsma, A.: Possible hemodynamic basis for beneficial effects of a monoamine oxidase inhibitor in angina pectoris. Circulation24, 959–960 (1961).
Johnston, P.: Some observations upon a new inhibitor of monoamine oxidase in brain tissue. Biochem. Pharmacol.17, 1285–1297 (1968).
Kobayashi, Y.: The effect of three monoamine oxidase inhibitors on human plasma monoamine oxidase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol.15, 1287–1294 (1966).
Kopin, I.J., Fischer, J.E., Musacchio, J., Horst, W.D., Weise, V.K.: “False neurochemical transmitters” and the mechanism of sympathetic blockade by monoamine oxidase inhibitors. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.147, 186–193 (1965).
Lemmer, B., May, B.: Steigerung des Serotoningehaltes menschlicher Thrombozyten im Hungerzustand. Hormone metabol. Res. In press.
Levine, R.J.: Assessment of drug-induced inhibition of monoamine oxidase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol.15, 1645–1647 (1966).
—— Sjoerdsma, A.: Monoamine oxidase activity in human tissues and intestinal biopsy specimens. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med.109, 225–227 (1962).
—— —— Estimation of momoamine oxidase activity in man: techniques and applications. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.107, 966–974 (1963).
—— —— Direct measurement of monoamine oxidase inhibition in humans. Clin. pharmacol. Ther.4, 22–27 (1963a).
Maxwell, M.H., Roth, S.J., Pearce, M.L., Kleeman, C.R.: Hypotensive properties of a new monoamine oxidase inhibitor: D,L-serine-N2-isopropyl-hydrazide. Circulation20, 738–743 (1959).
May, B.: Herz- und Kreislaufwirkungen von MAO-Hemmern. Diss. Freiburg 1965.
—— Bak, I.J., Böhle, E., Hassler, R.: Electron microscopical and biochemical studies on the serotonin granules in carcinoid syndrome. Life Sci.7, 785–800 (1968).
—— Menkens, I., Westermann, E.: Freisetzung von Serotonin und Histamin aus Thrombozyten durch aliphatische und aromatische Amine. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak.265, 24–48 (1969).
McEwen, C.M., jr.: Human plasma monoamine oxidase. I. Purification and identification. J. biol. Chem.240, 2003–2010 (1965).
Medakovic, M., Spuzic, J.: 5-Hydroxytryptamine in blood during experimental shock in rats. Nature (London)183, 1685 (1959).
Oates, J.A.: Measurement of urinary tryptamine, tyramine and serotonin. In: Methods in medical research, vol. IX, ed. J.H. Quastel, p. 169–174. Chicago: Year Book Med. Publ., Inc., 1960/1961.
Otsuka, S., Kobayashi, Y.: A radioisotopic assay for monoamine oxidase determinations in human plasma. Biochem. Pharmacol.13, 995–1006 (1964).
Palm, D., Magnus, U.: Hemmung der Monoaminoxydase und Diaminoxydase durch Furazolidon (Furoxon®). Pharmakologische und biochemische Untersuchungen am Menschen. Klin. Wschr.46, 720–728 (1968).
—— Magnus, U., Grobecker, H., Jonsson, J.: Hemmung der Monoaminoxydase durch bakteriostatisch wirksame Nitrofuranderivate. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. exp. Path.256, 281–300 (1967).
-- May, B., Fengler, H.-J., Güllner, H.-G., Helmstaedt, D., Lemmer, B., Moon, H.K., Quiring, K.: Pharmacological and biochemical criteria of MAO inhibition in animals and man. Abstr. VIth Int. Congr. Pharmacol. Basel, 1969. p. 193.
-- May, B., Fengler, H.J., Güllner, H.-G., Helmstaedt, D., Lemmer, B., Moon, H.K., Quiring, K.: Kriterien einer irreversiblen Hemmung der Monoaminoxydase am Menschen. Verh. 76. Tag. Dtsch. Ges. Inn. Med. Wiesbaden 1970. In press.
Pettinger, W.A., Oates, J.A.: Supersensitivity to tyramine during monoamine oxidase inhibition in man. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.9, 341–344 (1968).
—— Soyangco, F.G., Oates, J.A.: Inhibition of monoamine oxidase in man by furazolidone. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.9, 442–447 (1968).
Pisano, J.J., Crout, J.R., Abraham, D.: Determination of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxymandelic acid in urine. Clin. chim. Acta7, 285–291 (1962).
Planz, G., Quiring, K., Palm, D.: On the irreversibility of monoamine oxidase inhibition. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak.266, 424–425 (1970).
Pletscher, A., Gey, K.F., Zeller, P.: Monoaminoxydase-Hemmer. Fortschr. Arzneimittelforsch.2, 417–590 (1960).
Praag, van, H.M., Leijnse, B.: The influence of so-called monoamine-oxidase inhibiting hydrazines on oral loading-test with serotonin and 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid. Psychopharmacologia (Berlin)3, 202–203 (1962).
Quiring, K., Palm, D.: Inhibition of amine oxidases by nitrofuran derivatives: possible structure-activity relations and criteria of irreversibility. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak.265, 397–410 (1970).
Robinson, D.S., Lovenberg, W., Keiser, H., Sjoerdsma, A.: Effects of drugs on human blood platelet and plasma amine oxidase activity in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol.17, 109–119 (1968).
Schellong, F., Lüderitz, B.: Regulationspfüfung des Kreislaufs. Funktionelle Differentialdiagnose von Herzund Gefäßstörungen. Darmstadt: Steinkopff 1954.
Schmid, E., Störmer, L.D., Haas, H., Tautz, N.A., Schön, H.: Klinisch-chemische Untersuchungen über das Verhalten des Serotonin-Stoffwechsels bei Monoaminoxydase-Hemmung. Arzneimittelforsch.14, 849–852 (1964).
Schmutzler, W., Bethge, K.P., Moritz, G.: Release of histaminase and its resynthesis in the guinea pig liver. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak. exp. Path.259, 192–193 (1968).
Shorter, R.G., Moertel, C.G., Titus, J.L., Reitemeier, R.J.: Cell kinetics in the jejunum and rectum of man. Amer. J. digest. Dis.9, 760–763 (1964).
Sjoerdsma, A.: Catecholamine-drug interactions in man. Pharmacol. Rev.18, 673–683 (1966).
—— Oates, J.A., Zaltzman, P., Udenfriend, S.: Identification and assay of urinary tryptamine; application as an index of monoamine oxidase inhibition in man. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.126, 217–222 (1959).
Sneddon, J.M., Turner, P.: Ephedrine and mydriasis in hypertension and the response to treatment. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.10, 64–71 (1969).
Stone, H.H., Horiguchi, S., Donnelly, C.C., Nemir, P.: Changes in plasma serotonin concentration in surgical patients: a possible significance. Surg. Forum12, 140–142 (1961).
Sturzenegger, E., Siegenthaler, W., Lüthy, E.: Der Einfluß von Guanethidin auf den Blutdruck des Normotonikers unter körperlicher Belastung. Dtsch. med. Wschr.85, 1275–1277 (1960).
Trendelenburg, U.: Supersensitivity and subsensitivity to sympathomimetic amines. Pharmacol. Rev.15, 225–276 (1963).
Turner, P., Sneddon, J.M.: Alpha receptor blockade by thymoxamine in the human eye. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.9, 45–49 (1968).
Udenfriend, S., Titus, E., Weissbach, H.: The identification of 5-hydroxy-3-indoleacetic acid in normal urine and a method for its assay. J. biol. Chem.216, 499–505 (1955).
Widner, W.R., Storer, J.B., Lushbaugh: Use of x-ray and nitrogen mustard to determine mitotic and intermitotic times in normal and malignant rat tissues. Cancer Res.11, 877–884 (1951).
Wurtman, R.J., Axelrod, J.: A sensitive and specific assay for the estimation of monoamine oxidase. Biochem. Pharmacol.12, 1439–1440 (1963).
Youdim, M.B.H., Collins, G.G.S., Sandler, M.: Multiple forms of rat brain monoamine oxidase. Nature (London)223, 626–628 (1969).
Zeller, E.A.: Monoamine and polyamine analogues. In: Metabolic inhibitors, vol. II, eds. R.M. Hochster and J.H. Quastel, p. 53–78. New York: Academic Press 1963.
—— Babu, H., Cavanaugh, M.J., Stanich, G.J.: On thein vivo inhibition of human platelet monoamine oxidase (1.4.3.4.) by pargyline. Pharmacol. Res. Comm.1, 20–24 (1969).
Zeller, V., Ramachander, G., Zeller, E.A.: Amine oxidases XXI. A rapid method for the determination of the activity of monoamine oxidase and monoamine oxidase inhibitors. J. med. Chem.8, 440–443 (1965).
Zickgraf, M.: Über Pathogenese und moderne Therapie des Hochdrucks. Münch. med. Wschr.106, 921–933 (1964).
Zirkle, C.L., Kaiser, C.: Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (nonhydrazines). In: Psychopharmacological agents, vol. I (ed. M. Gordon), p. 445–554. New York and London: Academic Press 1964.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Karl Wezler on the occasion of his 70th birthday.
Part of this work was presented to the 6th International Congress of Pharmacology, Basel 1969 (Palmet al., 1969), and to the 76. Tagung der Deutschen Gesselschaft für Innere Mcdizin, Wiesbaden 1970 (Palmet al., 1970).
This work was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palm, D., Fengler, H.J., Güllner, H.G. et al. Quantitation of irreversible inhibition of monoamine oxidase in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 3, 82–92 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00619299
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00619299